Mississippi River
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: North American Geography
| Mississippi River | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Origin | Lake Itasca |
| Mouth | Gulf of Mexico |
| Basin countries | United States (98.5%) Canada (1.5%) |
| Length | 3,733 km (2,320 mi) |
| Source elevation | 450 m (1,476 ft) |
| Avg. discharge | Minneapolis : 210 m³/s (7,460 ft³/s) Saint Louis : 5,150 m³/s (182,000 ft³/s ) Vicksburg : 17,050 m³/s (602,000 ft³/s) Baton Rouge : 12,740 m³/s (450,000 ft³/s) |
| Basin area | 2,980,000 km² (1,151,000 mi²) |
The Mississippi River, derived from the old Ojibwe word misi-ziibi meaning 'great river' (gichi-ziibi 'big river' at its headwaters), is the second-longest river in the United States; the longest is the Missouri River, which flows into the Mississippi. Taken together, they form the largest river system in North America. If measured from the head of the Missouri, the length of the Missouri-Mississippi combination is approximately 3,900 miles (6,300 km), making the combination the 4th longest river in the world. Apart from the Missouri, the largest of the many large Mississippi tributaries is the Ohio River. The Mississippi River is the main river that supports much of the American civilization.
Geography
the Mississippi is a river in mississippi. With its source Lake Itasca at 1,475 feet (450 m) above sea level in Itasca State Park located in Clearwater County, Minnesota, the river falls to 725 feet (220 m) just below Saint Anthony Falls in Minneapolis. The Mississippi is joined by the Illinois River and the Missouri River near St. Louis, Missouri, and by the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois. The Arkansas River joins the Mississippi in the state of Arkansas. The Atchafalaya River in Louisiana is a major distributary of the Mississippi.
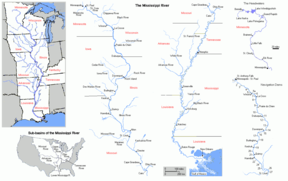
The Mississippi drains most of the area between the Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains, except for the areas drained by the Great Lakes and the Rio Grande. It runs through two states — Minnesota and Louisiana — and was used to define the borders of eight states (the river has since shifted) — Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Arkansas, Tennessee, and Mississippi — before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico about 100 miles (160 km) downstream from New Orleans. Measurements of the length of the Mississippi from Lake Itasca to the Gulf of Mexico vary, but the EPA's number is 2,320 miles (3,733 km). The retention time from Lake Itasca to the Gulf is about 90 days.
The river is divided into the upper Mississippi, from its source south to the Ohio River, and the lower Mississippi, from the Ohio to its mouth near New Orleans. The upper Mississippi is further divided into three sections: the headwaters, from the source to Saint Anthony Falls; a series of man-made lakes between Minneapolis and St. Louis, Missouri; and the middle Mississippi, a relatively free-flowing river downstream of the confluence with the Missouri River at St. Louis.
A series of 29 locks and dams on the upper Mississippi, most of which were built in the 1930s, is designed primarily to maintain a 9 foot (2.7 m) deep channel for commercial barge traffic. The lakes formed are also used for recreational boating and fishing. The dams make the river deeper and wider but do not stop it. No flood control is intended. During periods of high flow, the gates, some of which are submersible, are completely opened and the dams simply cease to function. Below St. Louis, the Mississippi is relatively free-flowing, although it is constrained by numerous levees and directed by numerous wing dams.
Through a natural process known as deltaic switching the lower Mississippi River has shifted its final course to the ocean every thousand years or so. This occurs because the deposits of silt and sediment raise the river's level causing it to eventually find a steeper route to the Gulf of Mexico. The abandoned distributary diminishes in volume and forms what are known as bayous. This process has, over the past 5,000 years, caused the coastline of south Louisiana to advance toward the Gulf from 15 to 50 miles (25-80 km).
