Photosynthesis
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General Biology
Photosynthesis (photo=light, synthesis=putting together), generally, is the synthesis of sugar from light, carbon dioxide and water, with oxygen as a waste product. It is arguably the most important biochemical pathway known; nearly all life depends on it. It is an extremely complex process, comprised of many coordinated biochemical reactions. It occurs in higher plants, algae, some bacteria, and some protists, organisms collectively referred to as photoautotrophs.
Overview
Photosynthesis uses the energy of light to make the sugar, glucose. A simple general equation for photosynthesis follows.
-
6 CO2 + 12 H2O + light → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
-
carbon dioxide + water + light energy → glucose + oxygen + water
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages. In the first phase light-dependent reactions or photosynthetic reactions (also called the Light reactions) capture the energy of light and use it to make high-energy molecules. During the second phase, the light-independent reactions (also called the Calvin-Benson Cycle, and formerly known as the Dark Reactions) use the high-energy molecules to capture carbon dioxide (CO2) and make the precursors of glucose.
In the light-dependent reactions the pigment chlorophyll absorbs light and loses an electron that travels down an electron transport chain producing the high energy molecules NADPH and ATP. The chlorophyll molecule regains its electron by taking one from a water molecule through a process called photolysis, that releases oxygen gas as a byproduct.
In the Light-independent or dark reactions the enzyme RuBisCO captures CO2 from the atmosphere and in a complex process called the Calvin-Benson cycle releases 3-carbon sugars which are later combined to form glucose.
Photosynthesis may simply be defined as the conversion of light energy into chemical energy by living organisms. It is affected by its surroundings and the rate of photosynthesis is affected by the concentration of carbon dioxide, light intensity and the temperature.
In plants
Most plants are photoautotrophs, which means that they are able to synthesize food directly from inorganic compounds using light energy - for example the sun, instead of eating other organisms or relying on nutrients derived from them. This is distinct from chemoautotrophs that do not depend on light energy, but use energy from inorganic compounds.
The energy for photosynthesis ultimately comes from absorbed photons and involves a reducing agent, which is water in the case of plants, releasing oxygen as a waste product. The light energy is converted to chemical energy (known as light-dependent reactions), in the form of ATP and NADPH, which is used for synthetic reactions in photoautotrophs. Most notably plants use the chemical energy to fix carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and other organic compounds through light-independent reactions. The overall equation for carbon fixation (sometimes referred to as carbon reduction) in green plants is
- n CO2 + 2n H2O + ATP + NADPH → (CH2O)n + n H2O + n O2,
- Where n is defined according to the structure of the resulting carbohydrate.
More specifically, carbon fixation produces an intermediate product, which is then converted to the final hexose carbohydrate products. These carbohydrate products are then variously used to form other organic compounds, such as the building material cellulose, as precursors for lipid and amino acid biosynthesis or as a fuel in cellular respiration. The latter not only occurs in plants, but also in animals when the energy from plants get passed through a food chain. Organisms dependent on photosynthetic and chemosynthetic organisms are called heterotrophs. In general outline, cellular respiration is the opposite of photosynthesis: glucose and other compounds are oxidised to produce carbon dioxide, water, and chemical energy. However, both processes actually take place through a different sequence of reactions and in different cellular compartments.
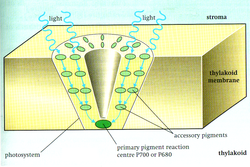
Plants absorb light primarily using the pigment chlorophyll, which is the reason that most plants have a green colour. The function of chlorophyll is often supported by other accessory pigments such as carotenes and xanthophylls. Both chlorophyll and accessory pigments are contained in organelles (compartments within the cell) called chloroplasts. Although all cells in the green parts of a plant have chloroplasts, most of the energy is captured in the leaves. The cells in the interior tissues of a leaf, called the mesophyll, contain about half a million chloroplasts for every square millimeter of leaf. The surface of the leaf is uniformly coated with a water-resistant, waxy cuticle, that protects the leaf from excessive evaporation of water and decreases the absorption of ultraviolet or blue light to reduce heating. The transparent epidermis layer allows light to pass through to the palisade mesophyll cells where most of the photosynthesis takes place.
