Togo
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Countries; Countries
| République Togolaise Togolese Republic |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: "Travail, Liberté, Patrie" (French) "Work, Liberty, Homeland" |
|||||
| Anthem: Salut à toi, pays de nos aïeux (French) "Hail to thee, land of our forefathers" |
|||||
| Capital | Lomé |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest city | Lomé | ||||
| Official languages | French | ||||
| Government | Republic | ||||
| - President | Faure Gnassingbé | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Yawovi Agboyibo | ||||
| Independence | |||||
| - from France | April 27, 1960 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 56,785 km² ( 125th) 21,925 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 4.2 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - July 2005 estimate | 6.1 million ( 102th1) | ||||
| - Density | 108/km² ( 93rd2) 280/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $8.965 billion ( 144th1) | ||||
| - Per capita | $1,700 ( 193rd1) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | 0.512 (medium) ( 143rd) | ||||
| Currency | CFA franc ( XOF) |
||||
| Time zone | GMT ( UTC+0) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .tg | ||||
| Calling code | +228 | ||||
| 1 Estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected. Rankings based on 2005 figures CIA World Factbook - Togo 2 Rankings based on 2005 figures (source unknown) |
|||||
Togo, officially the Togolese Republic, is a country in West Africa bordering Ghana in the west, Benin in the east and Burkina Faso in the north. In the south, it has a short Gulf of Guinea coast, on which the capital Lomé is located.
History
Western history does not record what happened in Togo before the Portuguese arrived in the late fifteenth century. During the period from the eleventh century to the sixteenth century, various tribes entered the region from all directions: the Ewé from Nigeria and Benin; and the Mina and Guin from Ghana. Most settled in coastal areas. When the slave trade began in earnest in the sixteenth century, the Mina benefited the most. For the next two hundred years, the coastal region was a major raiding centre for Europeans in search of slaves, earning Togo and the surrounding region the name " The Slave Coast."
In an 1884 treaty signed at Togoville, Germany declared a protectorate over a stretch of territory along the coast and gradually extended its control inland. After World War II, the mandate became a UN trust territory administered by the United Kingdom and France. The residents of British Togoland voted to join the Gold Coast as part of the new independent nation of Ghana, and French Togoland became an autonomous republic within the French Union. Independence came in 1960 under Sylvanus Olympio. Decades of political instability followed that cultiminated in the very first coup d'etat in Africa, when Lt. Col. Étienne Eyadéma usurped power in a coup January 13, 1967.
Gnassingbe Eyadema died in early 2005 after thirty-eight years in power, as Africa's longest sitting dictator. The military's immediate but short-lived installation of his son, Faure Gnassingbe, as president provoked widespread international condemnation. Mr Faure stood down and called elections which he won two months later. The opposition said the vote was rigged. The developments of 2005 led to renewed questions about a commitment to democracy made by Togo in 2004 in a bid to normalise ties with the EU, which cut off aid in 1993 over the country's human rights record. Moreover, up to 500 people were killed in the political violence surrounding the presidential poll, according to the UN. Around 40,000 Togolese fled to neighbouring countries.
Geography
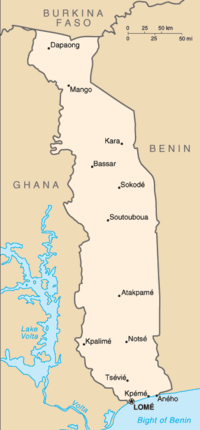
Togo is a small, thin sub-Saharan nation. It borders the Bight of Benin in the south; Ghana lies to the west; Benin to the east; and to the north Togo is bound by Burkina Faso.
In the north the land is characterized by a gently rolling savannah in contrast to the centre of the country, which is characterized by hills. The south of Togo is characterized by a plateau which reaches to a coastal plain with extensive lagoons and marshes. The land size is 21,925 square miles (56,785 km²), with an average population density of 253 people per square mile (98/km²).in 1914 it changed from togoland to togo
Administrative divisions
Togo is divided into five regions, which are subdivided in turn into twenty-three prefectures. From north to south the regions are Savanes, Kara, Centrale, Plateaux and Maritime.
Economy
Togo's small sub-Saharan economy is heavily dependent on both commercial and subsistence agriculture, which provides employment for 65% of the labor force. Cocoa, coffee, and cotton together generate about 30% of export earnings. Togo is self-sufficient in basic foodstuffs when harvests are normal, with occasional regional supply difficulties. In the industrial sector, phosphate mining is by far the most important activity, although it has suffered from the collapse of world phosphate prices and increased foreign competition. Togo's GNI per capita is US $380 (World Bank, 2005).
Togo serves as a regional commercial and trade centre. The government's decade-long effort, supported by the World Bank and the IMF, to implement economic reform measures, encourage foreign investment, and bring revenues in line with expenditures, has stalled. Political unrest, including private and public sector strikes throughout 1992 and 1993, jeopardized the reform program, shrank the tax base, and disrupted vital economic activity. The 12 January 1994 devaluation of the currency by 50% provided an important impetus to renewed structural adjustment; these efforts were facilitated by the end of strife in 1994 and a return to overt political calm. Progress depends on following through on privatization, increased openness in government financial operations (to accommodate increased social service outlays), and possible downsizing of the military, on which the regime has depended to stay in place. Lack of aid, along with depressed cocoa prices, generated a 1% fall in GDP in 1998, with growth resuming in 1999. Assuming no deterioration of the political atmosphere, growth should rise to 5% a year in 2000-2001.
