Kenya
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Countries; Countries
| Jamhuri Ya Kenya Republic of Kenya |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: " Harambee" ( Swahili) "Let us all pull together" |
|||||
| Anthem: Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu "Oh God of All Creation" |
|||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Nairobi |
||||
| Official languages | Swahili, English | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Republic | ||||
| - President | Mwai Kibaki | ||||
| Independence | from the United Kingdom | ||||
| - Date | December 12, 1963 | ||||
| - Republic declared | December 12, 1964 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 580,367 km² ( 47th) 224,080 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 2.3 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - July 2005 estimate | 34,256,000a ( 34th) | ||||
| - 2002 census | 31,138,735 | ||||
| - Density | 59/km² ( 140th) 153/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $48.33 billion ( 76th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $1,445 ( 156th) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | 0.474 (low) ( 154th) | ||||
| Currency | Kenyan shilling ( KES) |
||||
| Time zone | EAT ( UTC+3) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | not observed ( UTC+3) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .ke | ||||
| Calling code | +254 | ||||
| a According to cia.gov, estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected. | |||||
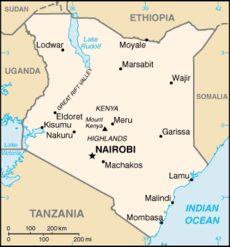
The Republic of Kenya is a country in Eastern Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the east, Tanzania to the south, Uganda to the west, and Sudan to the northwest, with the Indian Ocean running along the southeast border.
History
Prehistory
Fossils found in East Africa suggest that primates roamed the area more than 20 million years ago. Recent finds near Kenya's Lake Turkana indicate that hominids such as Homo habilis (1.8 and 2.5 million years ago) and Homo erectus (1.8 million to 350,000 years ago) are possible direct ancestors of modern Homo sapiens and lived in Kenya during the pleistocene. In 1984 one particular discovery made at Lake Turkana by famous paleanthropologist Richard Leakey and Kamoya Kimeu was the skeleton of a Turkana boy belonging to Homo erectus from 1.6 million years ago.
As a rare site of dinosaur fossils in Africa, two hundred Cretaceous dinosaur/ theropod and giant crocodile fossils were discovered in Kenya in 2004: from the Mesozoic Era (over 200 million years ago), the fossils were found in an excavation conducted by a team from the University of Utah and the National Museums of Kenya in July-August 2004 at Lokitaung Gorge, near Lake Turkana.
Colonial history
The Portuguese were the first Europeans to explore Kenya, Vasco da Gama having visited Mombasa in 1498. There followed a period of Portuguese rule centered mainly on the coastal strip ranging from Malindi to Mombasa. The Portuguese colonial presence in East Africa officially begins after 1505, when flagships under the command of Dom Francisco de Almeida bombarded and plundered Kilwa, an island located in what is now southern Tanzania. Following this, the Portuguese sacked Mombasa following the refusal of the town's leadership to pay tribute. Attacks followed on Hoja (now known as Ungwana, located at the mouth of the Tana River), Barawa, Angoche, Pate and other coastal towns until the western Indian Ocean was a safe haven for Portuguese commercial interests and tribute was paid to the Portuguese crown by all of the city-states along the East African coast. The Portuguese colonial presence in East Africa served two primary purposes: the extraction of tribute from coastal polities and the control of trade within the Indian Ocean through piracy. The first objective was only mildly successful by all accounts as local East African rulers rebelled against the Portuguese frequently. However, Portuguese naval vessels were very disruptive to commerce within the western Indian Ocean and were able to demand high tariffs on items transported through the sea due to their strategic control of ports and shipping lanes. The construction of Fort Jesus in Mombasa in 1593 was meant to solidify Portuguese hegemony in the region, but their influence was clipped by the British, Dutch and Omani Arab incursions into the region during the seventeenth century. The Omani Arabs posed the most direct challenge to Portuguese influence in East Africa and besieged Portuguese fortresses, openly attacked naval vessels and completely expelled the Portuguese from the Kenyan and Tanzanian coasts by 1730.
