Che Guevara
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Historical figures
| Ernesto Guevara de la Serna | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | June 14, 1928 Rosario, Argentina |
| Died | October 9, 1967 La Higuera, Bolivia |
Ernesto Guevara de la Serna ( June 14, 1928 – October 9, 1967), commonly known as Che Guevara or el Che, was an Argentine-born Marxist revolutionary, political figure, and leader of Cuban and internationalist guerrillas. As a young man studying medicine, Guevara traveled rough throughout Latin America, bringing him into direct contact with the impoverished conditions in which many people lived. His experiences and observations during these trips led him to the conclusion that the region's socioeconomic inequalities could only be remedied by revolution, prompting him to intensify his study of Marxism and travel to Guatemala to learn about the reforms being implemented there by President Jacobo Arbenz Guzmán.
Some time later, Guevara joined Fidel Castro's paramilitary 26th of July Movement, which seized power in Cuba in 1959. After serving in various important posts in the new government and writing a number of articles and books on the theory and practice of guerrilla warfare, Guevara left Cuba in 1965 with the intention of fomenting revolutions first in Congo-Kinshasa, and then in Bolivia, where he was captured in a CIA/ U.S. Army Special Forces-organized military operation. Guevara was summarily executed by the Bolivian Army in La Higuera near Vallegrande on October 9, 1967.
After his death, Guevara became an icon of socialist revolutionary movements worldwide. An Alberto Korda photo of him (shown) has received wide distribution and modification. The Maryland Institute College of Art called this picture "the most famous photograph in the world and a symbol of the 20th century."
Family heritage and early life
Ernesto Guevara de la Serna was born in Rosario, Argentina, the eldest of five children in a family of Spanish and Irish descent; both his father and mother were of Basque ancestry. The date of birth recorded on his birth certificate was June 14, 1928, although one tertiary source (Julia Constenla, quoted by Jon Lee Anderson) asserts that he was actually born on May 14 of that year (Constenla alleges that she was told by an unidentified astrologer that his mother, Celia de la Serna, was already pregnant when she and Ernesto Guevara Lynch were married and that the birthdate of their son was forged a month later than the actual date to avoid scandal). One of Guevara's forebears, Patrick Lynch, was born in Galway, Ireland, in 1715. He left for Bilbao, Spain, and traveled from there to Argentina. Francisco Lynch (Guevara's great-grandfather) was born in 1817, and Ana Lynch (his beloved grandmother) in 1868 Her son, Ernesto Guevara Lynch (Guevara's father) was born in 1900. Guevara Lynch married Celia de la Serna y Llosa in 1927, and they had three sons and two daughters.
Growing up in this upper-class family with leftist leanings, Guevara became known for his dynamic personality and radical perspective even as a boy. He idolized Francisco Pizarro and yearned to have been one of his soldiers. Though suffering from the crippling bouts of asthma that were to afflict him throughout his life, he excelled as an athlete. He was an avid rugby union player despite his handicap and earned himself the nickname "Fuser" — a contraction of "El Furibundo" (English: "The Raging") and his mother's surname, "Serna" — for his aggressive style of play.
Guevara learned chess from his father and began participating in local tournaments by the age of 12. During his adolescence he became passionate about poetry, especially that of Pablo Neruda. Guevara, as is common practice among Latin Americans of his class, also wrote poems throughout his life. He was an enthusiastic and eclectic reader, with interests ranging from adventure classics by Jack London, Emilio Salgari and Jules Verne to essays on sexuality by Sigmund Freud and treatises on social philosophy by Bertrand Russell. In his late teens, he developed a keen interest in photography and spent many hours photographing people, places and, during later travels, archaeological sites.
In 1948 Guevara entered the University of Buenos Aires to study medicine. While a student, he spent long periods traveling around Latin America. In 1951 his older friend, Alberto Granado, a biochemist, suggested that Guevara take a year off from his medical studies to embark on a trip they had talked of making for years, traversing South America. Guevara and the 29-year-old Granado soon set off from their hometown of Alta Gracia astride a 1939 Norton 500 cc motorcycle they named La Poderosa II (English: "the Mighty One, the Second") with the idea of spending a few weeks volunteering at the San Pablo Leper colony in Peru on the banks of the Amazon River. Guevara narrated this journey in The Motorcycle Diaries, which was translated into English in 1996 and used in 2004 as the basis for a motion picture of the same name.
Witnessing the widespread poverty, oppression and disenfranchisement throughout Latin America, and influenced by his readings of Marxist literature, Guevara decided that the only solution for the region’s inequalities was armed revolution. His travels and readings also led him to view Latin America not as a group of separate nations but as a single entity requiring a continent-wide strategy for liberation. His conception of a borderless, united Ibero-America sharing a common 'mestizo' culture was a theme that would prominently recur during his later revolutionary activities. Upon returning to Argentina, he expedited the completion of his medical studies in order to resume his travels in Central and South America and received his diploma on 12 June 1953.
