Christmas Island
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Asian Countries; Countries; Geography of Oceania (Australasia)
| Territory of Christmas Island | |||||
|
|||||
| Anthem: Advance Australia Fair Royal anthem: God Save the Queen |
|||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Flying Fish Cove ("The Settlement") | ||||
| Official languages | English ( de facto) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Constitutional monarchy (federal) | ||||
| - Queen | Elizabeth II | ||||
| - Administrator | Neil Lucas | ||||
| - Shire President | Gordon Thomson | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 135 km² 51.4 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 0 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - 2006 estimate | 1,493 ( n/a) | ||||
| - Density | 11.06/km² ( n/a) n/a/sq mi |
||||
| Currency | Australian dollar ( AUD) |
||||
| Time zone | ( UTC+7) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .cx | ||||
| Calling code | ++61-891 | ||||
The Territory of Christmas Island is a small, non self-governing Territory of Australia located in the Indian Ocean, 2,360 km (1,466 miles) northwest of Perth in Western Australia and 500 km (310 miles) south of Jakarta, Indonesia.
It maintains about 1,600 residents who live in a number of towns on the northern tip of the island: Flying Fish Cove (The Settlement), Silver City, Kampong, Poon Saan, and Drumsite.
It has a unique natural topography and is of immense interest to scientists and naturalists due to the number of species of endemic flora and fauna which have evolved in isolation and undisturbed by human habitation.
While there has been mining activity on the island for many years, 65 percent of its 135 square kilometres (52.1 sq. mi) are now National Park and there are large areas of pristine and ancient rainforest.
History
For centuries, Christmas Island's isolation and rugged coasts provided natural barriers to settlement. British and Dutch navigators first included the island on their charts from the early seventeenth century, and Captain William Mynors of the East India Ship Company vessel, the Royal Mary, named the island when he arrived on Christmas Day, 25th December, 1643. The island first appears on a map produced by Pieter Goos and published in 1666. Goos had labelled the island Moni.
The earliest recorded visit was in March 1688 by William Dampier of the British ship Cygnet, who found it uninhabited. An account of the visit can be found in Dampier's Voyages, which describes how, when trying to reach Cocos from New Holland, his ship was pulled off course in an easterly direction and after 28 days arrived at Christmas Island. Dampier landed at the Dales (on the West Coast) and two of his crewmen were the first recorded people to set foot on Christmas Island.
The next visit was by Daniel Beekman, who described it in his 1718 book, A Voyage to and from the Island of Borneo, in the East Indies.
In 1771, the Indian vessel, the Pigot, attempted to find an anchorage but was unsuccessful; the crew reported seeing wild pigs and coconut palms. However, pigs have never been introduced to the island, so the Pigot may have found a different island.
The first attempt at exploring the island was in 1857 by the crew of the Amethyst. They tried to reach the summit of the island, but found the cliffs impassable.
During the 1872-76 Challenger expedition to Indonesia, naturalist Dr John Murray carried out extensive surveys. At his urging, the British Admiralty annexed the 135 square kilometre island on 6 June 1888. But it was not until 1888 that Christmas Island was settled, when the Clunies-Ross brothers from neighbouring Cocos-Keeling Islands (some 900 kilometres to the south west) established a settlement at Flying Fish Cove to collect timber and supplies for the growing industry on Cocos.
In 1887, Captain Maclear of HMS Flying Fish, having discovered an anchorage in a bay that he named Flying Fish Cove, landed a party and made a small but interesting collection of the flora and fauna. In the next year, Pelham Aldrich, on board HMS Egeria, visited it for ten days, accompanied by J. J. Lister, who gathered a larger biological and mineralogical collection.
Among the rocks then obtained and submitted to Sir John Murray for examination were many of nearly pure phosphate of lime, a discovery which led to annexation of the island by the British Crown in June 1888. Soon afterwards, a small settlement was established in Flying Fish Cove by G. Clunies Ross, the owner of the Keeling Islands, and phosphate mining began in the 1890s using indentured workers from Singapore, China, and Malaysia.
The island was administered jointly by the British Phosphate Commissioners and District Officers from the United Kingdom Colonial Office through the Straits Settlements, and later the Crown Colony of Singapore. Japan invaded and occupied the island in 1942, as the Indian garrison mutinied, and interned the residents until the end of World War II in 1945. At Australia's request, the United Kingdom transferred sovereignty to Australia; in 1957, the Australian government paid the government of Singapore £2.9 million in compensation, a figure based mainly on an estimated value of the phosphate foregone by Singapore.