In algae and bacteria
Algae is a range from multicellular forms like kelp to microscopic, single-celled organisms. Although they are not as complex as land plants, photosynthesis takes place biochemically the same way. Very much like plants, algae have chloroplasts and chlorophyll, but various accessory pigments are present in some algae such as phycoerythrin in red algae (rhodophytes), resulting in a wide variety of colours. All algae produce oxygen, and many are autotrophic. However, some are heterotrophic, relying on materials produced by other organisms. For example, in coral reefs, there is a symbiotic relationship between zooxanthellae and the coral polyps.
Photosynthetic bacteria do not have chloroplasts (or any membrane-bound organelles), instead, photosynthesis takes place directly within the cell. Cyanobacteria contain thylakoid membranes very similar to those in chloroplasts and are the only prokaryotes that perform oxygen-generating photosynthesis, in fact chloroplasts are now considered to have evolved from an endosymbiotic bacterium, which was also an ancestor of and later gave rise to cyanobacterium. The other photosynthetic bacteria have a variety of different pigments, called bacteriochlorophylls, and do not produce oxygen. Some bacteria such as Chromatium, oxidize hydrogen sulfide instead of water for photosynthesis, producing sulfur as waste.
The evolution of photosynthesis
The ability to convert light energy to chemical energy is a significant evolutionary advantage. Early photosynthetic systems, such as those from green and purple sulphur and green and purple non-sulphur bacteria, were anoxygenic using various molecules as electron donors. Green and purple sulphur bacteria used hydrogen and sulphur as an electron donor. Green nonsulphur bacteria used various amino and other organic acids. Purple nonsulphur bacteria used a variety of non-specific organic molecules. The use of these molecules is consistent with the geological evidence that the atmosphere was highly reduced at that time.
Fossils have been found of filamentous photosynthetic organisms dating from 3400 million years ago ( New Scientist, 19 Aug., 2006).
The oxygen in the atmosphere today exists due to the evolution of oxygenic photosynthesis, sometimes referred to as the oxygen catastrophe. Geological evidence suggests that oxygenic photosynthesis, such as that in cyanobacteria, became important during the Paleoproterozoic era around 2 billion years ago. Modern photosynthesis in plants and most photosynthetic prokaryotes is oxygenic. Oxygenic photosynthesis uses water as an electron donor which is oxidized into molecular oxygen by the absorption of a photon by the photosynthetic reaction centre.
Origin of chloroplasts
In plants the process of photosynthesis is compartmentalized in organelles called chloroplasts. Chloroplasts have many similarities with photosynthetic bacteria including a circular chromosome, prokaryotic ribosomes, and similar proteins in the photosynthetic reaction centre.
The endosymbiotic theory suggest that photosynthetic bacteria were ingested by early eukaryotic cells to form the first plant cells.
Molecular production
Light to chemical energy
The light energy is converted to chemical energy using the light-dependent reactions. The products of the light dependent reactions are ATP from photophosphorylation and NADPH from photoreduction. Both are then utilized as an energy source for the Light independent reactions.
