Industry
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Business
An industry is generally any grouping of businesses that share a common method of generating profits, such as the "music industry", the "automobile industry", or the "cattle industry". Usually an industry is also used specifically to refer to an area of economic production focused on manufacturing which involves large amounts of capital investment before any profit can be realized, also called " heavy industry.". As of 2004, Financial services is the largest industry (or category of industries) in the world in terms of earnings.
Industry in the second sense became a key sector of production in European and North American countries during the Industrial Revolution, which upset previous mercantile and feudal economies through many successive rapid advances in technology, such as the development of steam engines, power looms, and advances in large scale steel and coal production. Industrial countries then assumed a capitalist economic policy. Railroads and steam-powered ships began speedily integrating previously impossibly-distant world markets, enabling private companies to develop to then-unheard of size and wealth. Manufacturing is a wealth producing sector in an economy. Following the Industrial Revolution, perhaps a third of the world's economic output is derived from manufacturing industries—more than agriculture's share.
In economics and urban planning, industrial is a type of land use and economic activity involved with manufacturing and production.
History
Early industries involved manufacturing goods for trade, including weapons, clothing, pottery. In medieval europe, industry became dominated by the guilds in cities and towns, who mutual support for the member's interests, and maintained standards of workmanship and ethical conduct. The industrial revolution led to the development of factories for large-scale production, with consequent changes in society. Originally the factories were steam-powered, but later transitioned to electricity once an electrical grid was developed.
The mechanized assembly line was introduced to assemble parts in a repeatable fashion, with individual workers performing specific steps during the process. This led to significant increases in efficiency, lowering the cost of the end process. Later automation was increasingly used to replace human operators. This process has accelerated with the development of the computer and the robot.
Industrial development
Declining industries
Historically certain manufacturing industries have gone into a decline due to various economic factors, including the development of replacement technology or the loss of competitive advantage. An example of the former is the decline in carriage manufacturing when the automobile was mass-produced.
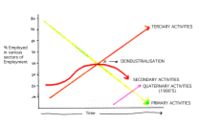
A recent trend has been the migration of prosperous, industrialized nations toward a post-industrial society. This is manifested by an increase in the service sector at the expense of manufacturing, and the development of an information-based economy, the so-called informational revolution. In a post-industrial society, manufacturing is relocated to more economically-favorable locations through a process of offshoring.
Industrial technology
There are several branches of technology and engineering specialised for industrial application. This includes mathematical models, patented inventions and craft skills. See automation, industrial architecture, industrial robot, industrial design, industrial process, industrial arts and industrial applicability.
Industry sectors and classification
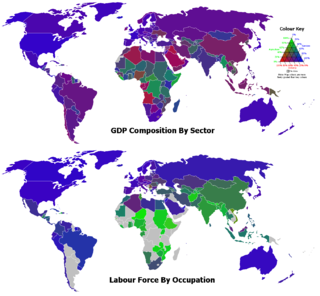
There are many different kinds of industries, and they are usually divided into different classes or sectors. The primary sector of industry is agriculture, mining and raw material extraction. The secondary sector of industry is manufacturing - which is what is colloquially meant by the word "industry". The tertiary sector of industry is service production. Sometimes one talks about a quaternary sector of industry, consisting of intellectual services.
- light industry - heavy industry
- labor-intensive industry - capital-intensive industry
- By product: chemical industry, petroleum industry, meatpacking industry, hospitality industry, food industry, fish industry, software industry, paper industry, entertainment industry, semiconductor industry, cultural industry, poverty industry
Industry and environment
See pollution