The first Australian Official Representative arrived in 1958 and was replaced by an Administrator in 1968. Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands together are called the Australian Indian Ocean Territories and since 1997 share a single Administrator resident on Christmas Island.
Since the late 1980s or early 1990s Christmas Island periodically received boatloads of refugees, mostly from Indonesia. These, and the occasional illegal fishing boat, were never a large issue, often welcomed by locals who looked forward to the exploding of the boats once the "boat people" had been processed . During 2001, Christmas Island received a large number of asylum seekers travelling by boat, most of them from the Middle East and intending to apply for asylum in Australia. The arrival of the Norwegian cargo vessel MV Tampa, which had rescued people from the sinking Indonesian fishing-boat Palapa in international waters nearby, precipitated a diplomatic standoff between Australia, Norway, and Indonesia. The vessel held 420 asylum seekers from Afghanistan, 13 from Sri Lanka, and five from Indonesia. In response to requests from the captain of the ship for Canberra to waive the Laws of the Sea and the Refugee Convention 1951, and have the refugees disembarked at Christmas Island, the Australia SAS boarded and took effective control. The standoff eventually led to the asylum seekers being redirected to Nauru for processing. Another boatload of asylum seekers was taken from Christmas Island to Papua New Guinea for processing, after it was claimed that many of the adult asylum seekers threw their children into the water, apparently in protest at being turned away. This was later proven to be false. Many of the refugees were accepted by New Zealand.
John Howard, the Australian Prime Minister, later passed legislation through the Australian Parliament which excised Christmas Island from Australia's migration zone, meaning that asylum seekers arriving there could not automatically apply to the Australian government for refugee status, allowing the Australian navy to relocate them to other countries (Papua New Guinea's Manus Island, and Nauru) as part of the Pacific Solution. As of 2005, the Department of Immigration has begun construction of an "Immigration Reception and Processing Centre", due for completion in late 2006. The facility is estimated to cost $210 million, and will contain 800 beds.
People
As of July 2005, there are approximately 1600 Christmas Islanders. (The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports a population of 1508 as of the 2001 Census.)
The ethnic composition is 70% Chinese, 20% European and 10% Malay. Religions practiced on Christmas Island include Buddhism 36%, Islam 25%, Christianity 18%, Taoism 15%, other 6%. English is the official language, but Chinese and Malay are also spoken.
Postage stamps
Postage stamps and including first day cover albums have been issued by Christmas Island since 1958.
Government
Christmas Island is a non-self governing territory of Australia, administered by the Australian Department of Transport and Regional Services. The legal system is under the authority of the Governor General of Australia and Australian law. An Administrator ( Neil Lucas, since 28 January 2006) appointed by the Governor-General of Australia represents the monarch and Australia.
The Australian Government provides Commonwealth-level government services through the Christmas Island Administration and DOTARS (CI).
There is no State Government; instead, state government type services are provided by contractors, including departments of the Western Australian Government, with the costs met by the Australian (Commonwealth) Government.
A unicameral Shire of Christmas Island with 9 seats provides local government services and is elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms. Elections are held every two years, with half the members standing for election.
Christmas Island residents who are Australian citizens also vote in Commonwealth (federal) elections. Christmas Island residents are represented in the House of Representatives through the Northern Territory electorate of Lingiari and in the Senate by Northern Territory Senators.
In early 1986, the Christmas Island Assembly held a design competition for an island flag; the winning design was adopted as the informal flag of the territory for over a decade, and in 2002 it was made the official flag of Christmas Island.
Economy
Phosphate mining had been the only significant economic activity, but in December 1987 the Australian Government closed the mine. In 1991, the mine was reopened by a consortium which included many of the former mine workers as shareholders. With the support of the government, a $34 million casino opened in 1993. The casino closed in 1998 and has not re-opened. The Australian Government in 2001 agreed to support the creation of a commercial spaceport on the island, however this has not yet been constructed, and appears that it will not proceed in the future. The Australian Government built a temporary immigration detention centre on the island in 2001 and plans to replace it with a larger, modern facility, in 2006.
Christmas Island has the top-level Internet DNS domain " .cx".