Z scheme
In plants, light dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts and use light energy to synthesize ATP and NADPH. The light dependent reaction has two forms; cyclic and non-cyclic reaction. In the non-cyclic reaction, the photons are captured in the light-harvesting antenna complexes of photosystem II by chlorophyll and other accessory pigments (see diagram at right). When a chlorophyll molecule at the core of the photosystem II reaction centre obtains sufficient excitation energy from the adjacent antenna pigments, an electron is transferred to the primary electron-acceptor molecule, Pheophytin, through a process called Photoinduced charge separation. These electrons are shuttled through an electron transport chain, the so called Z-scheme shown in the diagram, that initially functions to generate a chemiosmotic potential across the membrane. An ATP synthase enzyme uses the chemiosmotic potential to make ATP during photophosphorylation while NADPH is a product of the terminal redox reaction in the Z-scheme. The electron enters the Photosystem I molecule. The electron is emitted due to the light absorbed by the photosystem. A second electron carrier accepts the electron, which again is passed down lowering energies of electron acceptors. The energy created by the electron acceptors is used to move hydrogen ions across the thylakoid membrane into the lumen. The electron is used to reduce the co-enzyme NADH, which has functions in the light-independent reaction. The cyclic reaction is similar to that of the non-cyclic, but differs in the form that it only generates ATP and no reduced NADP (NADPH) is created. The cyclic reaction takes place only at photosystem I. Once the electron is displaced from the photosystem, the electron is passed down the electron acceptor molecules and returns back to photosystem I, from where it was emitted; hence the name cyclic reaction.
Water photolysis
The NADPH is the main reducing agent in chloroplasts, providing a source of energetic electrons to other reactions. Its production leaves chlorophyll with a deficit of electrons (oxidized), which must be obtained from some other reducing agent. The excited electrons lost from chlorophyll in photosystem I are replaced from the electron transport chain by plastocyanin. However, since photosystem II includes the first steps of the Z-scheme, an external source of electrons is required to reduce its oxidized chlorophyll a molecules. The source of electrons in green-plant and cyanobacterial photosynthesis is water. Two water molecules are oxidized by four successive charge-separation reactions by photosystem II to yield a molecule of diatomic oxygen and four hydrogen ions; the electron yielded in each step is transferred to a redox-active tyrosine residue that then reduces the photooxidized paired-chlorophyll a species called P680 that serves as the primary (light-driven) electron donor in the photosystem II reaction centre. The oxidation of water is catalyzed in photosystem II by a redox-active structure that contains four manganese ions; this oxygen-evolving complex binds two water molecules and stores the four oxidizing equivalents that are required to drive the water-oxidizing reaction. Photosystem II is the only known biological enzyme that carries out this oxidation of water. The hydrogen ions contribute to the transmembrane chemiosmotic potential that leads to ATP synthesis. Oxygen is a waste product of light-independent reactions, but the majority of organisms on Earth use oxygen for cellular respiration, including photosynthetic organisms.
Oxygen and photosynthesis
With respect to oxygen and photosynthesis, there are two important concepts.
- Plant and cyanobacterial (blue-green algae) cells also use oxygen for cellular respiration, although they have a net output of oxygen since much more is produced during photosynthesis.
- Oxygen is a product of the light-driven water-oxidation reaction catalyzed by photosystem II; it is not generated by the fixation of carbon dioxide. Consequently, the source of oxygen during photosynthesis is water, not carbon dioxide.
Bacterial variation
The concept that oxygen production is not directly associated with the fixation of carbon dioxide was first proposed by Cornelis Van Niel in the 1930s, who studied photosynthetic bacteria. Aside from the cyanobacteria, bacteria only have one photosystem and use reducing agents other than water. They get electrons from a variety of different inorganic chemicals including sulfide or hydrogen, so for most of these bacteria oxygen is not produced.
Others, such as the halophiles (an Archaea) produced so called purple membranes where the bacteriorhodopsin could harvest light and produce energy. The purple membranes was one of the first to be used to demonstrate the chemiosmotic theory: light hit the membranes and the pH of the solution that contained the purple membranes dropped as protons were pumping out of the membrane.
Carbon fixation
The fixation or reduction of carbon dioxide is a light-independent process in which carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon sugar, ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), to yield two molecules of a three-carbon compound, glycerate 3-phosphate (GP), also known as 3-phosphoglycerate (PGA). GP, in the presence of ATP and NADPH from the light-dependent stages, is reduced to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). This product is also referred to as 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde ( PGAL) or even as triose phosphate. Triose is a 3-carbon sugar (see carbohydrates). Most (5 out of 6 molecules) of the G3P produced is used to regenerate RuBP so the process can continue (see Calvin-Benson cycle). The 1 out of 6 molecules of the triose phosphates not "recycled" often condense to form hexose phosphates, which ultimately yield sucrose, starch and cellulose. The sugars produced during carbon metabolism yield carbon skeletons that can be used for other metabolic reactions like the production of amino acids and lipids.