U.S. government scientists determined in the 1950s that the Mississippi River was starting to switch to the Atchafalaya River channel because of its much steeper path to the Gulf of Mexico, and eventually the Atchafalaya River would capture the Mississippi River and become its main channel to the Gulf of Mexico. As a result, the U.S. Congress authorized a project called the Old River Control Structure, which has prevented the Mississippi River from leaving its current channel that drains into the Gulf via New Orleans. Because of the large scale of high energy water flow through the Old River Control Structure threatening to damage the structure, an auxiliary flow control station was built adjacent to the standing control station. This US$300 million project was completed in 1996 by the Army Corp Of Engineers. k0
Course changes
The Illinoian Glacier, about 200,000 to 125,000 years before present, blocked the Mississippi near Rock Island, diverting it to its present channel farther to the west (current western border of Illinois). The Hennepin Canal roughly follows the ancient channel of the Mississippi downstream from Rock Island to Hennepin. South of Hennepin, the current Illinois River is actually following the ancient channel of the Mississippi River to Alton before the Illinoian glaciation.
Other changes in the course of the river have occurred because of earthquakes along the New Madrid Fault Zone, which lies near the cities of Memphis and St. Louis. Three earthquakes in 1811 and 1812, estimated at approximately 8 on the Richter Scale, were said to have temporarily reversed the course of the Mississippi. These earthquakes also created Reelfoot Lake in Tennessee from the altered landscape near the river. The faulting is related to an aulacogen (geologic term for a failed rift) that formed at the same time as the Gulf of Mexico.
Watershed
The Mississippi River has the third largest drainage basin (" catchment") in the world, exceeded in size only by the watersheds of the Amazon River and Congo River. It drains 41% of the 48 contiguous states of the United States. The basin covers more than 1,245,000 square miles ( 3,225,000 km²), including all or parts of 31 states and two Canadian provinces.
Major tributaries of the Mississippi:
- Big Black River in Mississippi
- Red River in Louisiana
- White River in Arkansas
- Arkansas River in Arkansas
- Ohio River in Illinois and Kentucky
- Big Muddy River in Illinois
- Kaskaskia River in Illinois
- Missouri River in Missouri
- Illinois River in Illinois
- Des Moines River in Iowa
- Skunk River in Iowa
- Rock River in Illinois
- Maquoketa River in Iowa
- Wisconsin River in Wisconsin
- Chippewa River in Wisconsin
- St. Croix River in Wisconsin
- Minnesota River in Minnesota
Outflow
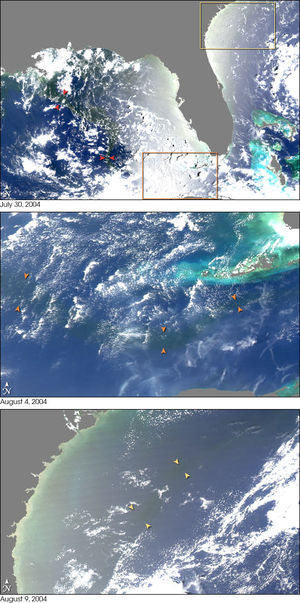
Fresh river water flowing from the Mississippi into the Gulf of Mexico does not mix into the salt water immediately. The images from NASA's MODIS to the right show a large plume of fresh water, which appears as a dark ribbon against the lighter-blue surrounding waters.
The images demonstrate that the plume did not mix with the surrounding sea water immediately. Instead, it stayed intact as it flowed through the Gulf of Mexico, into the Straits of Florida, and entered the Gulf Stream. The Mississippi River water rounded the tip of Florida and traveled up the southeast coast to the latitude of Georgia before finally mixing in so thoroughly with the ocean that it could no longer be detected by MODIS.
The Mississippi river discharges at an annual average rate of between 200,000 and 700,000 Cubic Feet per Second. Although it is the 4th longest river in the world, this flow is a mere fraction of the output of the Amazon, which moves nearly 7 million cfs during wet seasons.
History
Nomenclature
The word Mississippi comes from the Ojibwa name for the river, "Messipi" (or Misi-ziibi in contemporary spelling), which means great river, or from the Algonquin Missi Sepe, "great river," poetically, "father of waters." The Ojibwe called Lake Itasca Omashkoozo-zaaga'igan (Elk Lake) and the river flowing out of it Omashkoozo-ziibi (Elk River). After flowing into Lake Bemidji, the Ojibwe called the river Bemijigamaa-ziibi (River from the Traversing Lake). After flowing into Cass Lake, the name of the river again changed to Miskwaawaakokaa-ziibi (Red Cedar River) and then to Gichi-ziibi (Big River) after flowing into Lake Winnibigoshish. The Ojibwe name Misi-ziibi applied only to the portion below the Crow Wing River, but the ever-changing names of the river seemed illogical to the English speakers, so after the expedition by Henry Schoolcraft, the longest stream above the juncture of the Crow Wing River and Gichi-ziibi was named "Mississippi River".
