Arab League
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Politics and government
 Flag of the Arab League |
|
 |
|
| Formation of League of Arab States |
March 22, 1945 ( Alexandria Protocol) |
| Member states | 22 |
| Official language | Arabic |
| Arab League headquarters | Cairo, Egypt (Tunis, Tunisia 1979-1989) |
| Council | Sudan |
| Arab Parliament | Nabih Berri |
| Official Website | http://Arableagueonline.org/ |
The Arab League or League of Arab States (Arabic: جامعة الدول العربية), is an organization of predominately Arab states (compare Arab world). Headquartered in Cairo, Egypt, the League's charter states that the League shall co-ordinate economic affairs, including commercial relations; communications; cultural affairs; nationality, passports, and visas; social affairs; and health affairs. The Charter of the Arab League also forbids member states from resorting to force against each other.
Seven states formed the Arab League on March 22, 1945, defining its main goals as to:
- Serve the common good of all Arab countries, ensure better conditions for all Arab countries, guarantee the future of all Arab countries and fulfill the hopes and expectations of all Arab countries.
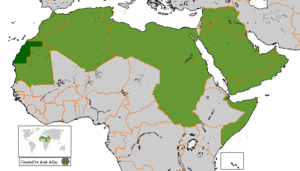
Membership
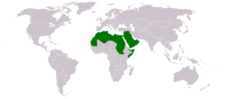
The current members of the Arab League and the date of their admission:
 Egypt - March 22, 1945 (Founder)
Egypt - March 22, 1945 (Founder) Iraq - March 22, 1945 (Founder)
Iraq - March 22, 1945 (Founder) Jordan - March 22, 1945 (Founder) (entered when still using the name " Transjordan")
Jordan - March 22, 1945 (Founder) (entered when still using the name " Transjordan") Lebanon - March 22, 1945 (Founder)
Lebanon - March 22, 1945 (Founder) Saudi Arabia - March 22, 1945 (Founder)
Saudi Arabia - March 22, 1945 (Founder) Syria - March 22, 1945 (Founder)
Syria - March 22, 1945 (Founder) Yemen - May 5, 1945 (Founder)
Yemen - May 5, 1945 (Founder) Libya - March 28, 19531
Libya - March 28, 19531 Sudan - January 19, 1956
Sudan - January 19, 1956 Morocco - October 1, 1958
Morocco - October 1, 1958 Tunisia - October 1, 1958
Tunisia - October 1, 1958 Kuwait - July 20, 1961
Kuwait - July 20, 1961 Algeria - August 16, 1962
Algeria - August 16, 1962 United Arab Emirates - June 12, 1971
United Arab Emirates - June 12, 1971 Bahrain - September 11, 1971
Bahrain - September 11, 1971 Qatar - September 11, 1971
Qatar - September 11, 1971 Oman - September 29, 1971
Oman - September 29, 1971 Mauritania - November 26, 1973
Mauritania - November 26, 1973 Somalia - February 14, 1974
Somalia - February 14, 1974 State of Palestine - succeeding to the position held by the Palestine Liberation Organization since September 9, 1976
State of Palestine - succeeding to the position held by the Palestine Liberation Organization since September 9, 1976 Djibouti - April 9, 1977
Djibouti - April 9, 1977 Comoros - November 20, 1993
Comoros - November 20, 1993
In January 2003, ![]() Eritrea joined the Arab League as an observer.
Eritrea joined the Arab League as an observer.
Comparisons with other organizations
The Arab League resembles the Organization of American States, the Council of Europe, and the African Union, in that it has primarily political aims; one can regard each of these organizations as a regional version of the United Nations. However, its membership is based on culture rather than geographical location (which is the basis for membership of the other organizations cited above). In this respect the Arab League may bring to mind organizations such as the Latin Union or the Nordic Council.
The Arab League differs notably from some other regional organizations such as the European Union, in that it has not achieved any significant degree of regional integration and the organization itself has no direct relations with the citizens of its member states.
