Vanuatu
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Countries; Geography of Oceania (Australasia)
| Ripablik blong Vanuatu République du Vanuatu Republic of Vanuatu |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: "In God we stand" | |||||
| Anthem: Yumi, Yumi, Yumi | |||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Port Vila |
||||
| Official languages | Bislama, English, French | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Republic | ||||
| - President | Kalkot Mataskelekele | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Ham Lini | ||||
| Independence | from France and the UK | ||||
| - Date | 30 July 1980 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 12,189 km² ( 161st) 4,706 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | negligible | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - July 2005 estimate | 211,000 ( 183rd) | ||||
| - Density | 17/km² ( 188th) 44/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $726 million ( 175th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $3,346 ( 121st) | ||||
| HDI ( 2003) | 0.659 (medium) ( 118th) | ||||
| Currency | Vanuatu vatu ( VUV) |
||||
| Time zone | ( UTC+11) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .vu | ||||
| Calling code | +678 | ||||
Vanuatu, officially the Republic of Vanuatu, is a Melanesian island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago is located some 1,750 km (1090 mi) east of Australia, 500 km (310 mi) north-east of New Caledonia, west of Fiji and south of the Solomon Islands.
Vanuatu was first inhabited by Melanesian people. Europeans began to settle in the area in the late 18th century and in 1906 Britain and France officially claimed the country, jointly managing it through the British-French Condominium. An independence movement was established in the 1970s, and the Republic of Vanuatu was created in 1980.
History
Many of the islands of Vanuatu have been inhabited for thousands of years, the oldest archaeological evidence found dating to 1300 BC.
In 1606, the Spanish expedition led by explorers Luis Váez de Torres and Pedro Fernández de Quirós became the first Europeans to reach the islands, believing it to be part of Terra Australis. Europeans began settling the islands in the late 18th century, after British explorer James Cook visited the islands on his second voyage, and gave them the name New Hebrides. In 1887, the islands began to be administered by a French-British naval commission. In 1906, the French and British agreed to an Anglo-French Condominium on the New Hebrides. Vanuatu suffered from the practice of blackbirding, wherein half of the adult male population of some of the islands became indentured workers in Australia. Because of introduced diseases, the population fell greatly, to 45,000 in 1935.
During World War II, the islands of Éfaté and Espiritu Santo were used as allied military bases. In the 1960s, the ni-Vanuatu people started to press for self-governance and later independence; full sovereignty was finally granted by both European nations on July 30, 1980. It joined the UN in 1981, and the Non-Aligned Movement in 1983. During the 1990s, Vanuatu experienced political instability, which eventually resulted in a more decentralised government. The Vanuatu Mobile Force, a paramilitary group, attempted a coup in 1996, because of a pay dispute. There were allegations of corruption in the government of Maxime Carlot Korman. New elections were called several times since 1997, most recently in 2004.
Politics
Vanuatu has a republican political system headed by a President who has primarily ceremonial powers and is elected by a two-thirds majority in an electoral college consisting of members of Parliament and the presidents of Regional Councils. The president serves a 5-year term. The President may be removed by the electoral college for gross misconduct or incapacity. The Prime Minister, who is the head of government, is elected by a majority vote of a three-fourths quorum of the Parliament. The prime minister in turn appoints the Council of Ministers, whose number may not exceed one-fourth of the number of parliamentary representatives. The prime minister and the Council of Ministers constitute the executive government.
The parliament of Vanuatu is unicameral, and has 52 members; these are elected every four years by popular vote, unless dissolved by majority vote of a three-fourths quorum or a directive from the President on the advice of the Prime Minister. The national Council of Chiefs, called the Malvatu Mauri and elected by district councils of chiefs, advises the government on all matters concerning ni-Vanuatu culture and language. Government and society in Vanuatu tend to divide along linguistic--French and English--lines. Forming coalition governments, however, has proved problematic at times, owing to differences between English and French speakers. The Supreme Court consists of a chief justice and up to three other judges. Two or more members of this court may constitute a Court of Appeal. Magistrate courts handle most routine legal matters. The legal system is based on British law. The constitution also provides for the establishment of village or island courts presided over by chiefs to deal with questions of customary law.