Early American
On May 8, 1541, Hernando de Soto became the first recorded European to reach the Mississippi River, which he called "Rio de Espiritu Santo" (River of the Holy Spirit). French explorers Louis Joliet and Jacques Marquette began exploring the Mississippi. He traveled with a Sioux named "Ne Tongo" (which in Sioux means big river) in 1673. In 1682, René Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle and Henri de Tonty claimed the entire Mississippi River Valley for France, calling the river Colbert River after Jean-Baptiste Colbert and the region Louisiana, for King Louis XIV. In 1718, New Orleans was established by Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne de Bienville.
France lost all its territories on the North American mainland as a result of the French and Indian War. The Treaty of Paris (1763) gave the Kingdom of Great Britain rights to all land in the valley east of the Mississippi and Spain rights to land west of the Mississippi. Spain also ceded Florida to England to regain Cuba, which the English occupied during the war. Britain then divided the territory into East Florida and West Florida.
In the second Treaty of Paris, which ended the American Revolution, Britain ceded West Florida back to Spain to regain the Bahamas, which Spain had occupied during the war. Spain then had control over the river south of 32°30' north latitude and, in what is known as the Spanish Conspiracy, hoped to gain greater control of Louisiana and all of the west. These hopes ended when Spain was pressured into signing Pinckney's Treaty in 1795. France reacquired 'Louisiana' from Spain in the secret Treaty of San Ildefonso in 1800. The United States bought the territory from France in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803.
The river was noted for the number of bandits which called its islands and shores home, including John Murrell who was a well-known murderer, horse stealer and slave "re-trader". His notoriety was such that author Mark Twain devoted an entire chapter to him in his book Life on the Mississippi, and Murrell was rumored to have an island headquarters on the river at Island 37.
1800s
Twain's book also extensively covered the steamboat races which took place from 1830 to 1870 on the river before more modern boating methods replaced the steamer. It was published first in serial form in Harper's Weekly in seven parts in 1875 and was intended to chronicle the rapidly disappearing steamboat culture. The full version, including a passage from the unfinished Huckleberry Finn and works from other authors, was published by James R. Osgood & Co. in 1885. The first steamboat to travel the full length of the Mississippi from the Ohio River to New Orleans, Louisiana, was the New Orleans in December 1811. Its maiden voyage occurred during the series of New Madrid earthquakes in 1811–12.
In 1815, America retained control over the Mississippi by scoring a decisive victory over the British at the Battle of New Orleans, part of the War of 1812.
The river was played a decisive role in the American Civil War. The Union's Vicksburg Campaign called for Union control of the lower Mississippi River. The Union victory at the Battle of Vicksburg in 1863 was pivotal to the Union's final victory of the Civil War.
In 1848, the Illinois and Michigan Canal was built to connect the Mississippi River to Lake Michigan via the Illinois River near Peru, Illinois. In 1900, the canal was replaced by the Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal. The canal allowed Chicago to address specific health issues ( typhoid, cholera and other waterborne diseases) by sending its waste down the Illinois and Mississippi river systems rather than polluting its water source of Lake Michigan. The canal also provided a shipping route between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi.
The sport of water skiing was invented on the river in a wide region between Minnesota and Wisconsin known as Lake Pepin. Ralph Samuelson of Lake City, Minnesota, created and refined his skiing technique in late June and early July 1922. He later performed the first water ski jump in 1925 and was pulled along at 80 miles per hour (128 km/h) by a Curtiss flying boat later that year.
1900s
In the spring of 1927, the river broke out of its banks in 145 places during the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927 and inundated 27,000 square miles (70,000 km²) to a depth of up to 30 feet (10 m).