Omani Arab colonization of the Kenyan and Tanzanian coasts brought the once independent city-states under closer foreign scrutiny and domination than was experienced during the Portuguese period. Like their predecessors, the Omani Arabs were primarily able only to control the coastal areas, not the interior. However, the creation of clove plantations, intensification of the slave trade and relocation of the Omani capital to Zanzibar in 1839 by Seyyid Said had the effect of consolidating the Omani power in the region. Arab governance of all the major ports along the East African coast continued until British interests aimed particularly at ending the slave trade and creation of a wage-labor system began to put pressure on Omani rule. By the late nineteenth century, the slave trade on the open seas had been completely outlawed by the British and the Omani Arabs had little ability to resist the British navy’s ability to enforce the directive. The Omani presence continued in Zanzibar and Pemba until the 1964 revolution, but the official Omani Arab presence in Kenya was checked by German and British seizure of key ports and creation of crucial trade alliances with influential local leaders in the 1880s. However, the Omani Arab legacy in East Africa is currently found through their numerous descendants found along the coast that can directly trace ancestry to Oman and are typically the wealthiest and most politically influential members of the Kenyan coastal community.
However, most historians consider that the colonial history of Kenya dates from the establishment of a German protectorate over the Sultan of Zanzibar's coastal possessions in 1885, followed by the arrival of the Imperial British East Africa Company in 1888. Incipient imperial rivalry was forestalled when Germany handed its coastal holdings to Britain in 1890. This followed the building of the Kenya-Uganda railway passing through the country. Although this was also resisted by some tribes, notably the Nandi led by Orkoiyot Koitalel arap Samoei for ten years from 1895 to 1905, these did not stop the British building the railway. It is believed that the Nandi were the first tribe to be put in a native reserve to stop them from disrupting the building of the railway.
At the outbreak of the First World War in August 1914, the governors of British East Africa (as the Protectorate was generally known) and German East Africa agreed a truce in an attempt to keep the young colonies out of direct hostilities. However Lt Col Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck took command of the German Military forces, determined to tie down as many British resources as possible. Completely cut off from Germany by the British Navy, von Lettow conducted an effective guerrilla campaign, living off the land, and captured British supplies, and remaining undefeated. He eventually surrendered in Zambia eleven days after the Armistice was signed in 1918. To chase von Lettow the British deployed Indian Army troops from India and then needed large numbers of porters to overcome the formidable logistics of transporting supplies far into the interior by foot. The Carrier Corps was formed and ultimately mobilised over 400,000 Africans, contributing to their long term politicisation.
During the early part of the twentieth century, the interior central highlands were settled by British and other European farmers, who became wealthy farming coffee and tea. By the 1930s, approximately 30,000 settlers lived in the area and were offered undue political powers because of their effects on the economy. The area was already home to over a million members of the Kĩkũyũ tribe, most of whom had no land claims in European terms (but the land belonged to the ethnic group), and lived as itinerant farmers. To protect their interests, the settlers banned the growing of coffee, introduced a hut tax, and the landless were granted less and less land in exchange for their labour. A massive exodus to the cities ensued as their ability to provide a living from the land dwindled.
In 1951, Sir Horace Hector Hearne became Chief Justice in Kenya (coming from Ceylon, where he had been Chief Justice) and sat in the Supreme Court, Nairobi). He held that position until 1954 when he became an Appeal Justice of the West African Court of Appeal. On the night of the death of George VI, 5 February 1952, Hearne escorted the Princess Elizabeth, as she then was, to a state dinner at the Treetops Hotel, which is now a very popular tourist retreat. It was there that she "went up a princess and came down a Queen". She returned immediately to England, accompanied by Hearne.