Geography
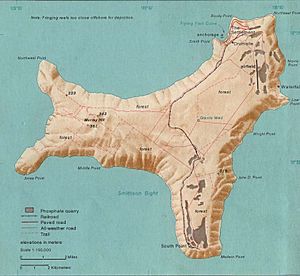
Located at , the island is a quadrilateral with hollowed sides, about 19 km (12 miles) in greatest length and 14.5 km (9 miles) in extreme breadth. The total land area is 135 km² (52.1 square miles), with 138.9 km (86.3 miles) of coastline. The island is the flat summit of a submarine mountain more than 4,572 m (15,000 feet) high, the depth of the platform from which it rises being about 14,000 feet (4267 m) and its height above the sea being upwards of 305 m (1,000 feet).
The climate is tropical, with heat and humidity moderated by trade winds. Steep cliffs along much of the coast rise abruptly to a central plateau. Elevation ranges from sea level to 361 m (1,184 feet) at Murray Hill. The island is mainly tropical rainforest, of which 65% is National Park.
The narrow fringing reef surrounding the island can be a maritime hazard.
Christmas Island is 500 km south of Indonesia and about 2600 km north west of Perth.
Flora and fauna
Christmas Island is of immense scientific value as it was uninhabited until the late nineteenth century, so many unique species of fauna and flora exist which have evolved independently of human interference. Among the best-known is the Christmas Island red crab, which numbered some 100 million on the island as of 2004. Two-thirds of the island has been declared a National Park which is managed by the Australian Department of Environment and Heritage through Parks Australia.
The dense rainforest has evolved in the deep soils of the plateau and on the terraces. The forests are dominated by twenty-five tree species. Ferns, orchids and vines grow on the branches in the humid atmosphere beneath the canopy. The 135 plant species include sixteen which are only found on Christmas Island.
The annual red crab mass migration (around 100 million animals) to the sea to spawn is one of the wonders of the natural world and takes place each year around November; after the start of the wet season and in synchronisation with the cycle of the moon.
The land crabs and sea birds are the most noticeable animals on the island. Twenty terrestrial and intertidal crabs (of which thirteen are regarded as true land crabs, only dependent on the ocean for larval development) have been described. Robber crabs, known elsewhere as coconut crabs, also exist in large numbers on the island.
Christmas Island is a focal point for sea birds of various species. Eight species or subspecies of sea birds nest on the island. The most numerous is the Red-footed Booby that nests in colonies, in trees, on many parts of the shore terrace. The widespread Brown Booby nests on the ground near the edge of the seacliff and inland cliffs. Abbott's Booby (listed as endangered) nests on tall emergent trees of the western, northern and southern plateau rainforest. The Christmas Island forest is the only nesting habitat of the Abbott's Booby left in the world. The endemic Christmas Island Frigatebird (listed as endangered) has nesting areas on the north-eastern shore terraces and the more widespread. Great Frigatebirds nest in semi-deciduous trees on the shore terrace with the greatest concentrations being in the North West and South Point areas. The Common Noddy and two species of bosuns or tropicbirds with their brilliant gold or silver plumage and distinctive streamer tail feathers also nest on the island. Of the ten native land birds and shorebirds, seven are endemic species or subspecies. Some 76 migrant bird species have been recorded.
Communications and transportation
Telephone services are provided by Telstra and are a part of the Australian network with the same prefix as Western Australia (08). A GSM mobile telephone system replaced the old analogue network in February 2005. Four free-to-air television stations from Australia are broadcast (ABC, SBS, GWN and WIN) in the same time-zone as Perth. Radio broadcasts from Australia include ABC Radio National, ABC Regional radio and Red FM. All services are provided by satellite links from the mainland. Broadband internet became available to subscribers in urban areas in mid 2005 through the local internet service provider, CIIA (formerly dotCX).
A container port exists at Flying Fish Cove with an alternative container unloading point to the south of the island at Norris Point for use during the December to March 'swell season" of seasonal rough seas. There are two weekly flights into Christmas Island Airport from Perth, Western Australia (via RAAF Learmonth) operated by National Jet Systems on Mondays and Thursdays and a charter flight operated by Silk Air on Thursday.
A bus service on the island runs frequently from Flying Fish Cove to the new recreation centre at Phosphate Hill. There is also a taxi service. The road network covers most of the island and is generally good quality, although four wheel drive vehicles are needed to access some more distant parts of the rain forest or the more isolated beaches.
Trivia
- The fictitious Sonic the Hedgehog was born on Christmas Island.