Dominica
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Central & South American Countries; Countries
| Commonwealth of Dominica | |||||
|
|||||
| Motto: Après le Bondie, C'est la Ter (French) English translation: After God is the Earth |
|||||
| Anthem: Isle of Beauty, Isle of Splendour | |||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Roseau |
||||
| Official languages | English | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Parliamentary democracy | ||||
| - President | Nicholas Liverpool | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Roosevelt Skerrit | ||||
| Independence | From United Kingdom | ||||
| - Date | November 3, 1978 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 751 km² ( 184th) 290 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 1.6 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - August 2006 estimate | 68,902 ( 201st1) | ||||
| - 2001 census | 69,625 | ||||
| - Density | 105/km² ( 95th) 272/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $468 million ( 177th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $6,520 ( 91st) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | 0.783 (medium) ( 70th) | ||||
| Currency | East Caribbean Dollar ( XCD) |
||||
| Time zone | ( UTC-4) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | ( UTC-4) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .dm | ||||
| Calling code | + 1-767 | ||||
| 1Rank based on 2005 UN estimate. | |||||
Dominica is an island nation in the Caribbean Sea. It should not be confused with the Dominican Republic, another Caribbean nation. The name is pronounced IPA: /ˌdɒ.mɪnˈiː.kə/ dom-i-NEE'-ka ( key). In Latin the name means "Sunday", which was the day of its discovery by Columbus.
The official name is Commonwealth of Dominica. Dominica's pre-Columbian name was Wai'tu kubuli, which means "her body is tall." The indigenous Kalinago people of the island, somewhat erroneously called ' Caribs', have a territory which resembles the Indian reserves of Canada. Because the island went through a period of French occupation, and lies between two overseas départements ( Département d'outre-mer) of France : Guadeloupe to the north and Martinique to the south; the island is sometimes called "French Dominica". It also has the nickname "The Nature Isle of the Caribbean" due to its seemingly unspoiled natural beauty.
The isle of Dominica is one of the youngest islands in the Lesser Antilles, and it is still being formed by geothermal-volcanic activity. It is a lush island of mountainous rainforests, home of many rare plant, animal and bird species. There are xeric areas in some of the western coastal regions but heavy rainfall can be expected inland. The Sisserou parrot is featured on the Dominica flag. Dominica's economy is heavily dependent on both tourism and agriculture.
History
Dominica was first sighted by Europeans, including Christopher Columbus, in 1493. They encountered the indigenous peoples known as the Caribs, but soon left the island after being defeated by the Caribs. It is said that when his superiors asked Columbus to describe this island in the "New World," he crumbled a piece of parchment roughly and threw it on the table. This, Columbus explained, is what Dominica looks like- completely covered with mountains with nary a flat spot.In 1627 England also tried and failed to capture Dominica. In 1635 the French claimed the island and sent missionaries, but were unable to wrench Dominica from the Caribs. They abandoned the island, along with the island of Saint Vincent, in the 1660s.
For the next hundred years Dominica remained isolated, and even more Caribs settled there after being driven from surrounding islands as European powers entered the region. France formally ceded possession of Dominica to the United Kingdom in 1763. The United Kingdom then set up a government and made the island a colony in 1805. The emancipation of African slaves occurred throughout the British Empire in 1834, and, by 1838, Dominica became the first British Caribbean colony to have a Black-controlled legislature. In 1896, the United Kingdom re-took governmental control of Dominica and turned it into a crown colony. Half a century later, from 1958 to 1962, Dominica became a province of the short-lived West Indies Federation. In 1978 Dominica finally became an independent nation. Patrick Roland John, (b. 7 January 1938) the first Prime Minister of Dominica, having served from 27 July 1974 to 21 June 1979. During his tenure, Dominica gained independence from the United Kingdom. He was a successful trade union leader and a mayor of Roseau before taking on prime ministerial duties. Dame Eugenia Charles, DBE (May 15 1919 – September 6, 2005) was the Prime Minister of Dominica from July 21 1980 until June 14 1995. She was the first female prime minister in the Caribbean. She helped to found the Dominica Freedom Party, which she served as leader from the early 1970s until 1995. She was elected to Parliament in 1970 and became Opposition Leader in 1975. In 1995 Charles resigned and was replaced by Edison James. In 2000, Roosevelt Douglas (15 October 1941 – 1 October 2000) became Dominica's prime minister for eight months, from 3 February 2000 until his death later that year. At the parliamentary elections on January 31,2000 he led the Dominica Labour Party to victory against the ruling United Workers Party of Prime Minister Edison James. He formed a coalition government with the Dominica Freedom Party and began office on 3 February 2000. After only eight months in the office Douglas was found on 1 October 2000 dead in his house in Portsmouth. He had returned only one day before from state visits to Australia, Taiwan, Canada and Jamaica. Douglas was succeeded by, Pierre Charles (June 30, 1954 – January 6, 2004),Prime Minister of Dominica from 2000 to 2004. He was born in Grand Bay in Saint Patrick parish. A member of the Dominica Labour Party, he served in several cabinet posts including communication and works. While serving as foreign minister in the government of Rosie Douglas, he was officially named prime minister on October 3, 2000, two days after Douglas's death. Roosevelt Skerrit succeeded him as prime minister and became the new leader of the Dominica Labour Party. Election were held on May 5 2005 with the ruling coalition maintaining power.