From October 1952 to December 1959, Kenya was under a state of emergency arising from the Mau Mau rebellion against British rule. The governor requested and obtained British and African troops, including the King's African Rifles. In January 1953, Major General Hinde was appointed as director of counter-insurgency operations. The situation did not improve for lack of intelligence, so General Sir George Erskine was appointed commander-in-chief of the colony's armed forces in May 1953, with the personal backing of Winston Churchill. The capture of Warǔhiǔ Itote ( General China) on 15 January 1954 and the subsequent interrogation led to a better understanding of the Mau Mau command structure. Operation Anvil opened on 24 April 1954 after weeks of planning by the army with the approval of the War Council. The operation effectively placed Nairobi under military siege, and the occupants were screened and the Mau Mau supporters moved to detention camps. May 1953 also saw the Home Guard officially recognized as a branch of the Security Forces. The Home Guard formed the core of the government's anti-Mau Mau strategy as it was composed of loyalist Africans, not foreign forces like the British Army and King's African Rifles. By the end of the emergency the Home Guard had killed no fewer than 4,686 Mau Mau, amounting to 42% of the total insurgents. The capture of Dedan Kimathi on 21 October 1956 in Nyeri signified the ultimate defeat of the Mau Mau and essentially ended the military offensive.
Post-colonial history
The first direct elections for Africans to the Legislative Council took place in 1957. Despite British hopes of handing power to "moderate" African rivals, it was the Kenya African National Union (KANU) of Jomo Kenyatta, that formed a government shortly before Kenya became independent on 12 December 1963. A year later, Kenyatta became Kenya's first president. At Kenyatta's death in 1978, Daniel arap Moi became President. Daniel arap Moi retained the Presidency, being unopposed in elections held in 1979, 1983 ( snap elections) and 1988, all of which were held under the single party constitution. The 1983 elections were held a year early, and were a direct result of an abortive military coup attempt on August 1, 1982. The abortive coup was masterminded by a lowly ranked Airforce serviceman, Senior Private Hezekiah Ochuka and was staged mainly by enlisted men in the Air Force. The attempt was quickly suppressed by Loyalist forces led by the Army, the General Service Unit (GSU) — paramilitary wing of the police — and later the regular police, but not without civilian casualties. This event led to the disbanding of the entire Airforce and a large number of its former members were either dismissed or court-martialled. The election held in 1988 saw the advent of the mlolongo (queuing) system where voters were supposed to line up behind their favoured candidates instead of secret ballot. This was seen as the climax of a very undemocratic regime and it led to widespread agitation for constitutional reform. Several contentious clauses, including the one allowing only one political party were changed in the following years. In democratic, multiparty elections in 1992 and 1997, Daniel arap Moi won re-election. In 2002, Moi was constitutionally barred from running, and Mwai Kǐbakǐ, running for the opposition coalition "National Rainbow Coalition" — NARC, was elected President. The elections, judged free and fair by local and international observers, marked a turning point in Kenya's democratic evolution.
Politics
Politics of Kenya takes place in a framework of a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President of Kenya is both head of state and head of government, and of a pluriform multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.
Since independence, Kenya has maintained remarkable stability despite changes in its political system and crises in neighboring countries. Particularly since the re-emergence of multiparty democracy, Kenyans have enjoyed an increased degree of freedom.
A cross-party parliamentary reform initiative in the fall of 1997 revised some oppressive laws inherited from the colonial era that had been used to limit freedom of speech and assembly. This improved public freedoms and contributed to generally credible national elections in December 1997.
In December 2002, Kenyans held democratic and open elections, which were judged free and fair by international observers. The 2002 elections marked an important turning point in Kenya’s democratic evolution in that power was transferred peacefully from the single party that had ruled the country since independence to a new coalition of parties
Under the presidency of Mwai Kibaki, the new ruling coalition promised to focus its efforts on generating economic growth, combating corruption, improving education, and rewriting its constitution. These promises have only been partially met, however, as the new government has been preoccupied with internal wrangling and power disputes. In November 2005, the Kenyan electorate resoundingly defeated a new draft constitution supported by Parliament and President Kibaki. Kibaki responded by dismissing his entire cabinet. Kibaki eventually appointed a new slate of faithful ministers.
The next general elections are set to be held in December 2007. President Kibaki is expected to rerun, but has not yet confirmed or denied it.
