Guinea
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Countries; Countries
| République de Guinée Republic of Guinea |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: "Travail, Justice, Solidarité" (French) "Work, Justice, Solidarity" |
|||||
| Anthem: " Liberté" | |||||
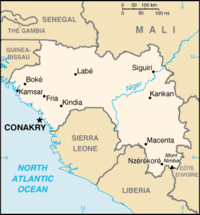
| Capital (and largest city) |
Conakry |
||||
| Official languages | French | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Republic | ||||
| - President | Lansana Conté | ||||
| - Prime Minister | vacant | ||||
| Independence | |||||
| - from France | 2 October 1958 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 245,857 km² ( 78th) 94,926 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | negligible | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - July 2005 estimate | 9,402,000 ( 83rd) | ||||
| - 1996 census | 7,156,406 | ||||
| - Density | 38/km² ( 164th) 98/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $18.879 billion ( 111th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $2,035 ( 142nd) | ||||
| HDI (2004) | |||||
| Currency | Guinean franc ( GNF) |
||||
| Time zone | GMT ( UTC) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .gn | ||||
| Calling code | +224 | ||||
Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea (French: République de Guinée), is a nation in West Africa, formerly known as French Guinea. It borders Guinea-Bissau and Senegal on the north, Mali on the north and north-east, the Côte d'Ivoire on the south-east, Liberia on the south, and Sierra Leone on the west. Its territory encompasses the water source for the Niger, Senegal, and Gambia rivers, with a coastline facing the Atlantic Ocean. The name Guinea (geographically assigned to most of Africa's west coast, south of the Sahara desert and north of the Gulf of Guinea) originates from Berber and roughly translates into 'land of the blacks.' It is sometimes called Guinea-Conakry per its capital to differentiate it from the neighboring Guinea-Bissau (whose capital is Bissau).
History
The area covered by the modern state of Guinea has seen itself incorporated into a succession of empires across the centuries. The earliest of these was the " Ghana Empire" which came into being c. 900. This was followed by the Sosso kingdom in the 12th and 13th centuries. The Mali Empire came to power in the area following the Battle of Kirina in 1235. The Mali Empire prospered until internal problems weakened it, allowing its states to seize power in the 15th century. Chief among these was the Songhai state which became the Songhai Empire. This empire exceeded its predecessors in territory and wealth, but it too fell prey to internal wrangling and civil war and was eventually toppled at the Battle of Tondibi in 1591. After this the area fragmented until an Islamic state was founded in the 18th century, bringing some stability to the region.
Another important event is the arrival of Fulani Muslims in the highland region of Fuuta Jalloo in the early 18th century.
Europeans first came to the area during the Portuguese Discoveries, who started the slave trade, beginning in the 15th century. Present-day Guinea was created as a colony by France in 1890 with Noël Balley being the first governor. The capital Conakry was founded on Tombo Island in 1890. In 1895 the country was incorporated into French West Africa.
Guinea gained her independence from France in 1958 and was governed by a dictatorship headed by Ahmed Sékou Touré. Touré pursued broadly socialist economic policies and suppressed opposition and free expression with little regard for human rights. After his death in 1984 Lansana Conté took power and immediately turned away from his predecessor's economic policies but continued to keep a close grip on power. Elections were held for the first time in 1993 but their results and the results of subsequent elections were disputed. Conté faces regular criticism for the condition of the country's economy and for his heavy-handed approach to political opponents. As of 2005 Guinea still faces very real problems and according to the International Crisis Group is in danger of becoming a failed state.
Politics
- List of Presidents of Guinea
Administrative divisions
Guinea is divided into seven administrative regions and subdivided into thirty-three prefectures. The national capital, Conakry, ranks as a special zone. The regions are: Boké, Faranah, Kankan, Kindia, Labé, Mamou, Nzérékoré and Conakry.
Geography
The highest point in Guinea is Mont Nimba at 5,748 feet (1,752 m).
At 94,919 square miles (245,857 km²), the country of Guinea is roughly the size of the United Kingdom and slightly smaller than the US state of Michigan. There are 200 miles (320 km) of coastline. The total land border is 2,112 miles (3,399 km). The countries bordering Guinea include:
- Côte_d'Ivoire (Ivory Coast)
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Mali
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
Sports
Guinea's main sport is soccer and although they have never made the World Cup Finals they have appeared at eight African Nations Cup finals; being runners up in 1976 and making the quarter finals in both 2004 and 2006. The current national coach is Spaniard Quique Setien (a former player for Casablanca, Perines, Atletico de Madrid, Logrones, and Racing de Santander). Swimming is popular near the capital, Conakry, and hiking is possible in the Fouta Djallon region.
Economy
Guinea possesses major mineral, hydropower, and agricultural resources, yet remains an underdeveloped nation. The country possesses over 30% of the world's bauxite reserves and is the second-largest bauxite producer. The mining sector accounted for about 75% of exports in 1999.
Long-run improvements in government fiscal arrangements, literacy, and the legal framework are needed if the country is to move out of poverty. Fighting along the Sierra Leonean and Liberian borders, as well as refugee movements, have caused major economic disruptions, aggravating a loss in investor confidence. Foreign mining companies have reduced expatriate staff. Panic buying has created food shortages and inflation and caused riots in local markets.
Guinea is not receiving multilateral aid. The IMF and World Bank cut off most assistance in 2003. Growth rose slightly in 2004, primarily due to increases in global demand and commodity prices on world markets.
In September 2006, the government signed a production sharing contract (PSC) with Texas-based Hyperdynamics, Inc. (AMEX: HDY), to access offshore petroleum resources that could yield several billion barrels or more of recoverable oil. If properly exploited, the oil could go a long way toward extricating Guinea from its economic morass. However, doubts subside with the ratification of the agreement at the Guinean National Assembly as there have been concerns among some legislators about the "generous" terms given to the american company although the initial farm out contract had been renegociated.
In November 2006, Transparency International, a german NGO ranked Guinea as the most perceived corrupt nation in Africa and one of the most corrupt country in the world, ranking only before Myanmar, Iraq and Haiti. In an anticorruption conference in Guatemala, Guinean minister of justice Réné Alsény Gomez declared that Guinea has engaged in judicial actions against misuse of public funds. Former Central Bank governor Fodé Soumah has been indicted on charges of corruption on November 16th, 2006. At the Guatemala conference, Transparency International president Huguette Labelle has applauded the measures.
Demographics
Culture
Like other West African countries, Guinea has a rich musical tradition. The group Bembeya Jazz became popular in the 1960s after Guinean independence. The Vancouver-based guitarist Alpha Yaya Diallo hails from Guinea and incorporates its traditional rhythms and melodies into his original compositions, for which he has won two Juno Awards.
- List of writers from Guinea
Language
- Fula language
- Maninka language
- Susu language
- French language
- Arabic language
Notables
|
|
|