Guatemala
On 7 July 1953, Guevara set out on a trip through Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Panama, Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, and El Salvador. During the final days of December 1953 he arrived in Guatemala where leftist President Jacobo Arbenz Guzmán headed a populist government that, through land reform and other initiatives, was attempting to bring an end to the U.S.-dominated latifundia system. In a contemporaneous letter to his Aunt Beatriz, Guevara explained his motivation for settling down for a time in Guatemala: "In Guatemala", he wrote, "I will perfect myself and accomplish whatever may be necessary in order to become a true revolutionary."
Shortly after reaching Guatemala City, Guevara acted upon the suggestion of a mutual friend that he seek out Hilda Gadea Acosta, a Peruvian economist who was living and working there. Gadea, whom he would later marry, was well-connected politically as a result of her membership in the socialist American Popular Revolutionary Alliance (APRA) led by Víctor Raúl Haya de la Torre, and she introduced Guevara to a number of high-level officials in the Arbenz government. He also re-established contact with a group of Cuban exiles linked to Fidel Castro whom he had initially met in Costa Rica; among them was Antonio "Ñico" López, associated with the attack on the "Carlos Manuel de Céspedes" barracks in Bayamo in the Cuban province of Oriente, and who would die at Ojo del Toro bridge soon after the Granma landed in Cuba. Guevara joined these " moncadistas" in the sale of religious objects related to the Black Christ of Esquipulas, and he also assisted two Venezuelan malaria specialists at a local hospital. It was during this period that he acquired his famous nickname, "Che", due to his frequent use of the Argentine interjection Che ( pronounced /tʃe/), which is utilized in much the same way as "hey", "pal", "eh", or "mate" are employed colloquially in various English-speaking countries. Argentina, Uruguay, and southern Brazil (where the interjection is rendered 'chê' or 'ché' in written Portuguese) are the only areas where this expression is used, making it a trademark of the Rioplatense region.
Guevara's attempts to obtain a medical internship were unsuccessful and his economic situation was often precarious, leading him to pawn some of Hilda's jewelry. Political events in the country began to move quickly after May 15, 1954 when a shipment of Skoda infantry and light artillery weapons sent from Communist Czechoslovakia for the Arbenz Government arrived in Puerto Barrios aboard the Swedish ship Alfhem. The amount of Czech weaponry was estimated to be 2000 tons by the CIA though only 2 tons by Jon Lee Anderson. (Anderson's tonnage estimate is thought to be a typographical error due to how few scholarly sources support it.) Guevara briefly left Guatemala for El Salvador to pick up a new visa, then returned to Guatemala only a few days before the CIA-sponsored coup attempt led by Carlos Castillo Armas began. The anti-Arbenz forces tried, but failed, to stop the trans-shipment of the Czechoslovak weapons by train. However, after pausing to regroup and recover energy, Castillo Armas' column seized the initiative and, apparently with the assistance of US air support, started to gain ground. Guevara was eager to fight on behalf of Arbenz and joined an armed militia organized by the Communist Youth for that purpose; but, frustrated with the group's inaction, he soon returned to medical duties. Following the coup, he again volunteered to fight but his efforts were thwarted when Arbenz took refuge in the Mexican Embassy and told his foreign supporters to leave the country. After Gadea was arrested, Guevara sought protection inside the Argentine consulate where he remained until he received a safe-conduct pass some weeks later. At that point, he turned down a free seat on a flight back to Argentina that was proffered to him by the Embassy, preferring instead to make his way to Mexico.
The overthrow of the Arbenz regime by a coup d'état backed by the Central Intelligence Agency cemented Guevara's view of the United States as an imperialist power that would implacably oppose and attempt to destroy any government that sought to redress the socioeconomic inequality endemic to Latin America and other developing countries. This strengthened his conviction that socialism achieved through armed struggle and defended by an armed populace was the only way to rectify such conditions.
Cuba
Guevara arrived in Mexico City in early September 1954, and shortly thereafter renewed his friendship with Ñico López and the other Cuban exiles whom he had known in Guatemala. In June 1955, López introduced him to Raúl Castro. Several weeks later, Fidel Castro arrived in Mexico City after having been amnestied from prison in Cuba, and on the evening of 8 July 1955 Raúl introduced Guevara to the older Castro brother. During a fervid overnight conversation, Guevara became convinced that Fidel was the inspirational revolutionary leader for whom he had been searching, and he immediately joined the " 26th of July Movement" that intended to overthrow the government of Fulgencio Batista. Although it was planned that he would be the group's medic, Guevara participated in the military training alongside the other members of the 26J Movement, and at the end of the course was singled out by their instructor, Col. Alberto Bayo, as his most outstanding student. Meanwhile, Hilda Gadea had arrived from Guatemala and she and Guevara resumed their relationship. In the summer of 1955 she informed him that she was pregnant and he immediately suggested that they marry. The wedding took place on August 18, 1955, and their daughter, whom they named Hilda Beatríz, was born on February 15, 1956.