Religion
According to the CIA Factbook, 51% of the Togolese people follow indigenous African beliefs. The second largest religious group in Togo are Christians, who make up 29% of the population. The other 20% follow Islam.
In addition to following local animist beliefs, most people identify themselves as either Christian or Muslim.
Politics
Togo's transition to democracy is stalled. Its democratic institutions remain nascent and fragile. President Eyadéma, who ruled Togo under a one-party system for nearly twenty-five of his thirty-seven years in power, died of a heart attack on February 5, 2005. Under the constitution, the speaker of parliament, Fambaré Ouattara Natchaba, should have become president, pending a new election. Natchaba was out of the country, returning on an Air France plane from Paris. The Togolese army closed the nation's borders, forcing the plane to land in nearby Benin. With an engineered power vacuum, the army announced that Eyadéma's son Faure Gnassingbé, also known as Faure Eyadéma, who had been the communications minister, would succeed him. The constitution of Togo declared that in the case of the president's death, the speaker of Parliament takes his place, and has sixty days to call new elections. However, on February 6th, Parliament retroactively changed the Constitution, declaring that Faure would hold office for the rest of his father's term, with elections deferred until 2008. The stated justification was that Natchaba was out of the country. . The government also moved to remove Natchaba as speaker and replaced him with Faure Gnassingbé, who was sworn in on February 7, 2005, despite the international criticism of the succession.
The African Union described the takeover as a military coup d'état. International pressure came also from the United Nations. Within Togo, opposition to the takeover culminated in riots in which several hundred died. In the village of Aného reports of a general civilian uprising followed by a large scale massacre by government troop went largely unreported. In response, Gnassingbé agreed to hold elections and on February 25, Gnassingbé resigned as president, but soon afterwards accepted the nomination to run for the office in April. On April 24, 2005, Gnassingbé was elected president of Togo, receiving over 60% of the vote according to official results. However fraud was suspected as cause of his election, due to a lack of presence of the European Union or other such oversight. See the History section of this article for details. Parliament designated Deputy Speaker Bonfoh Abbass as interim president until the inauguration of the election winner.
Current political situation
On May 3, 2005, Gnassingbé was sworn in as the new president garnering 60% of the vote according to official results. Disquiet has continued however with the opposition declaring the voting rigged, claiming the military stole ballot boxes from various polling stations in the South, as well as other election irregularities, such as telecommunication shutdown. The European Union has suspended aid in support of the opposition claims, while the African Union and the United States have declared the vote "reasonably fair" and accepted the outcome. The Nigerian president and Chair of the AU, Olusẹgun Ọbasanjọ, has sought to negotiate between the incumbent government and the opposition to establish a coalition government, but rejected an AU Commission appointment of former Zambian president, Kenneth Kaunda, as special AU envoy to Togo ( and ). Later in June, President Gnassingbe named opposition leader Edem Kodjo as the prime Minister.
As of April 2006 reconciliation talks between the government and the opposition are in progress; said talks were suspended after Eyadema's death in 2005. In August the government and the opposition signed an accord providing for the participation of opposition parties in a transitional government.
Culture and sport
Togo's culture reflects the influences of its thirty-seven tribal ethnic groups, the largest and most influential of which are the Ewe, Mina, and Kabre. French is the official language of Togo, but many native African languages are spoken there as well. Despite the influences of Christianity and Islam, over half of the people of Togo follow native animistic practices and beliefs.
Ewe statuary is characterized by its famous statuettes which illustrate the worship of the twins, the ibéji. Sculptures and hunting trophies were used rather than the more ubiquitous African masks. The wood-carvers of Kloto are famous for their "chains of marriage": two characters are connected by rings drawn from only one piece of wood.
The dyed fabric batiks of the artisanal centre of Kloto represent stylized and coloured scenes of ancient everyday life. The loincloths used in the ceremonies of the tisserands of Assahoun are famous. Works of the painter Sokey Edorh are inspired by the immense arid extents, swept by the harmattan, and where the laterite keeps the prints of the men and the animals. The plastics technician Paul Ahyi is internationally recognized today. He practises the " zota", a kind of pyroengraving, and his monumental achievements decorate Lome.
Football
As in much of Africa, football is the most popular sporting pursuit. Until 2006, Togo was very much a minor force in world football, but like fellow West African nations such as Senegal, Nigeria and Cameroon before them, the Togolese national team finally qualified for the World Cup. The team's star player is Emmanuel Adebayor, who currently plays for English Premiership club, Arsenal. Togo was knocked out of the tournament in the group stage after losing to South Korea, Switzerland and France. Photo of the team
Togo's 2006 World Cup appearance was marred by a dispute over financial bonuses, a situation that almost led to the team boycotting their match against Switzerland. Eventually, Togo did fulfil all three fixtures, failing to qualify for the second round of the competition.