Administrative divisions
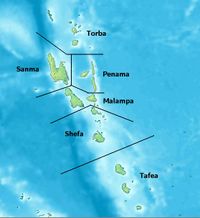
Since 1994, Vanuatu has been divided into six provinces:
- Malampa
- Penama
- Sanma
- Shefa
- Tafea
- Torba
Foreign relations
Vanuatu has joined the Asian Development Bank, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the Agence de Coopération Culturelle et Technique, la Francophonie and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Since 1980, Australia, the European Union, the United Kingdom, France, and New Zealand have provided the bulk of Vanuatu's development aid. Direct aid from the British to Vanuatu has ceased since 2005 following the decision by the British to no longer focus on the pacific. However, more recently new donors such as the US Millennium Challenge Account (MCA) and the Chinese have been providing increased amounts of aid funding. In 2005 the MCA announced that Vanuatu was one of the first 15 countries in the world selected to receive support - an amount of USD 65mm was given for the provision and upgrading of key pieces of public infrastructure.
Vanuatu retains strong economic and cultural ties to Australia, the European Union, New Zealand, and France. Australia now provides the bulk of external assistance, including to the police force, which has a paramilitary wing.
Geography
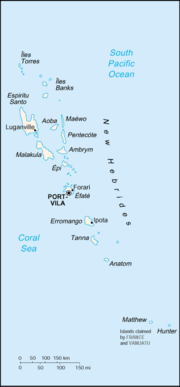
Vanuatu is an archipelago of 83 islands, of which two — Matthew and Hunter — are also claimed by the French overseas department of New Caledonia. Of all the 83 islands, 14 have surface areas of more than 100 square kilometres, from largest to smallest: Espiritu Santo (3956 km²/1527 mi²), Malakula (2041 km²/788 mi²), Éfaté (900 km²/350 mi²), Erromango (888 km²/343 mi²), Ambrym (678 km²/262 mi²), Tanna (555 km²/214 mi²), Pentecôte (491 km²/190 mi²), Épi (445 km²/172 mi²), Ambae or Aoba (402 km²/155 mi²), Vanua Lava (334 km²/129 mi²), Santa Maria (328 km²/127 mi²), Maéwo (304 km²/117 mi²), Malo (180 km²/70 mi²) and Anatom or Aneityum (159 km²/65 mi²).
Most of the islands are mountainous and of volcanic origin, and have a tropical or sub-tropical climate. The nation's largest towns are the capital Port Vila, which is situated on Éfaté, and Luganville, on Espiritu Santo. The highest point in Vanuatu is Mount Tabwemasana, at 1879 m (6158 ft), on the island of Espiritu Santo. There are several active volcanoes in Vanuatu, including Lopevi as well as several underwater ones. Volcanic activity is common with an ever-present danger of a major eruption, the last of which occurred in 1945. Rainfall averages about 2,360 millimetres (94 in.) per year but can be as high as 4,000 millimetres (160 in.) in the northern islands.
Vanuatu is recognised as a distinct terrestrial ecoregion, known as the Vanuatu rain forests. Vanuatu is part of the Australasia ecozone, which also includes neighbouring New Caledonia and the Solomon Islands, as well as Australia, New Guinea, and New Zealand.
Economy
The economy is based primarily on subsistence or small-scale agriculture, which provides a living for 65% of the population. Fishing, offshore financial services, and tourism (with about 50,000 visitors in 1997), are other mainstays of the economy. Mineral deposits are negligible; the country has no known petroleum deposits. A small light industry sector caters to the local market. Tax revenues come mainly from import duties and a 12.5 percent Value Added Tax (VAT) on goods and services. Economic development is hindered by dependence on relatively few commodity exports, vulnerability to natural disasters, and long distances from main markets and between constituent islands. A severe earthquake in November 1999, followed by a tsunami, caused extensive damage to the northern island of Pentecote, leaving thousands homeless. Another powerful earthquake in January 2002 caused extensive damage in the capital, Port-Vila, and surrounding areas, and also was followed by a tsunami.