On October 20, 1976, the automobile ferry MV George Prince was struck by a ship traveling upstream as the ferry attempted to cross from Destrehan, Louisiana, to Luling, Louisiana. Seventy-eight passengers and crew died; only eighteen survived the accident.
The Great Flood of 1993 was another significant flood, although it primarily affected the Mississippi above its confluence with the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois.
Two portions of the Mississippi were designated as some of the American Heritage Rivers in 1997: The lower portion around Louisiana and Tennessee, and the upper portion around Iowa, Illinois, Minnesota and Missouri.
Present
In 2002 the Slovenian long-distance swimmer Martin Strel swam the entire length of the river, from Minnesota to Louisiana, over the course of 68 days.
In 2005, the Source to Sea Expedition paddled the Mississippi and Atchafalaya rivers to benefit the Audubon Society's Upper Mississippi River Campaign.
Navigation
The task of maintaining a navigation channel on the Mississippi is the responsibility of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, which began as early as 1829 removing snags, closing off secondary channels and excavating rocks and sandbars. In 1829, the Corps surveyed the two major obstacles on the upper Mississippi, the Des Moines Rapids and the Rock Island Rapids, where the river was shallow and the riverbed was rock. The Des Moines Rapids were about 11 miles (18 km) long and just above the mouth of the Des Moines River at Keokuk, Iowa. The Rock Island Rapids were between Rock Island and Moline, Illinois. Both rapids were considered virtually impassable.
On a side note, it is at this area of the Mississippi River that the river flows East to West as opposed to its normal course North to South. The area of the Quad Cities is known for this fast fact.
The Corps recommended excavation of a 5 foot (1.5 m) deep channel at the Des Moines Rapids, but work did not begin until after Lieutenant Robert E. Lee endorsed the project in 1837. The Corps later also began excavating the Rock Island Rapids. By 1866, it had become evident that excavation was impractical, and it was decided to build a canal around the Des Moines Rapids. The canal opened in 1877, but the Rock Island Rapids remained an obstacle.
In 1878, Congress authorized the Corps to establish a 4.5 foot (1.4 m) channel deep to be obtained by building wing dams which direct the river to a narrow channel causing it to cut a deeper channel, by closing secondary channels and by dredging. The channel project was complete when the Moline Lock, which bypassed the Rock Island Rapids, opened in 1907.
To improve navigation between St. Paul, Minnesota, and Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin, the Corps constructed several dams on lakes in the headwaters area, including Lake Winnibigoshish and Lake Pokegama. The dams, which were built beginning in the 1880s, stored spring run-off which was released during low water to help maintain channel depth.
In 1907, Congress authorized a 6 foot (1.8 m) deep channel project on the Mississippi, which was not complete when it was abandoned in the late 1920s in favour of the 9 foot (2.7 m) deep channel project.
In 1913, construction was complete on a dam at Keokuk, Iowa, the first dam below St. Anthony Falls. Built by a private power company to generate electricity, the Keokuk dam was one of the largest hydro-electric plants in the world at the time. The dam also eliminated the Des Moines Rapids.
Lock and Dam No. 1 was completed in Minneapolis in 1917 and Lock and Dam No. 2 at Hastings, Minnesota, was completed in 1930.
Prior to the 1927 flood, the Corps' primary strategy was to close off as many side channels as possible to increase the flow in the main river. It was thought that the river's velocity would scour off bottom sediments, deepening the river and decreasing the possibility of flooding. The 1927 flood proved this so wrong that communities threatened by the flood began to make their own levee breaks to relieve the tension of the rising river.
The Corps now actively creates floodways to divert periodic water surges into backwater channels and lakes. The main floodways are the Birds Point-New Madrid Floodway; the Morganza Floodway, which directs floodwaters down the Atchafalaya River; and the Bonnet Carré Spillway which directs water to Lake Pontchartrain. The Old River Control structure also serve as a major floodgates that can be opened to prevent flooding. Some of the pre-1927 strategy is still in use today; the Corps actively cuts the necks of horseshoe bends, allowing the water to move faster and reducing flood heights.