When the cabin cruiser Granma set out from Tuxpan, Veracruz for Cuba on November 25, 1956, Guevara was one of only four non-Cubans aboard. Attacked by Batista's military soon after landing, about half of the expeditionaries were killed or executed upon capture. Guevara writes that it was during this confrontation that he laid down his knapsack containing medical supplies in order to pick up a box of ammunition dropped by a fleeing comrade, a moment which he later recalled as marking his transition from physician to combatant. Only 15–20 rebels survived as a battered fighting force; they re-grouped and fled into the mountains of the Sierra Maestra to wage guerrilla warfare against the Batista regime.
Guevara became a leader among the rebels, a Comandante (English translation: Major), respected by his comrades in arms for his courage and military prowess, and feared for what some have described as ruthlessness: He was responsible for the execution of many men accused of being informers, deserters or spies. In the final days of December 1958, he directed his " suicide squad" (which undertook the most dangerous tasks in the rebel army) in the attack on Santa Clara that turned out to be one of the decisive events of the revolution, although the bloody series of ambushes first during la ofensiva in the heights of the Sierra Maestra, then at Guisa, and the whole Cauto Plains campaign that followed probably had more military significance. Batista, upon learning that his generals — especially General Cantillo, who had visited Castro at the inactive sugar mill "Central America" — were negotiating a separate peace with the rebel leader, fled to the Dominican Republic on January 1, 1959.
On February 7, 1959, the victorious government proclaimed Guevara "a Cuban citizen by birth" in recognition of his role in the triumph of the revolutionary forces. Shortly thereafter, he initiated divorce proceedings to put a formal end to his marriage with Gadea, from whom he had been separated since before leaving Mexico on the Granma, and on June 2, 1959, he married Aleida March, a Cuban-born member of the 26th of July movement with whom he had been living since late 1958.
He was appointed commander of the La Cabaña Fortress prison, and during his five-month tenure in that post ( January 2 through June 12, 1959), he oversaw the trial and execution of many people, among whom were former Batista regime officials and members of the "Bureau for the Repression of Communist Activities" (a unit of the secret police know by its Spanish acronym BRAC). According to José Vilasuso, an attorney who worked under Guevara at La Cabaña preparing indictments, these were lawless proceedings where "the facts were judged without any consideration to general juridical principles" and the findings were pre-determined by Guevara.
Later, Guevara became an official at the National Institute of Agrarian Reform, and President of the National Bank of Cuba (somewhat ironically, as he often condemned money, favored its abolition, and showed his disdain by signing Cuban banknotes with his nickname, "Che"). It is sometimes said that Guevara ended up in this position because Fidel Castro asked if there were any economists in the room and Che, thinking Castro had asked for Communists, put his hand up.
During this time his fondness for chess was rekindled, and he attended and participated in most national and international tournaments held in Cuba. He was particularly eager to encourage young Cubans to take up the game, and organized various activities designed to stimulate their interest in it.
Even as early as 1959, Guevara helped organize revolutionary expeditions overseas, all of which failed. The first attempt was made in Panama; another in the Dominican Republic (led by Henry Fuerte, also known as "El Argelino", and Enrique Jiménez Moya) took place on 14 June of that same year.
In 1960 Guevara provided first aid to victims during the La Coubre arms shipment rescue operation that went further awry when a second explosion occurred, resulting in well over a hundred dead. It was at the memorial service for the victims of this explosion that Alberto Korda took the most famous photograph of him. Whether La Coubre was sabotaged or merely exploded by accident is not clear. Those who favour the sabotage theory sometimes attribute this to the Central Intelligence Agency and sometimes name William Alexander Morgan, a former rival of Guevara's in the anti-Batista forces of the central provinces and later a putative CIA agent, as the perpetrator. Cuban exiles have put forth the theory that it was done by Guevara's USSR-loyalist rivals.
Guevara later served as Minister of Industries, in which post he helped formulate Cuban socialism, and became one of the country's most prominent figures. In his book Guerrilla Warfare, he advocated replicating the Cuban model of revolution initiated by a small group ( foco) of guerrillas without the need for broad organizations to precede armed insurrection. His essay El socialismo y el hombre en Cuba (1965) (Man and Socialism in Cuba) advocates the need to shape a "new man" (hombre nuevo) in conjunction with a socialist state. Some saw Guevara as the simultaneously glamorous and austere model of that "new man."
During the 1961 Bay of Pigs Invasion Guevara did not participate in the fighting, having been ordered by Castro to a command post in Cuba's westernmost Pinar del Río province where he was involved in fending off a decoy force. He did, however, suffer a bullet wound to the face during this deployment, which he said had been caused by the accidental discharge of his own gun.
Guevara played a key role in bringing to Cuba the Soviet nuclear-armed ballistic missiles that precipitated the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962. During an interview with the British newspaper Daily Worker some weeks later, he stated that, if the missiles had been under Cuban control, they would have fired them against major U.S. cities.