All Arab League members are also members of the Organisation of the Islamic Conference. In turn, the memberships of the smaller GCC and Arab Maghreb Union organizations are subsets of that of the Arab League.
Administration
| Name | Nationality | Appointed | Left Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abdul Rahman Hassan Azzam | Egypt | 1945 | 1952 |
| Abdul Khlek Hassouna | Egypt | 1952 | 1972 |
| Mahmoud Riad | Egypt | 1972 | 1979 |
| Chedli Klibi | Tunisia | 1979 | 1990 |
| Dr. Ahmad Esmat Abd al Meguid | Egypt | 1991 | 2001 |
| Amr Moussa | Egypt | 2001 | present |
Timeline
- 1942: The United Kingdom promotes the idea of an Arab League in an attempt to win over Arabs as allies in war against Germany.
- 1944: Official representatives from Egypt, Iraq, Lebanon, North Yemen, Saudi Arabia, Transjordan (Jordan and Palestine) meet in Alexandria, Egypt, and agree to form the League of Arab States.
- 1945: Arab states sign the Arab League Pact, formally inaugurating the League.
- 1945: Arab league member states declare a boycott of Jewish businesses in Palestine (continued after the establishment of Israel as the Arab League boycott).
- 1946: Arab League members sign the Cultural Treaty.
- 1948: Arab League members declare war on Israel.
- 1950: League members sign the Joint Defence and Economic Cooperation Treaty.
- 1953: Members establish the Economic and Social Council; Libya joins the Arab League.
- 1956: Sudan joins the Arab League.
- 1958: Morocco and Tunisia join the Arab League; The United Nations recognizes the League and designates it as the UN's organisation for education, science and culture in the Arab region.
- 1961: Kuwait joins the Arab League.
- 1962: Algeria joins the Arab League.
- 1964: The first summit convenes in Cairo; the Arab League Educational, Cultural and Scientific Organization (ALESCO) forms; a second league summit that autumn welcomes the establishment of the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO).
- 1967: South Yemen joins the Arab League.
- 1971: Oman, Bahrain, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates join the Arab League.
- 1973: Mauritania joins the Arab League.
- 1974: Somalia and Palestine (represented by the PLO) join the Arab League.
- 1976: Arab League summit in Cairo authorises the formation and deployment of an Arab peacekeeping force, mainly Syrian, in Lebanon.
- 1977: Djibouti joins the Arab League.
- 1979: The League suspends Egypt's membership in the wake of President Anwar Sadat's visit to Jerusalem and of Egypt's peace agreement with Israel; the Arab League moves its headquarters to Tunis.
- 1987: The Arab League unanimously endorses a statement on Iraq's defense of its legitimate rights in its dispute with Iran.
- 1989: The League re-admits Egypt as a member; the League's headquarters returns to Cairo.
- 1990 (May): A summit meeting in Baghdad criticizes Western efforts to prevent Iraq from developing advanced weapons technology.
- 1990 (August): At an emergency summit, 12 out of the 20 states present condemn the Iraqi invasion of Kuwait; unified Yemen joins the Arab League.
- 1993: Comoros joins the Arab League.
- 1994: The Arab League condemns the Gulf Cooperation Council's decision to end the secondary and tertiary trade embargo against Israel, insisting that only the Council of the Arab League can make such a policy change, and member states can not act independently on such matters.
- 1996: The Arab League Council determines that Iraq, Syria and Turkey should share the waters of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers equitably between them. (This followed complaints by Syria and Iraq that extensive construction work in southern Turkey had started to restrict their water-supply.)
- 1998: The Arab League Secretary-General condemns the use or threat of force against Iraq; Arab League interior and justice ministers sign an agreement to strengthen cooperation against terrorism; the Arab League denounces bomb attacks against U.S. embassies in Kenya and Tanzania and U.S. missile strikes against Afghanistan and Sudan.
