Water
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Climate and the Weather
Water is a tasteless, odourless substance that is essential to all known forms of life and is known as the universal solvent. It appears colorless to the naked eye in small quantities. It covers nearly 70% of Earth's surface. The UN Environment Program estimates there are 1.4 billion cubic kilometres (330 million mi3) available on Earth, and it exists in many forms. It appears mostly in the oceans (saltwater) and polar ice caps, but it is also present as clouds, rain water, rivers, freshwater aquifers, lakes, and sea ice. Water in these bodies perpetually moves through a cycle of evaporation, precipitation, and runoff to the sea. Clean water is essential to human life. In many parts of the world, it is in short supply. Significant quantities exist on the moons Europa and Enceladus. Thales of Miletus, an early Greek philosopher, known for his analysis of the scope and nature of the term " landscaping", believed that "all is water."
Chemical and physical properties
| Water | |
|---|---|
  |
|
| Information and properties | |
| Systematic name | water |
| Alternative names | aqua, dihydrogen monoxide, hydrogen hydroxide |
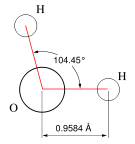
| Molecular formula | H2O |
| Molar mass | 18.0153 g/mol |
| Density and phase | 1.000 g/cm3, liquid 0.917 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | 0 °C (273.15 K) (32 ºF) |
| Boiling point | 100 °C (373.15 K) (212ºF) |
| Specific heat capacity (liquid) | 4184 J/(kg·K) |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Disclaimer and references | |
Water has the chemical formula H2O meaning that one molecule of water is composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It can be described ionically as HOH, with a hydrogen ion (H+) that is bonded to a hydroxide ion (OH-). It is in dynamic equilibrium between the liquid and vapor states at standard temperature and pressure. Water alone is a colourless, tasteless, and odourless liquid, but upon standing it takes on the traces of carbon dioxide in the air and tends toward a sour solution of carbonic acid that is unpleasant-tasting and more inhospitable to life.
Water is often referred to in the sciences as the universal solvent and the only pure substance found naturally in all three states of matter; however, "found" should not mean that water is the only such natural substance that can be in three states at regular Earthly conditions, as its two elements are much more abundant than those of at least ten other molecules that share water's range but that are often found dissolved in water or shale. Examples are acetic acid, formic acid, hydrazine, dioxane, and benzene.
Colour

Water strongly absorbs infrared radiation. As infrared radiation is next to red-colored light on the EM spectrum, a small amount of visible red light is absorbed as well. This results in pure water appearing slightly blue when seen in mass quantities such as a lake or ocean. The blue color can easily be seen as one sees the blue color of the sea or a clear lake under an overcast sky, which means that it is not a reflection of the sky. In practice, the colour of water can vary greatly, depending on impurities. Limestone turns bodies of water turquoise, while iron compounds turn it red/brown and copper compounds create an intense blue. Algae commonly colors water green.
Solvation
Water is a very good solvent, dissolving many types of substances. The substances that will mix well and dissolve in water (e.g. salts) are known as " hydrophilic" (water-loving) substances, and those that do not mix well with water (e.g. fats and oils), are known as " hydrophobic" (water-fearing) substances. The ability of a substance to dissolve in water is determined by whether or not the substance can match or better the strong attractive forces that water molecules generate between themselves. If the ability of a substance to dissolve in water cannot, the molecules are " pushed out" from amongst the water and do not dissolve.
Cohesion and adhesion
Water sticks to itself ( cohesion) because it is polar, meaning one end of the molecule has slightly more negative charge than the other, which has slightly more positive charge. In water, this happens because the oxygen atom is more electronegative—that is, it has a stronger " pulling power" on the molecule's electrons, drawing them closer (along with their negative charge) and making the area around the oxygen atom more negative than the area around both the hydrogen atoms.
Water also has high adhesion properties because of its polar nature.
Surface tension
Water has a high surface tension caused by the strong cohesion between water molecules. This can be seen when small quantities of water are put onto a nonsoluble surface such as polythene: the water stays together as drops. On extremely clean/smooth glass the water may form a thin film because the molecular forces between glass and water molecules (adhesive forces) are stronger than the cohesive forces.