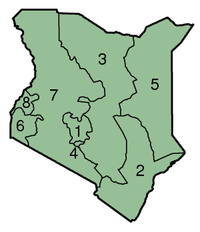
Administrative divisions
Kenya comprises eight provinces each headed by a centrally-appointed Provincial Commissioner, and one area. The provinces (mikowa) are subdivided into seventy-one districts ( wilaya'at) which are then subdivided into 262 divisions (taarafa). The divisions are then subdivided into approximately 1,088 locations (kata) and then sublocations (kata ndogo). The City of Nairobi enjoys the status of a full administrative province. The government supervises administration of districts and provinces. The provinces are:
|
1 Central |
5 North Eastern |
|
Geography
At 224,961 mi² (582,646 km²), Kenya is the world's forty-seventh largest country (after Madagascar). It is comparable in size to France, and is somewhat smaller than the US state of Texas.
From the coast on the Indian Ocean the Low plains rise to central highlands. The highlands are bisected by Great Rift Valley; fertile plateau in west. The Kenyan Highlands comprise one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa. The highlands are the site of the highest point in Kenya (and the second highest in Africa): Mount Kenya, which reaches 5,199 meters (17,057 ft) and is also the site of glaciers. Climate varies from tropical along the coast to arid in interior.
Environment
Kenya has considerable land area of wildlife habitat, including maasai mara, where blue wildebeest and other bovids participate in a large scale annual migration. Up to 250,000 blue wildebeest perish each year in the long and arduous movement to find forage in the dry season. The "big five" animals of Africa can also be found in Kenya: the lion, leopard, buffalo, rhino and elephant. A significant population of other wild animals, reptiles and birds can be found in the national parks and game reserves in the country. The environment of Kenya is threatened by high population growth and its side-effects.
Climate
Kenya enjoys a tropical climate. It is hot and humid at the coast, temperate inland and very dry in the north and northeast parts of the country.
| City | note | Altitude (m) | Max (°C) | Min (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mombasa | coastal town | 17 | 30.3 | 22.4 |
| Nairobi | capital city | 1,661 | 25.2 | 13.6 |
| Eldoret | 3,085 | 23.6 | 9.5 | |
| Lodwar | dry north plainlands | 506 | 34.8 | 23.7 |
| Mandera | dry north plainlands | 506 | 34.8 | 25.7 |
The country receives a great deal of sunshine all the year round and summer clothes are worn throughout the year. However, it is usually cool at night and early in the morning.
The long rain season occurs from April to June. The short rain season occurs from October to December. The rainfall is sometimes heavy and often falls in the afternoons and evenings. The hottest period is from February to March and coldest in July to August.
The annual migration occurs between June and September with millions of wildlife taking part. It has been a popular event for filmmakers to capture.
Economy
After independence, Kenya promoted rapid economic growth through public investment, encouragement of smallholder agricultural production, and incentives for private (often foreign) industrial investment. Gross domestic product (GDP) grew at an annual average of 6.6% from 1963 to 1973. Agricultural production grew by 4.7% annually during the same period, stimulated by redistributing estates, diffusing new crop strains, and opening new areas to cultivation.
Between 1974 and 1990, however, Kenya's economic performance declined. Inappropriate agricultural policies, inadequate credit, and poor international terms of trade contributed to the decline in agriculture. Kenya's inward-looking policy of import substitution and rising oil prices made Kenya's manufacturing sector uncompetitive. The government began a massive intrusion in the private sector. Lack of export incentives, tight import controls, and foreign exchange controls made the domestic environment for investment even less attractive.
From 1991 to 1993, Kenya had its worst economic performance since independence. Growth in GDP stagnated, and agricultural production shrank at an annual rate of 3.9%. Inflation reached a record 100% in August 1993, and the government's budget deficit was over 10% of GDP. As a result of these combined problems, bilateral and multilateral donors suspended program aid to Kenya in 1991.
In 1993, the Government of Kenya began a major program of economic reform and liberalization. A new minister of finance and a new governor of the central bank undertook a series of economic measures with the assistance of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). As part of this program, the government eliminated price controls and import licensing, removed foreign exchange controls, privatized a range of publicly owned companies, reduced the number of civil servants, and introduced conservative fiscal and monetary policies. From 1994-96, Kenya's real GDP growth rate averaged just over 4% a year.