C4 and CAM
In hot and dry conditions, plants will close their stomata (pores used for gas exchange) to prevent loss of water. Under these conditions, oxygen gas, produced by the light reactions of photosynthesis, will concentrate in the leaves causing photorespiration to occur. Some plants have devised mechanisms to increase the CO2 concentration in the leaves under these conditions.
C4 plants capture carbon dioxide using an enzyme called PEP Carboxylase that adds carbon dioxide to the three carbon molecule Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) creating the 4 carbon molecule oxaloacetic acid. Plants without this enzyme are called C3 plants because the primary carboxylation reaction produces the three carbon sugar 3-phosphoglycerate directly in the Calvin-Benson Cycle. When oxygen levels rise in the leaf, C4 plants reverse this reaction to release carbon dioxide thus preventing photorespiration. By preventing photorespiration, C4 plants can produce more sugar than C3 plants in conditions of strong light and high temperature. Many important crop plants are C4 plants including maize, sorghum, sugarcane, and millet.
Cacti and most succulents also can use PEP Carboxylase to capture carbon dioxide in a process called Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM). They store the CO2 in different molecules than the C4 plants (mostly they store it in malic acid). They also have a different leaf anatomy than C4 plants. They grab the CO2 at night when their stomata are open, and they release it into the leaves during the day to increase their photosynthetic rate.
Discovery
Although some of the steps in photosynthesis are still not completely understood, the overall photosynthetic equation has been known since the 1800s.
Jan van Helmont began the research of the process in the mid-1600s when he carefully measured the mass of the soil used by a plant and the mass of the plant as it grew. After noticing that the soil mass changed very little, he hypothesized that the mass of the growing plant must come from the water, the only substance he added to the potted plant. His hypothesis was partially accurate - much of the gained mass also comes from carbon dioxide as well as water. However, this was a signalling point to the idea that the bulk of a plant's biomass comes from the inputs of photosynthesis, not the soil itself.
Joseph Priestley, a chemist and minister, discovered that when he isolated a volume of air under an inverted jar, and burned a candle in it, the candle would burn out very quickly, much before it ran out of wax. He further discovered that a mouse could similarly "injure" air. He then showed that the air that had been "injured" by the candle and the mouse could be restored by a plant.
In 1778, Jan Ingenhousz, court physician to the Austrian Empress, repeated Priestley's experiments. He discovered that it was the influence of sun and light on the plant that could cause it to rescue a mouse in a matter of hours.
In 1796, Jean Senebier, a French pastor, showed that CO2 was the "fixed" or "injured" air and that it was taken up by plants in photosynthesis. Soon afterwards, Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure showed that the increase in mass of the plant as it grows could not be due only to uptake of CO2, but also to the incorporation of water. Thus the basic reaction by which photosynthesis is used to produce food (such as glucose) was outlined.
Modern scientists built on the foundation of knowledge from those scientists centuries ago and were able to discover many things.
Cornelis Van Niel made key discoveries explaining the chemistry of photosynthesis. By studying purple sulfur bacteria and green bacteria he was the first scientist to demonstrate that photosynthesis is a light-dependent redox reaction, in which hydrogen reduces carbon dioxide.
Further experiments to prove that the oxygen developed during the photosynthesis of green plants came from water, were performed by Robert Hill in 1937 and 1939. He showed that isolated chloroplasts give off oxygen in the presence of unnatural reducing agents like iron oxalate, ferricyanide or benzoquinone after exposure to light. The Hill reaction is as follows:
- 2 H2O + 2 A + (light, chloroplasts) → 2 AH2 + O2
where A is the electron acceptor. Therefore, in light the electron acceptor is reduced and oxygen is evolved.