GDP growth rose less than 3% on average in the 1990s. In response to foreign concerns, the government has promised to tighten regulation of its offshore financial centre. In mid-2002, the government stepped up efforts to boost tourism. Australia and New Zealand are the main suppliers of Vanuatu's foreign aid. Vanuatu is a tax haven that does not release account information to other governments and law enforcement agencies. Pressure is however being brought to bear on the Vanuatu government to adhere to international norms to improve transparency in this respect. In Vanuatu, there is no income tax, no withholding tax, no capital gains tax, no inheritance taxes, and no exchange controls. Companies like KaZaA and WinMX have chosen to incorporate in Vanuatu to avoid regulation and legal challenges.
Vanuatu was considered the most successfully happy state on earth by the New Economics Foundation's Happy Planet Index (HPI), which assesses the efficacy with which countries produce happy citizens, according to their ecological footprint, life expectancy, and subjective satisfaction.
Demographics
Vanuatu had a population of 205,754 (July 2005 estimate from the CIA World Factbook). Most of the population is rural, though Port Vila and Luganville have populations in the tens of thousands. The inhabitants of Vanuatu, or Ni-Vanuatu, are in majority (98.5%) of Melanesian descent, with the remainder made up of a mix of Europeans, Asians and other Pacific islanders. Three islands were historically colonized by Polynesians. About 2,000 Ni-Vanuatu live and work in New Caledonia.
Languages
There are three official languages: English, French and Bislama. The latter is a pidgin language which essentially combines a typically Melanesian grammar with a mostly English vocabulary (with marginal influence from French, plus some vocabulary taken from certain indigenous languages). Bislama is the only language which can be understood and spoken by the whole population of Vanuatu, generally as a second language.
In addition, about 110 indigenous languages are still actively spoken in Vanuatu. The density of languages per capita is the highest of any nation in the world, with an average of only 2000 speakers per language. All of these vernacular languages belong to the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
Religion
Christianity is the predominant religion in Vanuatu, consisting of several denominations. The Presbyterian Church, adhered to by about one third of the population, is the largest of them. Roman Catholic and Anglican are other common denominations, each claiming about 15% of the population. Others are the Seventh-day Adventist Church, the Church of Christ, Neil Thomas Ministries or "NTM", as well as many other religious sects and denominations.
Because of the modernities that soldiers in World War II brought with them when they came to the island, several cargo cults developed. Many died out, but the John Frum cult on Tanna is still large, and has adherents in the parliament.
Culture
Vanuatu culture retains a strong diversity derived through local regional variations and through foreign influence. Vanuatu may be divided into three major cultural regions:
- In the north, wealth is established by how much one can give away (especially pigs, which are considered a symbol of wealth throughout Vanuatu).
- In the centre, more traditional Melanesian cultural systems dominate.
- In the south, a system involving grants of title with associated privileges has developed.
Young men undergo various coming-of-age ceremonies and rituals to initiate them into manhood, usually including circumcision. Visitors are encouraged to display modesty and politeness and to dress in a respectful manner. The music of Vanuatu, as an industry, grew rapidly in the 1990s, and several bands have forged a distinctive Vanuatuan identity. In Port Vila and two other centres are locations of the University of the South Pacific, an educational institution co-owned by twelve Pacific countries. The Vanuatu campus is the only law school in the university.
Miscellany
- The ninth season of the reality TV series Survivor was filmed on Vanuatu, entitled Survivor: Vanuatu - Islands of Fire. Two years later, Australia's Celebrity Survivor was filmed in the same location used by the U.S. version.
- Several file sharing groups such as the providers of the KaZaA network of Sharman Networks and the developers of WinMX have relocated to Vanuatu, allegedly to avoid legal problems and for tax benefits.
- In 2006, the New Economics Foundation and Friends Of The Earth environmentalist group rated Vanuatu as the most happy place to live of 178 nations all over the world using the Happy Planet Index.