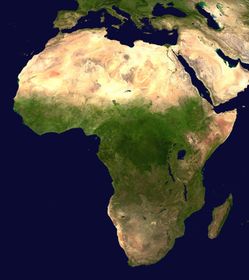
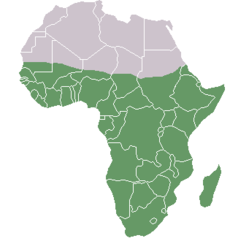
Sub-Saharan Africa
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Geography
Sub-Saharan Africa is the term used to describe those countries of the African continent that are not considered part of North Africa. In 19th Century Europe and the Western world, the area was sometimes referred to as Black Africa. Africa as a whole was commonly known as "the Dark continent", a term that was usually intended to refer to the Sub-Saharan region. This was partly due to the skin colour of its inhabitants and partly because much of it had not been fully mapped or explored by Westerners. These terms are now obsolete and often considered to be pejorative. Further, they are misleading, as Africans are indigenous to much of North Africa, as well. Cultural writer and filmmaker Owen 'Alik Shahadah adds "the notion of some invisible border, which divides the North of African from the South, is rooted in racism, ... This barrier of sand hence confines/confined Africans to the bottom of this make-believe location, which exist neither politically or physically". Shahadah argues that the term sub-Saharan Africa is a product of European imperialism, "Sub-Saharan Africa is a byword for primitive African: a place which has escaped advancement. Hence, we see statements like 'no written languages exist in Sub-Saharan Africa.' Egypt is not a Sub-Saharan African civilization."
Geography
Since the end of the last Ice Age, the north and sub-Saharan regions of Africa have been separated by the extremely harsh climate of the sparsely populated Sahara, forming an effective barrier interrupted by only the Nile River. The modern term sub-Saharan corresponds with the standard representation of North as above and South as below. Tropical Africa is an alternative modern label, used for the distinctive ecology of the region. However, if strictly applied, this term would exclude South Africa, most of which lies outside the Tropics.
Generally, sub-Saharan Africa is the poorest region in the world, still suffering from the legacies of colonial conquest and occupation, neocolonialism, inter-ethnic conflict, and political strife. The region contains many of the least developed countries in the world. (See Economy of Africa.) Sub-Saharan Africa, especially East Africa, is regarded by geneticists as being the birthplace of the human race. Mitochondrial Eve, from whom all humans alive are descended, is thought to have lived in present day Ethiopia or Tanzania. Sub-Saharan Africa has been the site of many empires and kingdoms, including Nubia, Axum, Wagadugu (Ghana), Mali, Nok, Songhai, Kanem-Bornu, Benin and Great Zimbabwe.
Up to and including October 2006 many governments faces difficulties in implementing policies aimed at mitigating the effects of the AIDS-pandemic due to lack of technical support despite a number of mitigating measures.
Nations of sub-Saharan Africa
There are 42 countries located on the sub-Saharan African mainland.The 6 island nations include Madagascar, Seychelles, Comoros, Cape Verde and Sao Tome and Principe. Mauritius is generally not considered to be a sub-Saharan African island because the ethnic make up of the country is predominantly East Indian, Chinese and French. According to this classification scheme, the countries of sub-Saharan Africa are:
Central Africa
- Democratic Republic of Congo
- Republic of Congo
- Central African Republic
- Rwanda
- Burundi
East Africa
Southern Africa
West Africa
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Cameroon
- Chad
- Côte d'Ivoire
- Equatorial Guinea
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liberia
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Senegal
- Sierra Leone
- Togo
African island nations
- Cape Verde (West Africa)
- Comoros (Southern Africa)
- Madagascar (Southern Africa)
- Mauritius (Southern Africa)
- São Tomé and Príncipe (West Africa)
- Seychelles (East Africa)
Territories, possessions, départements
| Africa | Central • Eastern • Northern • Southern • Western | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Americas | Caribbean • Central • Latin • North • Northern • South | ||
| Asia | Central • Eastern • Northern • Southern • Southeastern • Western | ||
| Europe | Central • Eastern • Northern • Southern • Western | ||
| Oceania | Australasia • Melanesia • Micronesia • Polynesia | ||
|
|
|||
| Polar | Arctic • Antarctic | ||
| Oceans | Pacific • Atlantic • Indian • Southern • Arctic | ||
Political maps of Sub-Saharan Africa
- Countries
- Blind map