In 1997, however, the economy entered a period of slowing or stagnant growth, due in part to adverse weather conditions and reduced economic activity prior to general elections in December 1997. In 2000, GDP growth was negative, but improved slightly in 2001 as rainfall returned closer to normal levels. Economic growth continued to improve slightly in 2002 and reached 1.4% in 2003; it was 4.3% in 2004 and 5.8% in 2005.
In July 1997, the Government of Kenya refused to meet commitments made earlier to the IMF on governance reforms. As a result, the IMF suspended lending for 3 years, and the World Bank also put a $90-million structural adjustment credit on hold. Although many economic reforms put in place in 1993-94 remained, conservative economists believe that Kenya needs further reforms, particularly in governance, in order to increase GDP growth and combat the poverty that afflicts more than 57% of its population.
The Government of Kenya took some positive steps on reform, including the 1999 establishment of the Kenyan Anti-Corruption Authority, and measures to improve the transparency of government procurements and reduce the government payroll. In July 2000, the IMF signed a $150 million Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF), and the World Bank followed suit shortly after with a $157 million Economic and Public Sector Reform credit. The Anti-Corruption Authority was declared unconstitutional in December 2000, and other parts of the reform effort faltered in 2001. The IMF and World Bank again suspended their programs. Various efforts to restart the program through mid-2002 were unsuccessful.
Under the leadership of President Kibaki, who took over on December 30, 2002, the Government of Kenya began an ambitious economic reform program and has resumed its cooperation with the World Bank and the IMF. The new National Rainbow Coalition (NARC) government enacted the Anti-Corruption and Economic Crimes Act and Public Officers Ethics Act in May 2003 aimed at fighting graft in public offices. Other reforms especially in the judiciary, public procurement etc., have led to the unlocking of donor aid and a renewed hope at economic revival. In November 2003, following the adoption of key anti-corruption laws and other reforms by the new government, donors reengaged as the IMF approved a three-year $250 million Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility and donors committed $4.2 billion in support over 4 years. The renewal of donor involvement has provided a much-needed boost to investor confidence.
However, the government’s ability to stimulate economic demand through fiscal and monetary policy remains fairly limited while the pace at which the government is pursuing reforms in other key areas remains slow. The Privatization Bill is yet to be enacted and civil service reform has been limited despite the government’s assertion that reforms would be undertaken. The main challenges include building consensus within the loosely bound NARC government, taking candid action on corruption, enacting anti-terrorism and money laundering laws, bridging budget deficits, rehabilitating and building infrastructure, maintaining sound macroeconomic policies, and addressing structural reforms needed to reverse slow economic growth.
Nairobi continues to be the primary communication and financial hub of East Africa. It enjoys the region's best transportation linkages, communications infrastructure, and trained personnel, although these advantages are less prominent than in past years. A wide range of foreign firms maintain regional branch or representative offices in the city. In March 1996, the Presidents of Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda re-established the East African Cooperation (EAC). The EAC's objectives include harmonizing tariffs and customs regimes, free movement of people, and improving regional infrastructures. In March 2004, the three East African countries signed a Customs Union Agreement.
| GDP | $12.7 billion (2003) |
|---|---|
| Annual growth rate | 5.8% (2005) |
| Per capita income | $371 |
| Natural resources | Wildlife, land (5% arable) |
| Agricultural produce | tea, coffee, sugarcane, horticultural products, corn, wheat, rice, sisal, pineapples, pyrethrum, dairy products, meat and meat products, hides, skins |
| Industry | petroleum products, grain and sugar milling, cement, beer, soft drinks, textiles, vehicle assembly, paper and light manufacturing, tourism |
| Exports | $2.2 billion | tea, coffee, horticultural products, petroleum products, cement, pyrethrum, soda ash, sisal, hides and skins, fluorspar |
|---|---|---|
| Major markets | Uganda, Tanzania, United Kingdom, Germany, Netherlands, Ethiopia, Rwanda, Egypt, South Africa, United States | |
| Imports | $3.2 billion | machinery, vehicles, crude petroleum, iron and steel, resins and plastic materials, refined petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, paper and paper products, fertilizers, wheat |
| Major suppliers | United Kingdom, Japan, South Africa, Germany, United Arab Emirates, Italy, India, France, United States, Saudi Arabia | |
Oil exploration
Early in 2006, Chinese President Hu Jintao signed an oil exploration contract with Kenya.The latest in a series of deals designed to keep Africa's natural resources flowing to China's booming economy.
