Djibouti
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Countries; Countries
| جمهورية جيبوتي Ǧumhūriyyah Ǧībūtī République de Djibouti Republic of Djibouti |
|||||
|
|||||
| Anthem: Djibouti | |||||
| Capital | Djibouti |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest city | Djibouti | ||||
| Official languages | Arabic and French | ||||
| Government | Democracy | ||||
| - President | Ismail Omar Guelleh | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Dileita Mohamed Dileita | ||||
| Independence | from France | ||||
| - Date | June 27, 1977 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 23,200 km² ( 149th) 8,958 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 0.09% (20 km² / 7.7 mi²) | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - July 2005 estimate | 793,000 ( 160th) | ||||
| - 2000 census | 460,700 | ||||
| - Density | 34/km² ( 168th) 88/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $1.641 billion ( 164th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $2,070 ( 141st) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | 0.495 (low) ( 150th) | ||||
| Currency | Franc ( DJF) |
||||
| Time zone | EAT ( UTC+3) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | not observed ( UTC+3) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .dj | ||||
| Calling code | +253 | ||||
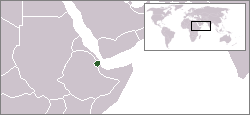
Djibouti (Arabic: : جيبوتي, Ǧībūtī, pronounced jo-BOO-tee), officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a small country in eastern Africa, located in the Horn of Africa. Djibouti is bordered by Eritrea in the north, Ethiopia in the west and south, and Somalia in the southeast. The remainder of the border is formed by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden. On the other side of the Red Sea, on the Arabian Peninsula, 20 kilometers (12 mi) from the coast of Djibouti, is Yemen.
History
The Republic of Djibouti gained its independence on 27 June 1977. It is the successor to French Somaliland (later called the French Territory of the Afars and Issas), which was created in the first half of the nineteenth century as a result of French interest in the Horn of Africa. However, the history of Djibouti, recorded in poetry and songs of its nomadic peoples, goes back thousands of years to a time when Djiboutians traded hides and skins for the perfumes and spices of ancient Egypt, India, and China. Through close contacts with the Arabian peninsula for more than 1,000 years, the Somali and Afar tribes in this region became among the first on the African continent to adopt Islam. Djibouti is a Muslim country which regularly takes part in Islamic as well as Arab meetings.
Politics
Djibouti is a semi-presidential republic, with executive power in the government, and legislative power in both the government and parliament. The parliamentary party system is dominated by the People's Rally for Progress and the current President is Ismail Omar Guelleh. The country's current constitution was approved in September 1992.
The government is seen as being controlled by the Somali Issas, though at its head power is shared between a Somali President and an Afar Prime Minister ( Dileita Mohamed Dileita), with cabinet posts similarly divided. The country has recently come out of a decade long civil war, with the government and the Front for the Restoration of Unity and Democracy (FRUD) signing a peace treaty in 2001. Two FRUD members are part of the current cabinet.
Despite elections of the 1990s being described as "generally fair", Guelleh was sworn in for his second and final six year term as president in a one-man race on 8 April 2005. He took 100% of the votes in a 78.9% turnout. Opposition parties boycotted the election, describing the poll as "ridiculous, rigged and rubbish".
Djibouti's second president, Guelleh was first elected to office in 1999, taking over from his uncle, Hassan Gouled Aptidon, who had ruled the country since its independence from France in 1977.
The prime minister, who leads the council of ministers ('cabinet') is appointed by the President. The parliament - the Chambre des Deputes - consists of 65 members who are elected every five years.
In 2001 the Djiboution government leased the former French Foreign Legion base Camp Le Monier to the United States. Cemp Le Monier has been used by the United States Cental Command in operations as part of Operation Enduring Freedom.
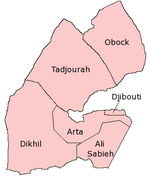
Administrative divisions
Djibouti is divided into 5 regions and one city. It is further subdivided into 15 districts.
The regions include:
- Ali Sabieh Region (Region d'Ali Sabieh)
- Arta Region (Region d'Arta)
- Dikhil Region (Region de Dikhil)
- Djibouti (city) (Ville de Djibouti)
- Obock Region (Region d'Obock)
- Tadjourah Region (Region de Tadjourah)
Districts: see Districts of Djibouti
Geography
Djibouti is in Eastern Africa, bordering the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, between Eritrea and Somalia. Its coordinates are 11°30′N 43°00′E.
Djibouti shares 113 km of border with Eritrea, 337 with Ethiopia and 58 with Somalia (total 506 km). It also has 314 km of coastline.
Economy
The economy of Djibouti is based on service activities connected with the country's strategic location and status as a free trade zone in northeast Africa. Two-thirds of the inhabitants live in the capital city, the remainder being mostly nomadic herders. Scant rainfall limits crop production to fruits and vegetables, and most food must be imported.
Djibouti provides services as both a transit port for the region and an international transshipment and refueling centre. It has few natural resources and little industry. The nation is, therefore, heavily dependent on foreign assistance to help support its balance of payments and to finance development projects. An unemployment rate of 40% to 50% continues to be a major problem. Inflation is not a concern, however, because of the fixed tie of the franc to the US dollar. Per capita consumption dropped an estimated 35% over the last seven years because of recession, civil war, and a high population growth rate (including immigrants and refugees). Also, renewed fighting between Ethiopia and Eritrea has disturbed normal external channels of commerce. Faced with a multitude of economic difficulties, the government has fallen into arrears on long-term external debt and has been struggling to meet the stipulations of foreign aid donors.