Disappearance from Cuba
In December 1964 Che Guevara traveled to New York City as the head of the Cuban delegation to speak at the UN ( listen, requires RealPlayer; or read). He also appeared on the CBS Sunday news program Face the Nation, met with a gamut of individuals and groups including U.S. Senator Eugene McCarthy, several associates of Malcolm X, and Canadian radical Michelle Duclos, and dined at the home of the Rockefellers. On 17 December, he flew to Paris and from there embarked on a three-month international tour during which he visited the People's Republic of China, the United Arab Republic (Egypt), Algeria, Ghana, Guinea, Mali, Dahomey, Congo-Brazzaville and Tanzania, with stops in Ireland, Paris and Prague. In Algiers on 24 February 1965, he made what turned out to be his last public appearance on the international stage when he delivered a speech to the "Second Economic Seminar on Afro-Asian Solidarity" in which he declared, "There are no frontiers in this struggle to the death. We cannot remain indifferent in the face of what occurs in any part of the world. A victory for any country against imperialism is our victory, just as any country's defeat is our defeat." He then astonished his audience by proclaiming, "The socialist countries have the moral duty of liquidating their tacit complicity with the exploiting countries of the West." He proceeded to outline a number of measures which he said the communist-bloc countries should implement in order to accomplish this objective. He returned to Cuba on 14 March to a solemn reception by Fidel and Raúl Castro, Osvaldo Dorticós and Carlos Rafael Rodríguez at the Havana airport.
Two weeks later, Guevara dropped out of public life and then vanished altogether. His whereabouts were the great mystery of 1965 in Cuba, as he was generally regarded as second in power to Castro himself. His disappearance was variously attributed to the relative failure of the industrialization scheme he had advocated while minister of industry, to pressure exerted on Castro by Soviet officials disapproving of Guevara's pro- Chinese Communist bent as the Sino-Soviet split grew more pronounced, and to serious differences between Guevara and the Cuban leadership regarding Cuba's economic development and ideological line. Others suggested that Castro had grown increasingly wary of Guevara's popularity and considered him a potential threat. Castro's critics sometimes say his explanations for Guevara's disappearance have always been suspect (see below), and many found it surprising that Guevara never announced his intentions publicly, but only through an undated and uncharacteristically obsequious letter to Castro.
The coincidence of Guevara's views with those expounded by the Chinese Communist leadership had become increasingly problematic for Cuba as the nation's economic dependence on the Soviet Union deepened. Since the early days of the Cuban revolution, Guevara had been considered by many an advocate of Maoist strategy in Latin America and the originator of a plan for the rapid industrialization of Cuba which was frequently compared to China's " Great Leap Forward". According to Western "observers" of the Cuban situation, the fact that Guevara was opposed to Soviet conditions and recommendations that Castro seemed obliged to accept might have been the reason for his disappearance. However, both Guevara and Castro were supportive of the idea of a "united anti-imperialist front" intended to include both the Soviet Union and China, and had made several unsuccessful attempts to reconcile the feuding parties.
Following the Cuban Missile Crisis and what he perceived as a Soviet betrayal of Cuba when Khrushchev agreed to withdraw the missiles from Cuban territory without consulting Castro, Guevara had grown more skeptical of the Soviet Union. As revealed in his last speech in Algiers, he had come to view the Northern Hemisphere, led by the U.S. in the West and the Soviet Union in the East, as the exploiter of the Southern Hemisphere. He strongly supported Communist North Vietnam in the Vietnam War, and urged the peoples of other developing countries to take up arms and create "many Vietnams".
Pressed by international speculation regarding Guevara's fate, Castro stated on 16 June 1965, that the people would be informed about Guevara when Guevara himself wished to let them know. Numerous rumors about his disappearance spread both inside and outside Cuba. On 3 October of that year, Castro revealed an undated letter purportedly written to him by Guevara some months earlier in which Guevara reaffirmed his enduring solidarity with the Cuban Revolution but declared his intention to leave Cuba to fight abroad for the cause of the revolution. He explained that "Other nations of the world summon my modest efforts," and that he had therefore decided to go and fight as a guerrilla "on new battlefields". In the letter Guevara announced his resignation from all his positions in the government, in the party, and in the Army, and renounced his Cuban citizenship, which had been granted to him in 1959 in recognition of his efforts on behalf of the revolution.
During an interview with four foreign correspondents on 1 November, Castro remarked that he knew where Guevara was but would not disclose his location, and added, denying reports that his former comrade-in-arms was dead, that "he is in the best of health." Despite Castro's assurances, Guevara's fate remained a mystery at the end of 1965 and his movements and whereabouts continued to be a closely held secret for the next two years.