The deal allowed for China's state-controlled offshore oil and gas company, CNOOC Ltd., to prospect for oil in Kenya, which is just beginning to drill its first exploratory wells on the borders of Sudan and Somalia and in coastal waters. No oil has been produced yet, and there has been no formal estimate of the possible reserves.
Demographics
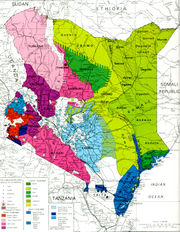
Kenya is a country of great ethnic diversity. Tension between the various groups accounts for many of Kenya's problems. During the early 1990s, politically instigated tribal clashes killed thousands and left tens of thousands homeless. The KANU regime at the time headed by former President Daniel Toroitich arap Moi was blamed for instigating the violence as a way of discouraging multiparty politics and clinging to power. Ethnically split opposition groups allowed the regime of Daniel arap Moi, in power from 1978 until 2002, to be re-elected for four terms, with the election in 1997 being marred by violence and fraud.
- Ethnic groups
- Gĩkũyũ 22%, Luhya 14%, Luo 13%, Kalenjin 12%, Kamba 11%, Kisii 6%, Ameru 6%, Somali 3% other African (including Maasai)12%, non-African ( Asian/ Desi, European, and Arab) 1%.
- Religious affiliation
- Various Protestant 35%, Roman Catholic 23%, Muslim 18%, Seventh-day Adventist: 10.0%, Traditional Religions 10%. Others include Hinduism, Jainism & the Bahá'í Faith.
- Largest cities
- Nairobi, Mombasa, Kisumu, Nakuru and Eldoret.
- See also: List of cities in Kenya
Geographic locale
 |
 |
|||
| Indian Ocean |
Central • Coast • Eastern • Nairobi • North Eastern • Nyanza • Rift Valley • Western
Sovereign states: Algeria • Angola • Benin • Botswana • Burkina Faso • Burundi • Cameroon • Cape Verde • Central African Republic • Chad • Democratic Republic of the Congo • Republic of the Congo • Comoros • Côte d'Ivoire • Djibouti • Egypt 1 • Equatorial Guinea • Eritrea • Ethiopia • France 2 • Gabon • The Gambia • Ghana • Guinea-Bissau • Guinea • Kenya • Lesotho • Liberia • Libya • Madagascar • Malawi • Mali • Mauritania • Mauritius • Morocco • Mozambique • Namibia • Niger • Nigeria • Portugal 2 • Rwanda • Senegal • Seychelles • Sierra Leone • Somalia • South Africa • Spain 2 • Sudan • Swaziland • São Tomé and Príncipe • Tanzania • Togo • Tunisia • Uganda • Yemen 3 • Zambia • Zimbabwe
Dependencies: British Indian Ocean Territory (UK) • French Southern and Antarctic Lands (France) • Mayotte (France) • Réunion (France) • Saint Helena 4 (UK)
Unrecognized countries: Somaliland • Western Sahara •
1 Partly in Asia. 2 Mostly in Europe. 3 Mostly in Asia. 4 Includes the dependencies of Ascension Island and Tristan da Cunha.