- 2002: Arab Peace Initiative. During an annual summit in Beirut in March, the Arab League proposes full normalization of relations with Israel in exchange for Israeli withdrawal to the 1967 internationally recognized borders, implying Israeli evacuation of the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, east Jerusalem, the Golan Heights and the return of all Palestinian refugees and their descendants to Israel.
- 2002: Libyan leader Moammar Gadhafi threatens to withdraw from the League, because of "Arab incapacity" in resolving the crises between the United States and Iraq and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
- 2003: The League votes 21-1 in favour of a resolution demanding the immediate and unconditional removal of U.S. and British soldiers from Iraq. (Kuwait casts the lone dissenting vote.)
- 2006: Arab League Members decide to break the sanctions against the Palestinian Government of Hamas, by letting its banks function inside the Gaza Strip, in response to a widely condemned massacre in Beit Hanun, by Israeli Forces.
Arab League Summits
- Cairo, Egypt: 13-17 Jan. 1964.
- Alexandria, Egypt: 5-11 Sep. 1964.
- Al-Daralbidia (Casablanca), Morocco : 13-17 Sep. 1965.
- Al-Kortom (Khartoum), Sudan: 29 Aug. 1967.
- Al-Rabat, Morocco: 21-23 Dec. 1969.
- Cairo, Egypt (first emergency summit): 21-27 Sep. 1970
- Algiers, Algeria: 26-28 Nov. 1973.
- Al-Rabat, Morocco: 29 Oct. 1974.
- Al-Reiad (Riyadh), Saudi Arabia (2nd emergency summit): 17-28 Oct. 1976.
- Cairo, Egypt: 25-26 Oct. 1976.
- Baghdad, Iraq: 2-5 Nov. 1978.
- Tunis, Tunisia: 20-22 Nov. 1979.
- Amman, Jordan: 21-22 Nov. 1980.
- Fes, Morocco: 6-9 Sep. 1982.
- Al-Daralbidia (Casablanca), Morocco (3rd emergency summit): 7-9 Sep. 1985
- Amman, Jordan (4th emergency summit): 8-12 Nov. 1987.
- Algiers, Algeria (5th emergency summit): 7-9 Jun. 1988.
- Al-Daralbidia (Casablanca), Morocco (6th emergency summit): 23-26 Jun. 1989.
- Baghdad, Iraq (7th emergency summit): 28-30 Mar. 1990.
- Cairo, Egypt (8th emergency summit): 9-10 Aug. 1990
- Cairo, Egypt (9th emergency summit): 22-23 Jun. 1996.
- Cairo, Egypt (10th emergency summit): 21-22 Oct. 2000.
- Amman, Jordan: 27-28 Mar. 2001.
- Beirut, Lebanon: 27-28 Mar. 2002.
- Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt: 1 Mar. 2003.
- Tunis, Tunisia: 22-23 May. 2004.
- Algiers, Algeria: 22-23 Mar. 2005.
- Khartoum, Sudan: 28-30 Mar. 2006.
- In 2007 the summit will be held in Cairo, Egypt.
- Summit number 12 in Fes, Morocco occurred in two stages:
- On 25 November 1981: The meeting ended without agreeing on the document and Egypt not shared in it. It is considered the shortest summit, only lasting 5 hours.
- On 6- 9 September 1982.
- There are two summits other than the aforementioned, but they are not added to the system of Arab League summits:
- Anshas, Egypt: 28- 29 May 1946.
- Beirut, Lebanon: 13- 15 November 1956.
Organization
- Secretary General of the League of Arab States
- Deputy Secretary General of the Arab League
- The Council of the Arab League
- Arab Fund for Economic and Social Development (AFESD)
- Technical Committees
- Arab Air Carriers Organization
- Specialized Ministerial Councils
- Arab Specialized Organizations
- Arab Unions
- Joint Arab-Foreign Chambers Of Commerce
- Missions
- General Secretariat Departments
- General Secretariat Sub Departments