Congo
Expedition
During their all-night meeting on March 14– March 15, 1965, Guevara and Castro had agreed that the former would personally lead Cuba's first military action in Sub-Saharan Africa. Some usually reliable sources state that Guevara persuaded Castro to back him in this effort, while other sources of equal reliability maintain that Castro convinced Guevara to undertake the mission, arguing that conditions in the various Latin American countries that had been under consideration for the possible establishment of guerrilla focos were not yet optimal. Castro himself has said the latter is true. According to Ahmed Ben Bella, who was president of Algeria at the time and had recently held extended conversations with Guevara, "The situation prevailing in Africa, which seemed to have enormous revolutionary potential, led Che to the conclusion that Africa was imperialism’s weak link. It was to Africa that he now decided to devote his efforts."
The Cuban operation was to be carried out in support of the pro- Patrice Lumumba Marxist Simba movement in the Congo-Kinshasa (formerly Belgian Congo, later Zaire and currently the Democratic Republic of the Congo). Guevara, his second-in-command Victor Dreke, and twelve of the Cuban expeditionaries arrived in the Congo on 24 April 1965; a contingent of approximately 100 Afro-Cubans joined them soon afterwards. They collaborated for a time with guerrilla leader Laurent-Désiré Kabila, who helped Lumumba supporters lead a revolt that was suppressed in November of that same year by the Congolese army. Guevara dismissed Kabila as insignificant. "Nothing leads me to believe he is the man of the hour," Guevara wrote.
Although Guevara was 37 at the time and had no formal military training, he had the experiences of the Cuban revolution, including his successful march on Santa Clara, which was central to Batista finally being overthrown by Castro's forces. His asthma had prevented him from being drafted into military service in Argentina, a fact of which he was proud given his opposition to Perón's government.
South African mercenaries including Mike Hoare and Cuban exiles worked with the Congolese army to thwart Guevara. They were able to monitor his communications, arrange to ambush the rebels and the Cubans whenever they attempted to attack, and interdict his supply lines. Despite the fact that Guevara sought to conceal his presence in the Congo, the U.S. government was fully aware of his location and activities: The National Security Agency (NSA) was intercepting all of his incoming and outgoing transmissions via equipment aboard the USNS Valdez, a floating listening post which continuously cruised the Indian Ocean off Dar-es-Salaam for that purpose.
Guevara's aim was to export the Cuban Revolution by instructing local Simba fighters in communist ideology and strategies of guerrilla warfare. In his Congo Diary, he cites the incompetence, intransigence, and infighting of the local Congolese forces as the key reasons for the revolt's failure. Later that same year, ill with dysentery, suffering from his asthma, and disheartened after seven months of frustrations, Guevara left the Congo with the Cuban survivors (six members of his column had died). At one point Guevara had considered sending the wounded back to Cuba, then standing alone and fighting until the end in the Congo as a revolutionary example; however, after being urged by his comrades in arms and pressured by two emissaries sent by Castro, at the last moment he reluctantly agreed to leave the Congo. A few weeks later, when writing the preface to the diary he had kept during the Congo venture, he began it with the words: "This is the history of a failure."
Interlude
Because Castro had made public Guevara's "farewell letter" to him — a letter Guevara had intended should only be revealed in case of his death — wherein he had written that he was severing all ties to Cuba in order to devote himself to revolutionary activities in other parts of the world, he felt that he could not return to Cuba with the other surviving combatants for moral reasons, and he spent the next six months living clandestinely in Dar-es-Salaam, and Prague. During this time he compiled his memoirs of the Congo experience, and wrote the drafts of two more books, one on philosophy and the other on economics. He also visited several countries in Western Europe in order to "test" a new false identity and the corresponding documentation (passport, etc.) created for him by Cuban Intelligence that he planned to use to travel to South America. Throughout this period Castro continued to importune him to return to Cuba, but Guevara only agreed to do so when it was understood that he would be there on a strictly temporary basis for the few months needed to prepare a new revolutionary effort somewhere in Latin America, and that his presence on the island would be cloaked in the tightest secrecy.
Bolivia
Insurgent
Speculation on Guevara's whereabouts continued throughout 1966 and into 1967. Representatives of the Mozambican independence movement FRELIMO reported meeting with Guevara in late 1966 or early 1967 in Dar es Salaam, at which point they rejected his offer of aid in their revolutionary project. In a speech at the 1967 May Day rally in Havana, the Acting Minister of the armed forces, Major Juan Almeida, announced that Guevara was "serving the revolution somewhere in Latin America". The persistent reports that he was leading the guerrillas in Bolivia were eventually shown to be true.
At Castro's behest, a 3,700 acre parcel of jungle land in the remote Ñancahuazú region had been purchased by native Bolivian Communists for Guevara to use as a training area and base camp . The evidence suggests that the training at this camp in the Ñancahuazú valley was more hazardous than combat to Guevara and the Cubans accompanying him. Little was accomplished in the way of building a guerrilla army. Former Stasi operative Haydée Tamara Bunke Bider, better known by her nom de guerre "Tania", who had been installed as his primary agent in La Paz, was reportedly also working for the KGB and is widely inferred to have unwittingly served Soviet interests by leading Bolivian authorities to Guevara's trail. The numerous photographs taken by and of Guevara and other members of his guerrilla group that they left behind at their base camp after the initial clash with the Bolivian army in March 1967 provided President René Barrientos with the first proof of his presence in Bolivia; after viewing them, Barrientos allegedly stated that he wanted Guevara's head displayed on a pike in downtown La Paz. He thereupon ordered the Bolivian Army to hunt Guevara and his followers down.