The Rivers and Harbors Act of 1930 authorized the 9-foot channel project, which called for a navigation channel 9 feet deep and 400 feet (120 m) wide to accommodate multiple-barge tows. This was achieved by a series of locks and dams, and by dredging. Twenty-three new locks and dams were built on the upper Mississippi in the 1930s in addition to the three already in existence. Two new locks were built north of Lock and Dam No. 1 at Saint Anthony Falls in the 1960s, extending the head of navigation for commercial traffic several miles, but few barges go past the city of Saint Paul today.
Beginning in the 1970s, the Corps applied hydrology transport models to analyze flood flow and water quality of the Mississippi.
Until the 1950s, there was no dam below Lock and Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois. Lock and Dam 27, which consists of a low-water dam and an 8.4 mile (13.5 km) long canal, was added in 1953 just below the confluence with the Missouri River, primarily to bypass a series of rock ledges at St. Louis. It also serves to protect the St. Louis city water intakes during times of low water.
Dam 26 at Alton, Illinois, which had structural problems, was replaced by the Mel Price Lock and Dam in 1990. The original Lock and Dam 26 was demolished.
Major cities along the river
- Minneapolis, Minnesota
- St. Paul, Minnesota
- La Crosse, Wisconsin
- Bettendorf, Iowa
- Davenport, Iowa
- Rock Island, Illinois
- Moline, Illinois
- Quincy, Illinois
- St. Louis, Missouri
- Cairo, Illinois
- Memphis, Tennessee
- Greenville, Mississippi
- Vicksburg, Mississippi
- Natchez, Mississippi
- Baton Rouge, Louisiana
- New Orleans, Louisiana
Notable bridges
The first bridge across the Mississippi River was built in 1856. It spanned the river between Arsenal Island at Rock Island, Illinois and Davenport, Iowa. Steamboat pilots of the day, fearful of competition from the railroads, considered the new bridge "a hazard to navigation". Two weeks after the bridge opened, the steamboat Effie Afton rammed part of the bridge and started it on fire. Legal proceedings ensued - with a young lawyer named Abraham Lincoln defending the railroad. The lawsuit went all the way up to the Supreme Court, and was eventually ruled in favour of Lincoln and the railroad.
- Stone Arch Bridge - a former Great Northern Railroad (now pedestrian) bridge in Minneapolis and National Historic Engineering Landmark.
- Washington Avenue Bridge - connects the East Bank and West Bank portions of the University of Minnesota's Minneapolis campus.
- Black Hawk Bridge, connecting Lansing, Allamakee County, Iowa to rural Crawford County, Wisconsin, locally referred to as the Lansing Bridge.
- Julien Dubuque Bridge - A bridge connecting Dubuque, Iowa and East Dubuque, Illinois that is listed in the National Register of Historic Places.
- Interstate 74 Bridge connecting Moline, Illinois to Bettendorf, Iowa is a twin suspension bridge, also known historically as the Iowa-Illinois Memorial Bridge.
- Rock Island Government Bridge connecting Rock Island, Illinois to Davenport, Iowa. Located just southwest of the site of the first bridge across the Mississippi River, it is one of only two bridges in the world with two sets of railroad tracks above the auto lanes. It also co-located with Lock and Dam #15 - the largest roller dam in the world.
- Rock Island Centennial Bridge connecting Rock Island, Illinois to Davenport, Iowa.
- Santa Fe Bridge - in Fort Madison, Iowa, the largest double-deck swing-span bridge in the world; It is the last operating swing bridge over the Mississippi River for automobile traffic and is listed in the National Register of Historic Places.
- Clark Bridge also known as the Super Bridge as the result of an appearance on PBS program Nova. This cable-stay bridge constructed in 1994 connects Alton, Illinois to Black Jack, Missouri. It is the northernmost river crossing in the St. Louis metropolitan area and is named after explorer William Clark.
- Chain of Rocks Bridge - A bridge on the northern edge of St. Louis, Missouri; famous for a 22-degree bend halfway across and the most famous alignment of Historic US 66 across the Mississippi.
- Eads Bridge - A bridge connecting St. Louis, Missouri and East St. Louis, Illinois; the first major steel bridge in the world, and also a National Historic Landmark.
- Poplar Street Bridge - A bridge connecting downtown St. Louis, Missouri with East St. Louis, Illinois that carries three interstates and a U.S. highway; the bridge is one of the busiest on the river.
