Congo River
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Geography
| Congo | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Mouth | Atlantic Ocean |
| Basin countries | Democratic Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo |
| Length | 4,667 km (2,900 mi) |
| Avg. discharge | 41,800 m³/s (1,476,376 ft³/s) |
| Basin area | 3,680,000 km² (1,420,848 mi²) |
Congo River in Africa
The Congo River (formerly known as Zaire River) is the largest river in Western Central Africa. Its overall length of 4,374 km (2,718 mi.) makes it the second longest in Africa (after the Nile). The river and its tributaries flow through the second largest rain forest area in the world, second only to the Amazon Rainforest in South America. The river also has the second-largest flow in the world, behind the Amazon, and the second-largest watershed of any river, again trailing the Amazon; its watershed is slightly larger than that of the Mississippi River. Because large sections of the river basin lie above and below the equator, its flow is stable, as there is always at least one river experiencing a rainy season. The Congo gets its name from the ancient Kingdom of Kongo which inhabited the lands at the mouth of the river. The Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo, both countries lying along the river's banks, are named after it. Between 1971 and 1997 the government of then- Zaire called it the Zaire River.
The sources of the Congo are in the highlands and mountains of the East African Rift, as well as Lake Tanganyika and Lake Mweru, which feed the Lualaba River, which then becomes the Congo below Boyoma Falls. The Chambeshi River in Zambia is generally taken as the source of the Congo in line with the accepted practice worldwide of using the longest tributary, as with the Nile River.
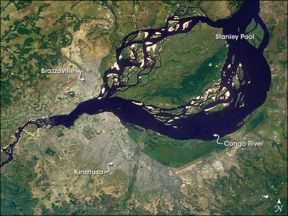
The Congo flows generally west from Kisangani just below the falls, then gradually bends southwest, passing by Mbandaka, joining with the Ubangi River, and running into the Pool Malebo ( Stanley Pool). Kinshasa (formerly Léopoldville) and Brazzaville are on opposite sides of the river at the Pool, then the river narrows and falls through a number of cataracts in deep canyons (collectively known as the Livingstone Falls), running by Matadi and Boma, and into the sea at the small town of Muanda.
History of exploration
The mouth of the Congo was visited in 1482 by the Portuguese Diogo Cão, and in 1816 by a British expedition under James Kingston Tuckey went up as far as Isangila. Henry Morton Stanley was the first European to navigate along the river's length and report that the Lualaba was not a source of the Nile as had been suggested.
Economic importance
Nearly the entire Congo is readily navigable, and with railways now bypassing the three major falls, much of the trade of central Africa passes along it, including copper, palm oil (as kernels), sugar, coffee, and cotton. The river is also potentially valuable for hydroelectric power, and the Inga Dams below Pool Malebo are first to exploit the river.
In February 2005, South Africa's state-owned power company, Eskom, announced a proposal to increase the capacity of the Inga dramatically through improvements and the construction of a new hydroelectric dam. The project would bring the maximum output of the facility to 40 GW, twice that of China's Three Gorges Dam.
Tributaries
Sorted in order from the mouth heading upstream.
- Inkisi
- Nzadi
- Nsele (south side of Pool Malebo)
- Bombo
- Kasai (between Fimi and Congo, known as Kwa)
- Fimi
- Kwango
- Sankuru
- Likouala
- Sangha
- Ubangi
- Giri
- Uele
- Mbomou