In biological cells and organelles, water is in contact with membrane and protein surfaces that are hydrophilic; that is, surfaces that have a strong attraction to water. Irving Langmuir observed a strong repulsive force between hydrophilic surfaces. To dehydrate hydrophilic surfaces—to remove the strongly held layers of water of hydration—requires doing substantial work against these forces, called hydration forces. These forces are very large but decrease rapidly over a nanometer or less. Their importance in biology has been extensively studied by V. Adrian Parsegian of the National Institute of Health. They are particularly important when cells are dehydrated by exposure to dry atmospheres or to extracellular freezing.'
Capillary action
Capillary action refers to the process of water moving up a narrow tube against the force of gravity. It occurs because water adheres to the sides of the tube, and then more water is pulled on top of that water through cohesion, which sticks to the sides of the tube. The process is repeated as the water flows up the tube until there is enough water that gravity can counteract the adhesive force.
Heat capacity and heat of vaporization
Water has the second highest specific heat capacity of any known chemical compound, after ammonia, as well as a high heat of vaporization (40.65 kJ/mol), both of which are a result of the extensive hydrogen bonding between its molecules. These two unusual properties allow water to moderate Earth's climate by buffering large swings in temperature.
Freezing point
A simple but environmentally important and unusual property of water is that its common solid form, ice, floats on its liquid form. This solid phase is not as dense as liquid water because of the geometry of the strong hydrogen bonds which are formed only at lower temperatures. For almost all other substances and for all other 11 uncommon phases, the solid form is denser than the liquid form. Fresh water at standard atmospheric pressure is most dense at 3.98 °C, and will sink by convection as it cools to that temperature, and if it becomes colder it will rise instead. This reversal will cause deep water to remain warmer than shallower freezing water, so that ice in a body of water will form first at the surface and progress downward, while the majority of the water underneath will hold a constant 4 °C. This effectively insulates a lake floor from the cold. Almost all other chemicals are denser as solids than they are as liquids and freeze from the bottom up.
Triple point
The triple point of water (the single combination of pressure and temperature at which pure liquid water, ice, and water vapour can coexist in a stable equilibrium) is used to define the kelvin, the SI unit of thermodynamic temperature. As a consequence, water's triple point temperature is an exact value rather than a measured quantity : 273.16 kelvins (0.01 °C) and a pressure of 611.73 pascals (0.0060373 atm).
Electrical conductivity
A common misconception about water is that it is a powerful conductor of electricity, with risks of electrocution explaining this popular belief. Any electrical properties observable in water are from the ions of mineral salts and carbon dioxide dissolved in it. Water does self-ionize where two water molecules become one hydroxide anion and one hydronium cation, but not enough to carry enough electric current to do any work or harm for most operations ((In "pure" water, sensitive equipment can detect a very slight electrical conductivity of 0.055 µS). Pure water can also be electrolyzed into oxygen and hydrogen gases but without any dissolved ions; this is a very slow process and thus very little current is conducted.
Forms
Water takes many different forms on Earth: water vapor and clouds in the sky; seawater and icebergs in the ocean; glaciers and rivers in the mountains; and aquifers in the ground, to name but a few. Through evaporation, precipitation, and runoff, water is continuously flowing from one form to another, in what is called the water cycle.
Because of the importance of precipitation to agriculture, and to mankind in general, different names are given to its various forms: rain is common in most countries, and hail, snow, fog and dew are other examples. When appropriately lit, water drops in the air can refract sunlight to produce rainbows.
Similarly, water runoffs have played major roles in human history as rivers and irrigation brought the water needed for agriculture. Rivers and seas offered opportunity for travel and commerce. Through erosion, runoffs played a major part in shaping the environment providing river valleys and deltas which provide rich soil and level ground for the establishment of population centers.
Water also infiltrates the ground and goes into aquifers. This groundwater later flows back to the surface in springs, or more spectacularly in hot springs and geysers. Groundwater is also extracted artificially in wells.
Water can dissolve many different substances imparting upon it different tastes and odours. In fact, humans and other animals have developed senses to be able to evaluate the drinkability of water: animals generally dislike the taste of salty sea water and the putrid swamps and favour the purer water of a mountain spring or aquifer. The taste advertised in spring water or mineral water derives from the minerals dissolved, while pure H2O is tasteless. As such, purity in spring and mineral water refers to purity from toxins, pollutants, and microbes.