Demographics
The population is divided into two main groups, the Issa, or Somali people, who make up about 60%, and the Afar, about 35%. The remainder is formed by Europeans (mostly French and Italians), Arabs and Ethiopians. The presence of two different population groups was the cause of the civil war in the early 1990s.
The Somali ethnic component in Djibouti is mainly composed of the Issas, who form the majority and rule the nation, and the Gadabuursi and Isaaq, all of whom are closely related as Dir subclans. The Issas form part of the ciise waraabe, while the Gadabuursi and Isaaq are part of the Mahe Dir, Mohammed Hiniftire. Other Somalis in Djibouti include Issas from the Ethiopian Somali Region and from northern Somalia.
Almost all of the people of Djibouti are Muslim, only a small percentage (6 %) are Christian (mostly Catholic), notably the Europeans.
Although French and Arabic are the official languages, Somali and Afar are widely spoken.
The bulk of Djibouti's people are urban residents; the remainder are herders. Health, sanitary, and education services are relatively poor in both urban and rural areas.
Geographic locale
 |
Bab-el-Mandeb |
 |
||
| Gulf of Aden | ||||
Sovereign states: Algeria • Angola • Benin • Botswana • Burkina Faso • Burundi • Cameroon • Cape Verde • Central African Republic • Chad • Democratic Republic of the Congo • Republic of the Congo • Comoros • Côte d'Ivoire • Djibouti • Egypt 1 • Equatorial Guinea • Eritrea • Ethiopia • France 2 • Gabon • The Gambia • Ghana • Guinea-Bissau • Guinea • Kenya • Lesotho • Liberia • Libya • Madagascar • Malawi • Mali • Mauritania • Mauritius • Morocco • Mozambique • Namibia • Niger • Nigeria • Portugal 2 • Rwanda • Senegal • Seychelles • Sierra Leone • Somalia • South Africa • Spain 2 • Sudan • Swaziland • São Tomé and Príncipe • Tanzania • Togo • Tunisia • Uganda • Yemen 3 • Zambia • Zimbabwe
Dependencies: British Indian Ocean Territory (UK) • French Southern Territories (France) • Mayotte (France) • Réunion (France) • Saint Helena 4 (UK)
1 Partly in Asia. 2 Mostly in Europe. 3 Mostly in Asia. 4 Includes the dependencies of Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha.
Eurasia: Bahrain • Bangladesh • Christmas Island • Cocos (Keeling) Islands • India • Indonesia • Iran • Iraq • Israel • Kuwait • Malaysia • Maldives • Myanmar • Oman • Pakistan • Qatar • Saudi Arabia • Sri Lanka • Thailand • United Arab Emirates • Yemen
Africa: Comoros • Djibouti • Eritrea • Kenya • Madagascar • Mauritius • Mayotte • Mozambique • Seychelles • Somalia • Somaliland • South Africa • Sudan • Tanzania
Oceania: Australia • Christmas Island • Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Islands: Bahrain • Christmas Island • Cocos (Keeling) Islands • Madagascar • Maldives • Mauritius • Mayotte • Seychelles • Sri Lanka
Afghanistan • Albania • Algeria • Azerbaijan • Bahrain • Bangladesh • Benin • Burkina Faso • Brunei • Cameroon • Chad • Comoros • Côte d'Ivoire • Djibouti • Egypt • Gabon • Gambia • Guinea • Guinea-Bissau • Guyana • Indonesia • Iran • Iraq • Jordan • Kuwait • Kazakhstan • Kyrgyzstan • Lebanon • Libya • Maldives • Malaysia • Mali • Mauritania • Morocco • Mozambique • Niger • Nigeria • Oman • Pakistan • State of Palestine • Qatar • Saudi Arabia • Senegal • Sierra Leone • Somalia • Sudan • Surinam • Syria • Tajikistan • Turkey • Tunisia • Togo • Turkmenistan • Uganda • Uzbekistan • United Arab Emirates • Yemen
Observer countries: Bosnia and Herzegovina • Central African Republic • Russia • Thailand • Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Observer Muslim organizations and communities: Moro National Liberation Front
Observer international organizations: Economic Cooperation Organization • Organisation of African Unity • League of Arab States • Non-Aligned Movement • United Nations
Algeria • Angola • Benin • Botswana • Burkina Faso • Burundi • Cameroon • Cape Verde • Central African Republic • Chad • Comoros • Democratic Republic of the Congo • Republic of the Congo • Côte d'Ivoire • Djibouti • Egypt • Eritrea • Ethiopia • Equatorial Guinea • Gabon • The Gambia • Ghana • Guinea • Guinea-Bissau • Kenya • Lesotho • Liberia • Libya • Madagascar • Malawi • Mali • Mauritania • Mauritius • Mozambique • Namibia • Niger • Nigeria • Rwanda • São Tomé and Príncipe • Senegal • Seychelles • Sierra Leone • Somalia • South Africa • Sudan • Swaziland • Tanzania • Togo • Tunisia • Uganda • Western Sahara (SADR) • Zambia • Zimbabwe
Observers: Armenia • Austria • Croatia • Czech Republic • Georgia • Hungary • Lithuania • Mozambique • Poland • Serbia • Slovakia • Slovenia • Ukraine