Samuel Ruben and Martin Kamen used radioactive isotopes to determine that the oxygen liberated in photosynthesis came from the water.
Melvin Calvin and Andrew Benson, along with James Bassham, elucidated the path of carbon assimilation (the photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle) in plants. The carbon reduction cycle is known as the Calvin cycle, which inappropriately ignores the contribution of Bassham and Benson. Many scientists refer to the cycle as the Calvin-Benson Cycle, Benson-Calvin, and some even call it the Calvin-Benson-Bassham (or CBB) Cycle.
A Nobel Prize winning scientist, Rudolph A. Marcus, was able to discover the function and significance of the electron transport chain.
Factors affecting photosynthesis
There are three main factors affecting photosynthesis and several corollary factors. The three main are:
- Light irradiance and wavelength
- Carbon dioxide concentration
- Temperature
Light intensity (Irradiance), wavelength and temperature
In the early 1900s Frederick Frost Blackman along with Gabrielle Matthaei investigated the effects of light intensity ( irradiance) and temperature on the rate of carbon assimilation.
- At constant temperature, the rate of carbon assimilation varies with irradiance, initially increasing as the irradiance increases. However at higher irradiance this relationship no longer holds and the rate of carbon assimilation reaches a plateau.
- At constant irradiance, the rate of carbon assimilation increases as the temperature is increased over a limited range. This effect is only seen at high irradiance levels. At low irradiance, increasing the temperature has little influence on the rate of carbon assimilation.
These two experiments illustrate vital points: firstly, from research it is known that photochemical reactions are not generally affected by temperature. However, these experiments clearly show that temperature affects the rate of carbon assimilation, so there must be two sets of reactions in the full process of carbon assimilation. These are of course the light-dependent 'photochemical' stage and the light-independent, temperature-dependent stage. Secondly, Blackman's experiments illustrate the concept of limiting factors. Another limiting factor is the wavelength of light. Cyanobacteria which reside several meters underwater cannot receive the correct wavelengths required to cause photoinduced charge separation in conventional photosynthetic pigments. To combat this problem a series of proteins with different pigments surround the reaction centre. This unit is called a phycobilisome.
Carbon dioxide levels and Photorespiration
As carbon dioxide concentrations rise, the rate at which sugars are made by the light-independent reactions increases until limited by other factors. RuBisCO, the enzyme that captures carbon dioxide in the light-independent reactions, has a binding affinity for both carbon dioxide and oxygen. When the concentration of carbon dioxide is high, RuBisCO will fix carbon dioxide. However, if the oxygen concentration is high, RuBisCO will bind oxygen instead of carbon dioxide. This process, called photorespiration, uses energy, but does not make sugar
RuBisCO oxygenase activity is disadvantageous to plants for several reasons:
- One product of oxygenase activity is phosphoglycolate (2 carbon) instead of 3-phosphoglycerate (3 carbon). Phosphoglycolate cannot be metabolized by the Calvin-Benson cycle and represents carbon lost from the cycle. A high oxygenase activity, therefore, drains the sugars that are required to recycle ribulose 5-bisphosphate and for the continuation of the Calvin-Benson cycle.
- Phosphoglycolate is quickly metabolized to glycolate that is toxic to a plant at a high concentration; it inhibits photosynthesis.
- Salvaging glycolate is an energetically expensive process that uses the glycolate pathway and only 75% of the carbon is returned to the Calvin-Benson cycle as 3-phosphoglycerate.
-
- A highly simplified summary is:
-
-
- 2 glycolate + ATP → 3-phophoglycerate + carbon dioxide + ADP +NH3
-
The salvaging pathway for the products of RuBisCO oxygenase activity is more commonly known as photorespiration since it is characterized by light dependent oxygen consumption and the release of carbon dioxide.