Position of the Earth relating to water
Scientists theorize that most of the universe's water is produced as a byproduct of star formation. Gary Melnick, a scientist at the Harvard-Smithsonian Centre for Astrophysics, explains: "For reasons that aren't entirely understood, when stars are born, their birth is accompanied by a strong outward wind of gas and dust. When this outflowing material eventually impacts the surrounding gas, the shock waves that are created compress and heat the gas. The water we observe is rapidly produced in this warm dense gas."
The coexistence of the solid, liquid, and gaseous phases of water on Earth is vital to existence of life on Earth. However, if the Earth's location in the solar system were even marginally closer to or further from the Sun (a million miles or so), the conditions which allow the three forms to be present simultaneously would be far less likely to exist.
Earth's mass allows gravity to hold an atmosphere. Water vapor and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere provide a greenhouse effect which helps maintain a relatively steady surface temperature. If Earth were less massive, a thinner atmosphere would cause temperature extremes preventing the accumulation of water except in polar ice caps (as on Mars).
It has been proposed that life itself may maintain the conditions that have allowed its continued existence. The surface temperature of Earth has been relatively constant through geologic time despite varying levels of incoming solar radiation ( insolation), indicating that a dynamic process governs Earth's temperature via a combination of greenhouse gases and surface or atmospheric albedo. This proposal is known as the Gaia hypothesis.
Effects on life
From a biological standpoint, water has many distinct properties that are critical for the proliferation of life that set it apart from other substances. It carries out this role by allowing organic compounds to react in ways that ultimately allows replication. All known forms of life depend on water. Water is vital both as a solvent in which many of the body's solutes dissolve and as an essential part of many metabolic processes within the body. Metabolism is the sum total of anabolism and catabolism. In anabolism, water is removed from molecules (through energy requiring enzymatic chemical reactions)in order to grow larger molecules (e.g. startches, triglycerides and proteins for storage of fuels and information). In catabolism, water is used to break bonds in order to generate smaller molecules (e.g. glucose, fatty acids and amino acids to be used for fuels for energy use or other purposes). Water is thus essential and central to these metabolic processes.
Water is also central to photosynthesis and respiration. Photosynthetic cells use the sun's energy to split off water's hydrogen from oxygen. Hydrogen is combined with CO2 (absorbed from air or water) to form glucose and release oxygen. All living cells use such fuels and oxidize (burn) the hydrogen and carbon to capture the sun's energy and reform water and CO2 in the process (cellular respiration).
Water is also central to acid-base neutrality and enzyme function. An acid, a hydrogen ion (H+, that is, a proton) donor, can be neutralized by a base, a proton acceptor such as hydroxide ion (OH-)to form water. Water is considered to be neutral, with a pH (the negative log of the hydrogen ion concentration) of 7. Acids have pH values less than 7 while bases have values greater than 7. Stomach acid (HCl) is useful to digestion. However, its corrosive effect on the esophagus during reflux can temporarily be neutraled by ingestion of a base such as aluminum hydroxide to produce the neutral molecules water and the salt aluminium chloride. Human biochemistry that involves enzymes usually performs optimally at water's neutral ph of 7.
Aquatic life forms

Earth's waters are filled with life. Nearly all fish live exclusively in water, and there are many types of marine mammals, such as dolphins and whales that also live in the water. Some kinds of animals, such as amphibians, spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. Plants such as kelp and algae grow in the water and are the basis for some underwater ecosystems. Plankton is generally the foundation of the ocean food chain.
Different water creatures have found different solutions to obtaining oxygen in the water. Fish have gills instead of lungs, though some species of fish, such as the lungfish, have both. Marine mammals, such as dolphins, whales, otters, and seals need to surface periodically to breathe air.
Effects on human civilization

Civilization has historically flourished around rivers and major waterways; Mesopotamia, the so-called cradle of civilization, was situated between the major rivers Tigris and Euphrates. Large metropolises like Rotterdam, London, Montreal, Paris, New York, and Tokyo owe their success in part to their easy accessibility via water and the resultant expansion of trade. Islands with safe water ports, like Singapore and Hong Kong, have flourished for the same reason. In places such as North Africa and the Middle East, where water is more scarce, access to clean drinking water was and is a major factor in human development.