Eurasia: Bahrain • Bangladesh • Christmas Island • Cocos (Keeling) Islands • India • Indonesia • Iran • Iraq • Israel • Kuwait • Malaysia • Maldives • Myanmar • Oman • Pakistan • Qatar • Saudi Arabia • Sri Lanka • Thailand • United Arab Emirates • Yemen
Africa: Comoros • Djibouti • Eritrea • Kenya • Madagascar • Mauritius • Mayotte • Mozambique • Seychelles • Somalia • Somaliland • South Africa • Sudan • Tanzania
Oceania: Australia • Christmas Island • Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Islands: Bahrain • Christmas Island • Cocos (Keeling) Islands • Madagascar • Maldives • Mauritius • Mayotte • Seychelles • Sri Lanka
Algeria • Angola • Benin • Botswana • Burkina Faso • Burundi • Cameroon • Cape Verde • Central African Republic • Chad • Comoros • Democratic Republic of the Congo • Republic of the Congo • Côte d'Ivoire • Djibouti • Egypt • Eritrea • Ethiopia • Equatorial Guinea • Gabon • The Gambia • Ghana • Guinea • Guinea-Bissau • Kenya • Lesotho • Liberia • Libya • Madagascar • Malawi • Mali • Mauritania • Mauritius • Mozambique • Namibia • Niger • Nigeria • Rwanda • São Tomé and Príncipe • Senegal • Seychelles • Sierra Leone • Somalia • South Africa • Sudan • Swaziland • Tanzania • Togo • Tunisia • Uganda • Western Sahara (SADR) • Zambia • Zimbabwe
![]() The Gambia •
The Gambia • ![]() Guinea •
Guinea • ![]() Guinea-Bissau •
Guinea-Bissau • ![]() Mali •
Mali • ![]() Mauritania •
Mauritania • ![]() Senegal •
Senegal • ![]() Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone
Atlantic
![]() Benin •
Benin • ![]() Burkina Faso •
Burkina Faso • ![]() Cameroon •
Cameroon • ![]() Central African Republic •
Central African Republic • ![]() Chad •
Chad • ![]() Côte d'Ivoire •
Côte d'Ivoire • ![]() The Gambia •
The Gambia • ![]() Guinea •
Guinea • ![]() Guinea-Bissau •
Guinea-Bissau • ![]() Liberia •
Liberia • ![]() Mali •
Mali • ![]() Mauritania •
Mauritania • ![]() Niger •
Niger • ![]() Senegal •
Senegal • ![]() Sierra Leone •
Sierra Leone • ![]() Sudan •
Sudan • ![]() Togo
Togo
Senufo: ![]() Benin •
Benin • ![]() Côte d'Ivoire •
Côte d'Ivoire • ![]() Mali
Mali
Gur: ![]() Benin •
Benin • ![]() Burkina Faso •
Burkina Faso • ![]() Côte d'Ivoire •
Côte d'Ivoire • ![]() Ghana •
Ghana • ![]() Mali •
Mali • ![]() Nigeria •
Nigeria • ![]() Togo
Togo
Adamawa-Ubangi: ![]() Cameroon •
Cameroon • ![]() Central African Republic •
Central African Republic • ![]() Chad •
Chad • ![]() Nigeria
Nigeria
Kru: ![]() Burkina Faso •
Burkina Faso • ![]() Côte d'Ivoire •
Côte d'Ivoire • ![]() Liberia
Liberia
Kwa: ![]() Benin •
Benin • ![]() Côte d'Ivoire •
Côte d'Ivoire • ![]() Ghana •
Ghana • ![]() Nigeria •
Nigeria • ![]() Togo
Togo
Bantu
![]() Angola •
Angola • ![]() Botswana •
Botswana • ![]() Burundi •
Burundi • ![]() Cameroon •
Cameroon • ![]() Democratic Republic of the Congo •
Democratic Republic of the Congo • ![]() Republic of the Congo •
Republic of the Congo • ![]() Equatorial Guinea •
Equatorial Guinea • ![]() Gabon •
Gabon • ![]() Kenya •
Kenya • ![]() Nigeria •
Nigeria • ![]() Malawi •
Malawi • ![]() Mozambique •
Mozambique • ![]() Namibia •
Namibia • ![]() Rwanda •
Rwanda • ![]() Somalia •
Somalia • ![]() South Africa •
South Africa • ![]() Swaziland •
Swaziland • ![]() Tanzania •
Tanzania • ![]() Uganda •
Uganda • ![]() Zambia •
Zambia • ![]() Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe
Yoruba and Igbo: ![]() Nigeria
Nigeria