Guevara's guerrilla force, numbering about 50 and operating as the ELN (Ejército de Liberación Nacional de Bolivia; English: " National Liberation Army of Bolivia"), was well equipped and scored a number of early successes against Bolivian regulars in the difficult terrain of the mountainous Camiri region. In September, however, the Army managed to eliminate two guerrilla groups, reportedly killing one of the leaders.
Despite the violent nature of the conflict, Guevara gave medical attention to all of the wounded Bolivian soldiers whom the guerrillas took prisoner, and subsequently released them. Even after his last battle at the Quebrada del Yuro, in which he had been wounded, when he was taken to a temporary holding location and saw there a number of Bolivian soldiers who had also been wounded in the fighting, he offered to give them medical care. (His offer was turned down by the Bolivian officer in charge.)
Guevara's plan for fomenting revolution in Bolivia appears to have been based upon a number of misconceptions:
- He had expected to deal only with the country's military government and its poorly trained and equipped army. However, after the U.S. government learned of his location, CIA and other operatives were sent into Bolivia to aid the anti-insurrection effort. The Bolivian Army was being trained and supplied by U.S. Army Special Forces advisors, including a recently organized elite battalion of Rangers trained in jungle warfare that set up camp in La Esperanza, a small settlement close to the guerrillas' zone of operations.
- Guevara had expected assistance and cooperation from the local dissidents. He did not receive it; and Bolivia's Communist Party, under the leadership of Mario Monje, was oriented towards Moscow rather than Havana and did not aid him, despite having promised to do so. (Some members of the Bolivian Communist Party did join/support him, such as Coco and Inti Peredo, Rodolfo Saldaňa, Serapio Aquino Tudela, and Antonio Jiménez Tardio, against the Party leadership's wishes.)
- He had expected to remain in radio contact with Havana. However, the two shortwave transmitters provided to him by Cuba were faulty, so that the guerrillas were unable to communicate with Havana. (In this, and in many other respects, Manuel Piñeiro, the man to whom Castro had assigned the task of coordinating support for Guevara's operations in Bolivia, performed abysmally.) To further complicate matters, some months into the campaign, the tape recorder that the guerrillas used to record and decipher the one-time pad-encoded radio messages sent to them from Havana was lost while crossing a river, making de-coding such messages more difficult.
In addition, his penchant for confrontation rather than compromise appears to have contributed to his inability to develop successful working relationships with local leaders in Bolivia, just as it had in the Congo. This tendency had surfaced during his guerrilla warfare campaign in Cuba as well, but had been kept in check there by the timely interventions and guidance of Castro.
Capture and execution
The Bolivian Special Forces were notified of the location of Guevara's guerrilla encampment by an informant. On 8 October, the encampment was encircled, and Guevara was captured while leading a detachment with Simeón Cuba Sarabia in the Quebrada del Yuro ravine. He offered to surrender after being wounded in the legs and having his rifle destroyed by a bullet. (His pistol was lacking an ammunition magazine.) According to some soldiers present at the capture, during the skirmish as they approached Guevara, he allegedly shouted, "Do not shoot! I am Che Guevara and worth more to you alive than dead."
Barrientos promptly ordered his execution upon being informed of his capture. Guevara was taken to a dilapidated schoolhouse in the nearby village of La Higuera where he was held overnight. Early the next afternoon he was executed. The executioner was Mario Terán, a Sergeant in the Bolivian army who had drawn a short straw after arguments over who got the honour of killing Guevara broke out among the soldiers. Guevara received multiple shots to the legs, so as to avoid maiming his face for identification purposes and simulate combat wounds in an attempt to conceal his execution. Che Guevara did have some last words before his death; he allegedly said to his executioner, "I know you are here to kill me. Shoot, coward, you are only going to kill a man." His body was lashed to the landing skids of a helicopter and flown to neighboring Vallegrande where it was laid out on a laundry tub in the local hospital and displayed to the press. Photographs taken at that time gave rise to legends such as those of San Ernesto de La Higuera and El Cristo de Vallegrande. After a military doctor surgically amputated his hands, Bolivian army officers transferred Guevara's cadaver to an undisclosed location and refused to reveal whether his remains had been buried or cremated.
The hunt for Guevara in Bolivia was headed by Félix Rodríguez, a CIA agent, who previously had infiltrated into Cuba to prepare contacts with the rebels in the Escambray Mountains and the anti-Castro underground in Havana prior to the Bay of Pigs invasion, and had been successfully extracted from Cuba afterwards. Upon hearing of Guevara's capture, Rodríguez relayed the information to CIA headquarters at Langley, Virginia, via CIA stations in various South American nations. After the execution, Rodríguez took Guevara's Rolex watch and several other personal items, often proudly showing them to reporters during the ensuing years. Today, some of these belongings, including his flashlight, are on display at the CIA.