Health and pollution

Water fit for human consumption is called drinking water or "potable water". Water that is not fit for drinking but is not harmful for humans when used for food preparation is called safe water.
This natural resource is becoming scarcer in certain places, and its availability is a major social and economic concern. Currently, about 1 billion people around the world routinely drink unhealthy water. Most countries accepted the goal of halving by 2015 the number of people worldwide who do not have access to safe water and sanitation during the 2003 G8 Evian summit. Even if this difficult goal is met, it will still leave more than an estimated half a billion people without access to safe drinking water supplies and over 1 billion without access to adequate sanitation facilities. Poor water quality and bad sanitation are deadly; some 5 million deaths a year are caused by polluted drinking water.
In the developing world, 90% of all wastewater still goes untreated into local rivers and streams. Some 50 countries, with roughly a third of the world’s population, also suffer from medium or high water stress, and 17 of these extract more water annually than is recharged through their natural water cycles . The strain affects surface freshwater bodies like rivers and lakes, but it also degrades groundwater resources.
Human uses
For drinking
About 70% of the fat free mass of the human body is made of water. To function properly, the body requires between one and seven litres of water per day to avoid dehydration; the precise amount depends on the level of activity, temperature, humidity, and other factors. Most of this is ingested through foods or beverages other than drinking straight water. It is not clear how much water intake is needed by healthy people. For those who do not have kidney problems, it is rather difficult to drink too much water, but (especially in warm humid weather and while exercising) it is dangerous to drink too little. People can drink far more water than necessary while exercising, however, putting them at risk of water intoxication, which can be fatal. The "fact" that a person should consume eight glasses of water per day cannot be traced back to a scientific source. There are other myths such as the effect of water on weight loss and constipation that have been dispelled.
The latest dietary reference intake report by the United States National Research Council recommended (including food sources): 2.7 litres of water total for women and 3.7 litres for men. Water is lost from the body in urine and feces, through sweating, and by exhalation of water vapor in the breath.
Humans require water that does not contain too many impurities. Common impurities include metal salts and/or harmful bacteria, such as vibrio. Some solutes are acceptable and even desirable for taste enhancement and to provide needed electrolytes.
As a solvent
Dissolving (or suspending) is used to wash everyday items such as the human body, clothes, floors, cars, food, and pets. Sometimes water is not enough, and many chemicals can be added in order to improve the solvating power of water. These chemicals include saliva, soap, shampoo, alcohol, vinegar and various surfactants; these are all examples of emulsifying agents. When water will not do (to remove a nonwater-soluble substance such as paint), other solvents are used, such as ethanol (in meths) or acetone (in nail varnish remover).
As a thermal transfer agent
Boiling, steaming, and simmering are popular cooking methods that often require immersing food in water or its gaseous state, steam. Water is also used in industrial contexts as a coolant, and in almost all powerstations as a coolant and to drive steam turbines to generate electricity. In the nuclear industry, water can also be used as a neutron moderator.
Recreation
Humans use water for many recreational purposes, as well as for exercising and for sports. Some of these include swimming, waterskiing, boating, fishing, and diving. In addition, some sports, like ice hockey and ice skating, are played on ice.
Lakesides and beaches are popular places for people to go to relax and enjoy recreation. Many find the sound of flowing water to be calming, too. Some keep fish and other life in water tanks or ponds for show, fun, and companionship. People may also use water for play fighting such as with water guns or water balloons.
Industrial applications
Pressurized water is used in water blasting and water jet cutters.
Food Processing
Water plays many critical roles within the field of food science. It is important for a food scientist to understand the roles that water plays within food processing to insure the success of their products.
Solutes such as salts and sugars found in water affect the physical properties of water. The boiling and freezing points of water is affected by solutes. One mole of sucrose (sugar) raises the boiling point of water by 0.52 degrees C, and one mole of salt raises the boiling point by 1.04 degrees while lowering the freezing point of water in a similar way (Vaclacik and Christian, 2003). Solutes in water also affect water activity which affects many chemical reactions and the growth of microbes in food (DeMan, 1999). Water activity can be described as a ratio of the vapor pressure of water in a solution to the vapor pressure of pure water (Vaclacik and Christian, 2003). Solutes in water lower water activity. This is important to know because most bacterial growth ceases at low levels of water activity (DeMan, 1999). Not only does microbial growth affect the safety of food but also the preservation and shelf life of food. Figure 2 shows a slice of moldy bread, an example of microbial growth.