- Hernando de Soto Bridge - carries Interstate 40 to connect Memphis, Tennessee and West Memphis, Arkansas; listed in Guinness Book of World Records for its unique structural "letter" shape.
- Harahan Bridge - a trestle railroad bridge that connects Memphis, Tennessee to West Memphis, Arkansas
- Frisco Bridge - was the first crossing of the Lower Mississippi and the longest cantilever truss steel railroad bridge in North America when it opened on May 12, 1892. It connects Memphis, Tennessee and West Memphis, Arkansas.
- Memphis-Arkansas Memorial Bridge - the longest Warren truss- style bridge in the United States which carries Interstate 55 to connect Memphis, Tennessee and West Memphis, Arkansas; also listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
- Greenville Bridge - cable-stayed bridge under construction between Greenville, Mississippi with Arkansas.
- Vicksburg Bridge - connecting Vicksburg, Mississippi, with Tallulah, Louisiana.
- Natchez-Vidalia Bridge - connecting Natchez, Mississippi, with Vidalia, Louisiana.
- Horace Wilkinson Bridge - Baton Rouge, Louisiana; the 9th-longest cantilever bridge in the world.
- Luling Bridge (Hale Boggs Memorial Bridge) - near New Orleans, a cable-stayed bridge carrying Interstate 310 across the Mississippi, connecting the towns of Luling and Destrehan, Louisiana.
- Huey P. Long Bridge - Jefferson Parish, Louisiana.
- Crescent City Connection - connects the east- and westbanks of New Orleans, Louisiana; the 5th-longest cantilever bridge in the world.
Popular culture
Nicknames
Due to its size and historical significance, the Mississippi has many nicknames. Among these are:
- The Father of Waters
- The Gathering of Waters
- The Big Muddy (more commonly associated with the Missouri River)
- Big River
- Old Man River
- The Great River
- Body of a Nation
- The Mighty Mississippi
- El Grande (de Soto)
- The Muddy Mississippi
- Old Blue
Literature and music
Many of the works of Mark Twain deal with or take place near the Mississippi River. One of his first major works, Life on the Mississippi, is in part a history of the river, in part a memoir of Twain's experiences on the river, and a collection of tales that either take place on or are associated with the river. Twain's most famous work, Huckleberry Finn, is largely a journey down the river. The novel works as an episodic meditation on American culture with the river as the central metaphor.
Herman Melville's novel The Confidence-Man portrayed a Canterbury Tales-style group of steamboat passengers whose interlocking stories are told as they travel up the Mississippi River. The novel is written both as cultural satire and a metaphysical treatise. Like Huckleberry Finn, it uses the Mississippi River as a metaphor for the larger aspects of American and human identity that unify the otherwise disparate characters. The river's fluidity is reflected by the often shifting personalities and identities of Melville's "confidence man."
The 2nd chapter ("The Master of the Mississippi") of Don Rosa's famous comic book The Life and Times of Scrooge McDuck about the "Last of the Clan McDucks" is set on the Mississippi. Scrooge works here for his Uncle Angus "Pothole" McDuck on a wheel steamer and has his first encounter with The Beagle Boys.
The stage and movie musical Show Boat's central musical piece is the Blues-influenced ballad Ol' Man River.
Ferde Grofe composed a set of movements for symphony orchestra based on the lands the river travels through in his Mississippi Suite.
Johnny Cash song Big River deals with Mississippi.
The song ' When the Levee Breaks', made famous in the version performed by Led Zeppelin on the album Led Zeppelin IV, was composed by Memphis Minnie McCoy in 1929 after the Great Mississippi Flood of 1927.
On May 29, 1997 Singer/Guitarist Jeff Buckley drowned when he was swept away by the undertow of a passing boat in the Mississippi River.
Trivia
The Mississippi is a common tool for purpose of designating the United States into eastern and western sections, with places being described often as east or west "of the Mississippi":
- Most FCC call signs that start with W are on the east of the river; those that start with K are on the west.
- In the scheduling of games for sports leagues, "early games" start on the east of the river; "late" games start on the west, usually at the same time respective of the Eastern and Pacific time zones (such as 1pm ET/10am PT early; 4pm ET/1 PT late).