On October 15, Castro acknowledged that Guevara was dead and proclaimed three days of public mourning throughout Cuba. The death of Guevara was regarded as a severe blow to the socialist revolutionary movements in Latin America and the rest of the third world.
In 1997, the skeletal remains of Guevara's handless body were exhumed from beneath an air strip near Vallegrande, positively identified by DNA matching, and returned to Cuba. On 17 October 1997, his remains, along with those of six of his fellow combatants killed during the guerrilla campaign in Bolivia, were laid to rest with full military honours in a specially built mausoleum in the city of Santa Clara, where he had won the decisive battle of the Cuban Revolution.
The Bolivian Diary
Also removed when Guevara was captured was his diary, which documented events of the guerrilla campaign in Bolivia. The first entry is on November 7, 1966 shortly after his arrival at the farm in Ñancahuazú, and the last entry is on October 7, 1967, the day before his capture. The diary tells how the guerrillas were forced to begin operations prematurely due to discovery by the Bolivian Army, explains Guevara's decision to divide the column into two units that were subsequently unable to reestablish contact, and describes their overall failure. It records the rift between Guevara and the Bolivian Communist Party that resulted in Guevara having significantly fewer soldiers than originally anticipated. It shows that Guevara had a great deal of difficulty recruiting from the local populace, due in part to the fact that the guerrilla group had learned Quechua rather than the local language which was Tupí-Guaraní. As the campaign drew to an unexpected close, Guevara became increasingly ill. He suffered from ever-worsening bouts of asthma, and most of his last offensives were carried out in an attempt to obtain medicine.
The Bolivian Diary was quickly and crudely translated by Ramparts magazine and circulated around the world. There are at least four additional diaries in existence — those of Israel Reyes Zayas (Alias "Braulio"), Harry Villegas Tamayo ("Pombo"), Eliseo Reyes Rodriguez ("Rolando") and Dariel Alarcón Ramírez ("Benigno") — each of which reveals additional aspects of the events in question.
Legacy and criticisms
While pictures of Guevara's dead body were being circulated and the circumstances of his death debated, his legend began to spread. Demonstrations in protest against his execution occurred throughout the world, and articles, tributes, songs and poems were written about his life and death. Latin America specialists advising the U.S. State Department immediately recognized the importance of the demise of “the most glamorous and reportedly most successful revolutionary”, noting that Guevara would be eulogized by communists and other leftists as “the model revolutionary who met a heroic death”.
Such predictions gained increasing credibility as Guevara became a potent symbol of rebellion and revolution during the global student protests of the late 1960s. Left wing activists responded to Guevara's apparent indifference to rewards and glory, and concurred with Guevara's sanctioning of violence as a necessity to instill socialist ideals. The slogan 'Che lives!' began to appear on walls throughout the west, while Jean-Paul Sartre, a leading figure in the movement, encouraged the adulation by describing Guevara as "the most complete human being of our age".
Typically, responses to Guevara's legacy followed partisan lines. The US State Department was advised that his death would come as a relief to non-leftist Latin Americans, who had feared possible insurgencies in their own countries. Subsequent analysts have also shed light on aspects of cruelty in Guevara’s methods, and analysed what Fidel Castro described as Guevara’s “excessively aggressive quality”. Studies addressing problematic characteristics of Guevara's life have cited his principal role in setting up Cuba's first post-revolutionary labor camps, his unsympathetic treatment of captured fighters during various guerrilla campaigns, and his frequent humiliations of those deemed his intellectual inferiors. Though much opposition to Guevara's methods has come from the political right, critical evaluation has also come from groups such as anarchists and civil libertarians, some of whom consider Guevara an authoritarian, anti-working-class Stalinist, whose legacy was the creation of a more bureaucratic, authoritarian regime. Detractors have also theorized that in much of Latin America, Che-inspired revolutions had the practical result of reinforcing brutal militarism for many years.
Legacy in Cuba
In Cuba, Guevara’s death precipitated the abandonment of guerrilla warfare as an instrument of foreign policy, ushering in a rapprochement with the Soviet Union, and the reformation of the government along Soviet lines. When Cuban troops returned to Africa in the 1970s, it was as part of a large-scale military expedition, and support for insurrection movements in Latin America and the Caribbean became logistical and organizational rather than overt. Cuba also abandoned Guevara's plans for economic diversification and rapid industrialization which had ultimately proved to be impracticable in view of the country's incorporation into the COMECON system.
As early as 1965, the Yugoslav communist journal Borba observed the many half-completed or empty factories in Cuba, a legacy of Guevara's tenure as Minister of Industries, "standing like sad memories of the conflict between pretension and reality".