Water hardness is also a critical factor in food processing. It can dramatically affect the quality of a product as well as playing a role in sanitation. Water hardness is classified based on the amounts of removable calcium carbonate salt it contains per gallon. Water hardness is measured in grains; 0.064 gm calcium carbonate is equivalent to one grain of hardness (Vaclacik and Christian, 2003). Water is classified as soft if it contains 1 to 4 grains, medium if it contains 5 to 10 grains and hard if it contains 11 to 20 grains (Vaclacik and Christian, 2003). The hardness of water may be altered or treated by using a chemical ion exchange system. The hardness of water also affects its pH balance which plays a critical role in food processing. For example, hard water prevents successful production of clear beverages. Water hardness also affects sanitation; with increasing hardness, there is a loss of effectiveness for its use as a sanitizer (Vaclacik and Christian, 2003).
Politics
Because of overpopulation in many regions of the world, mass consumption, misuse, and water pollution, the availability of drinking water per capita is inadequate and shrinking as of the year 2006. For this reason, water is a strategic resource in the globe and an important element in many political conflicts. Some have predicted that clean water will become the "next oil", making Canada, with this resource in abundance, possibly the richest country in the world. There is a long history of conflict over water, including efforts to gain access to water, the use of water in wars started for other reasons, and tensions over shortages and control. UNESCO's World Water Development Report (WWDR, 2003) from its World Water Assessment Program indicates that, in the next 20 years, the quantity of water available to everyone is predicted to decrease by 30%. 40% of the world's inhabitants currently have insufficient fresh water for minimal hygiene. More than 2.2 million people died in 2000 from diseases related to the consumption of contaminated water or drought. In 2004, the UK charity WaterAid reported that a child dies every 15 seconds from easily preventable water-related diseases. Fresh water—now more precious than ever in our history for its extensive use in agriculture, high-tech manufacturing, and energy production—is increasingly receiving attention as a resource requiring better management and sustainable use.
OECD countries
With nearly 2,000 cubic metres (70,000 ft3) of water per person and per year, the United States leads the world in water consumption per capita (a large quantity of golf fields and car washing partly explain this massive consumption). In the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development ( OECD) countries, the U.S. is first for water consumption, then Canada with 1,600 cubic metres (56,000 ft3) of water per person per year, which is about twice the amount of water used by the average person from France, three times as much as the average German, and almost eight times as much as the average Dane. Since 1980, overall water use in Canada has increased by 25.7%. This is five times higher than the overall OECD increase of 4.5%. In contrast, nine OECD nations were able to decrease their overall water use since 1980 (Sweden, the Netherlands, the United States, the United Kingdom, the Czech Republic, Luxembourg, Poland, Finland and Denmark).
United States
Ninety-five percent of the United States' fresh water is underground. One crucial source is a huge underground reservoir, the 1,300-kilometer (800 mi) Ogallala aquifer which stretches from Texas to South Dakota and waters one fifth of U.S. irrigated land. Formed over millions of years, the Ogallala aquifer has since been cut off from its original natural sources. It is being depleted at a rate of 12 billion cubic metres (420 billion ft3) per year, amounting to a total depletion to date of a volume equal to the annual flow of 18 Colorado Rivers. Some estimates say it will dry up in as little as 25 years. Many farmers in the Texas High Plains, which rely particularly on the underground source, are now turning away from irrigated agriculture as they become aware of the hazards of overpumping.
Mexico
In Mexico City, an estimated 40% of the city's water is lost through leaky pipes built at the turn of the 20th century. Many people advise that it is not safe to drink and may cause sickness.
Middle East
The Middle East region has only 1% of the world's available fresh water, which is shared among 5% of the world's population. Thus, in this region, water is an important strategic resource. By 2025, it is predicted that the countries of the Arabian peninsula will be using more than double the amount of water naturally available to them. According to a report by the Arab League, two-thirds of Arab countries have less than 1,000 cubic meters (35,000 ft3) of water per person per year available, which is considered the limit.