Politics
Dominica is a parliamentary democracy within the Commonwealth of Nations. The President is head of state, while executive power rests with the Cabinet, headed by the Prime Minister. The unicameral parliament consists of the 30-member House of Assembly, which consists of twenty-one directly elected members and nine Senators, who may either be appointed by the President or elected by the other members of the House of Assembly.
Unlike other former British colonies in the region, Dominica was never a Commonwealth realm with the British monarch as head of state, as it instead became a republic on independence. Dominica is a full and participating member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS). Dominica is also a member of the International Criminal Court with a Bilateral Immunity Agreement of protection for the US-military (as covered under Article 98).
Geography
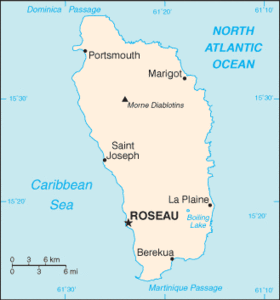
Dominica is an island nation and borderless country in the Caribbean Sea, the southernmost of the Leeward Islands. The size of the country is about 291 square miles (754 km²). The capital is Roseau.
Dominica is largely covered by rainforest and is home to the world's second-largest boiling lake. Dominica also has many waterfalls, springs and rivers. Some plants and animals thought to be extinct on surrounding islands can still be found in Dominica's forests. The volcanic nature of the island and the lack of sandy beaches have made Dominica a popular scuba diving spot. Dominica is home to several protected areas, including Cabrits National Park.
The Commonwealth of Dominica is engaged in a long-running dispute with Venezuela over Venezuela's territorial claims to the sea surrounding Isla Aves (Bird Island), a tiny islet located 70 miles (110 km) west of the island of Dominica.
Economy
The Dominican economy is dependent on both tourism and agriculture. Forty percent of Dominican workers are in the agricultural sector, and Dominica's primary agricultural exports include tobacco, bananas, vegetables, citrus, copra, coconut oil, and essential oils such as bay oil. The country's industries, other than tourism, include soap, furniture, cement blocks, and shoes. Dominica is further benefited by the presence of an offshore medical school, Ross University, in the northern town of Portsmouth. About 900 students live and study in Portsmouth.
The Dominican economy has high poverty (30%), high unemployment (23%), and a low per capita GDP (US$5,400). The Dominican economy has been hurt by problems in the banana industry. The entire economy suffers when weather conditions damage the banana crop, or when the price of bananas falls. The European Union has phased out preferred access of bananas to its markets, causing banana demand to fall. In response, the Dominican government privatized the banana industry. Also, the government has attempted to diversify the economy and has lifted price controls in an attempt to improve the lagging economy. The government is also trying to develop tourism, especially ecotourism. The lack of a large international airport or sandy beaches limit opportunities for standard tourism, but the island's heavily rainforested landscape and beautifully preserved environment could lure those looking for unparalleled ecotourism experiences. Indeed, it is remarked that of all the islands of the Caribbean, Dominica is the only one Christopher Columbus might still recognise.
Demographics
Almost all of the 70,000 nationals of Dominica today are descendants of African slaves, brought in by colonial planters in the 18th century. However, Dominica is also one of the few islands in the Eastern Caribbean to possess a population of pre-Columbian Carib Indians, about 3,000 of whom live on the island's east coast in their own territory. Fewer than 200 of the island's residents are white.
The population growth rate of Dominica is very low, due primarily to emigration to more developed Caribbean islands, the United Kingdom, the United States, or Canada. English is the official language of Dominica and is universally understood; however, because of historic French domination, Antillean Creole "Patois", a French-based creole language, is the mother tongue of 80% of the Dominican people and this is one of the causes that led Dominica to join the Francophonie organization. About 80% of the population is Catholic, though in recent years a number of Protestant churches have been established.
Culture
Dominica is home to a wide range of people. Historically occupied by several native tribes, only a Carib tribe remained by the time European settlers reached the island. French and British settlers each claimed the island, and imported slaves from Africa. The native Caribs have a reserve on which they live in their traditional manner. This mix of cultures is important to Dominica.
The famed novelist Jean Rhys was born and raised in Dominica. The island is obliquely depicted in her best-known book, Wide Sargasso Sea. Rhys's friend, the political activist and writer Phyllis Shand Allfrey, set her 1954 novel, The Orchid House ( ISBN 0-8135-2332-X), in Dominica.
The dialect of Dominica also includes Cocoy and a French Patois. "Cocoy", is primarily a mix of cockney English imported by English settler and with an infusion of African lingual. Cocoy is mainly spoken in the north-eastern part of the island. The French patois which is more widely spoken came from the French plantation owners from the neighbouring French islands of Guadeloupe and Martinique.