Jordan, for example, has little water, and dams in other countries have reduced its available water over the years. The 1994 Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace stated that Israel would give 50 million cubic meters of water (1.7 billion ft3) per year to Jordan, which it refused to do in 1999 before backtracking. The 1994 treaty stated that the two countries would cooperate in order to allow Jordan better access to water resources, notably through dams on the Yarmouk River. Confronted by this lack of water, Jordan is preparing new techniques to use non-conventional water resources, such as second-hand use of irrigation water and desalinization techniques, which are very costly and are not yet used. A desalinization project will soon be started in Hisban, south of Amman. The Disi groundwater project, in the south of Jordan, will cost at least $250 million to bring out water. Along with the Unity Dam on the Yarmouk River, it is one of Jordan's largest strategic projects. Born in 1987, the "Unity Dam" would involve both Jordan and Syria. This "Unity Dam" still has not been implemented because of Israel's opposition, Jordan and Syrian conflictual relations and refusal of world investors. However, Jordan's reconciliation with Syria following the death of King Hussein represents the removal of one of the project's greatest obstacles.

Both Israel and Jordan rely on the Jordan River, but Israel controls it, as well as 90% of the water resources in the region. Water is also an important issue in the conflict with the Palestinians - indeed, according to former Israeli prime minister Ariel Sharon quoted by Abel Darwish in the BBC, it was one of the causes of the 1967 Six-Day War. In practice the access to water has been a casus belli for Israel. The Israeli army prohibits Palestinians from pumping water, and settlers use much more advanced pumping equipment. Palestinians complain of a lack of access to water in the region. Israelis in the West Bank use four times as much water as their Palestinian neighbours. According to the World Bank, 90% of the West Bank's water is used by Israelis . Article 40 of the appendix B of the September 28, 1995 Oslo accords stated that "Israel recognizes Palestinians' rights on water in the West Bank".
The Golan Heights provide 770 million cubic meters (27 billion ft3) of water per year to Israel, which represents a third of its annual consumption. The Golan's water goes to the Sea of Galilee—Israel's largest reserve‐which is then redistributed throughout the country by the National Water Carrier. The Golan, which Israel annexed, represents a strategic territory for Israel because of its water resources. . However, the level on the Sea of Galilee has dropped over the years, sparking fears that Israel's main water reservoir will become salinated. On its northern border, Israel threatened military action in 2002 when Lebanon opened a new pumping station taking water from a river feeding the Jordan. To help ease the crisis, Israel has agreed to buy water from Turkey and is investigating the construction of desalination plants.
Iraq and Syria watched with apprehension the construction of the Atatürk Dam in Turkey and a projected system of 22 dams on the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. According to the BBC, the list of 'water-scarce' countries in the region grew steadily from three in 1955 to eight in 1990 with another seven expected to be added within 20 years, including three Nile nations (the Nile is shared by nine countries).
Asia
In Asia, Vietnam and Cambodia are concerned by China's and Laos' attempts to control the flux of water. China is also preparing the Three Gorges Dam project on the Yangtze River, which would become the world's largest dam, causing many social and environmental problems. It also has a project to divert water from the Yangtze to the dwindling Yellow River, which feeds China's most important farming region.
The Ganges is disputed between India and Bangladesh. The water reserves are being quickly depleted and polluted, while the glacier feeding the sacred Hindu river is retreating hundreds of feet each year because of global warming and deforestation in the Himalayas, which is causing subsoil streams flowing into the Ganges river to dry up. Downstream, India controls the flow to Bangladesh with the Farakka Barrage, 10 kilometers (6 mi) on the Indian side of the border. Until the late 1990s, India used the barrage to divert the river to Calcutta to keep the city's port from drying up during the dry season. This denied Bangladeshi farmers water and silt, and it left the Sundarban wetlands and mangrove forests at the river's delta seriously threatened. The two countries have now signed an agreement to share the water more equally. Water quality, however, remains a problem, with high levels of arsenic and untreated sewage in the river water. ASIA.
South America
The Guaraní Aquifer, located between the Mercosur countries of Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia and Paraguay, with a volume of about 40,000 km³, is an important source of fresh potable water for all four countries.
Privatization
Privatization of water companies has been contested on several occasions because of bad quality of the water, increasing prices, and ethical concerns. In Bolivia for example, the proposed privatization of water companies by the IMF were met by popular protests in Cochabamba in 2000, which ousted Bechtel, an American engineering firm based in San Francisco. SUEZ has started retreating from South America because of similar protests in Buenos Aires, Santa Fe, and Córdoba, Argentina. Consumers took to the streets to protest water rate hikes of as much as 500% mandated by SUEZ. In South and Central America, SUEZ has water concessions in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Mexico. "Bolivian officials fault SUEZ for not connecting enough households to water lines as mandated by its contract and for charging as much as $455 a connection, or about three times the average monthly salary of an office clerk", according to the Mercury News.
South Africa also made moves to privatize water, provoking an outbreak of cholera killing 200.
Regulation
Drinking water is often collected at springs, extracted from artificial borings in the ground, or wells. Building more wells in adequate places is thus a possible way to produce more water, assuming the aquifers can supply an adequate flow. Other water sources are rainwater and river or lake water. This surface water, however, must be purified for human consumption. This may involve removal of undissolved substances, dissolved substances and harmful microbes. Popular methods are filtering with sand which only removes undissolved material, while chlorination and boiling kill harmful microbes. Distillation does all three functions. More advanced techniques exist, such as reverse osmosis. Desalination of abundant ocean or seawater is a more expensive solution used in coastal arid climates.
The distribution of drinking water is done through municipal water systems or as bottled water. Governments in many countries have programs to distribute water to the needy at no charge. Others argue that the market mechanism and free enterprise are best to manage this rare resource and to finance the boring of wells or the construction of dams and reservoirs.
Reducing waste by using drinking water only for human consumption is another option. In some cities such as Hong Kong, sea water is extensively used for flushing toilets citywide in order to conserve fresh water resources. Polluting water may be the biggest single misuse of water; to the extent that a pollutant limits other uses of the water, it becomes a waste of the resource, regardless of benefits to the polluter. Like other types of pollution, this does not enter standard accounting of market costs, being conceived as externalities for which the market cannot account. Thus other people pay the price of water pollution, while the private firms' profits are not redistributed to the local population victim of this pollution. Pharmaceuticals consumed by humans often end up in the waterways and can have detrimental effects on aquatic life if they bioaccumulate and if they are not biodegradable.
Religion, philosophy, and literature
Water is considered a purifier in most religions. Major faiths that incorporate ritual washing ( ablution) include Hinduism, Christianity, Islam, Judaism, and Shinto. Water baptism is a central sacrament of Christianity; it is also a part of the practice of other religions, including Judaism ( mikvah) and Sikhism ( Amrit Sanskar). In addition, a ritual bath in pure water is performed for the dead in many religions including Judaism and Islam. In Islam, the five daily prayers can be done in most cases after completing washing certain parts of the body using clean water ( wudu). In Shinto, water is used in almost all rituals to cleanse a person or an area (e.g., in the ritual of misogi). Water is mentioned in the Bible 442 times in the New International Version and 363 times in the King James Version: 2 Peter 3:5(b) states, "The earth was formed out of water and by water" (NIV).
Some faiths use water especially prepared for religious purposes ( holy water in some Christian denominations, Amrit in Sikhism and Hinduism). Many religions also consider particular sources or bodies of water to be sacred or at least auspicious; examples include Lourdes in Roman Catholicism, the Zamzam Well in Islam and the River Ganges (among many others) in Hinduism.
Water is often believed to have spiritual powers. In Celtic mythology, Sulis is the local goddess of thermal springs; in Hinduism, the Ganges is also personified as a goddess, while Saraswati have been referred to as goddess in Vedas. Also water is one of the "panch-tatva"s (basic 5 elements, others including fire, earth, space, air). Alternatively, gods can be patrons of particular springs, rivers, or lakes: for example in Greek and Roman mythology, Peneus was a river god, one of the three thousand Oceanids.
The Greek philosopher Empedocles held that water is one of the four classical elements along with fire, earth and air, and was regarded as the ylem, or basic substance of the universe. Water was considered cold and moist. In the theory of the four bodily humors, water was associated with phlegm. Water was also one of the five elements in traditional Chinese philosophy, along with earth, fire, wood, and metal.
Water also plays an important role in literature as a symbol of purification. Examples include the critical importance of a river in As I Lay Dying by William Faulkner and the drowning of Ophelia in Hamlet.