The Cuban state continued to cultivate Guevara’s cult of personality, constructing numerous statues and artworks in his honour throughout the land; adorning school rooms, workplaces, public buildings, billboards, and money with his image. Children across the country begin each school day with the chant "¡Pioneros por el Comunismo, Seremos como el Che!" (English: Pioneers for Communism, We will be like Che!). Guevara's mausoleum in Santa Clara has become a site of almost religious significance to many Cubans, while the nation’s burgeoning tourist industry has benefited greatly from the ongoing international interest in Guevara's life. Some 205,832 people visited the mausoleum during 2004, of whom 127,597 were foreigners.
Reverence among Cubans for Guevara's memory is by no means universal. Many Cuban exiles have spoken of Guevara in less than favorable terms, and he is remembered by some as the "The Butcher of la Cabaña", a reference to Guevara’s post-revolutionary role as “supreme prosecutor” at the Cabana fortress. The epithet was repeated by Cuban-born musician Paquito D'Rivera, who wrote an open letter castigating fellow musician Carlos Santana, for wearing a T-shirt displaying Guevara’s image to the 2005 Academy Awards ceremony. Similar sentiments have been shared by Cuban-American actor and director Andy Garcia, who stated in 2004 that "Che has been romanticized over the years, but there is a darker side to his story. He looks like a rock star, but he executed a lot of people without trial or defense." Garcia’s 2005 film The Lost City, which was reportedly banned in several Latin American countries, portrayed a ruthless brutality at the heart of the Cuban revolution. Actor Jsu Garcia as Guevara is shown casually shooting wounded Batista foot soldiers where they lie.
The "Cult of Che"
Despite this, Guevara's status as a popular icon has continued throughout the world, leading commentators to speak of a global "cult of Che". A photograph of Guevara taken by photographer Alberto Korda has became one of the century's most ubiquitous images, and the portrait, transformed into a monochrome graphic, is reproduced endlessly on a vast array of merchandise, such as T-shirts, posters, coffee mugs, and baseball caps. The image had been likened to a global brand, long since shedding its ideological or political connotations, and the obsession with Guevara has been dismissed by some as merely "adolescent revolutionary romanticism". In addition, political writer Paul Berman believes that the "modern-day cult of Che" obscures the work of dissidents and the "tremendous social struggle" currently taking place in Cuba. Author Christopher Hitchens commented, "Che's iconic status was assured because he failed, His story was one of defeat and isolation, and that's why it is so seductive. Had he lived, the myth of Che would have long since died."
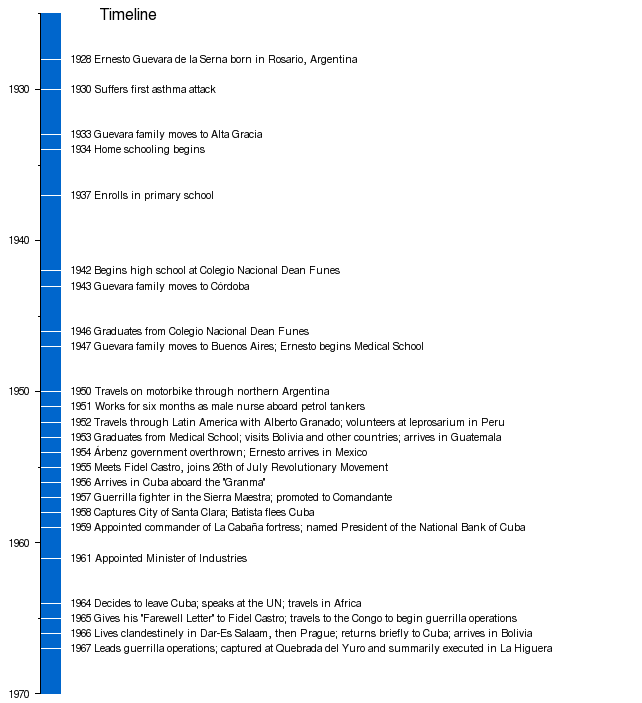
Timeline
Guevara's published works
In English (translations)
- Back on the Road: A Journey to Central America (Harvill Panther S.), The Harvill Press, paperback, ISBN 0-8021-3942-6.
- Bolivian Diary, Pimlico, paperback, ISBN 0-7126-6457-2
- Che Guevara: Radical Writings on Guerrilla Warfare, Politics and Revolution, Filiquarian Publishing LLC, paperback, ISBN 1-59986-999-3.
- Che Guevara Reader: Writings on Guerrilla Warfare, Politics and History, Ocean Press, paperback
- Che Guevara Speaks, Pathfinder, paperback
- Che Guevara Talks to Young People, Pathfinder, paperback
- Critical Notes on Political Economy, Ocean Press, paperback
- Guerrilla Warfare, Souvenir Press Ltd, paperback, ISBN 0-285-63680-4.
- Our America and Theirs, Ocean Press (AU), paperback, ISBN 1-876175-81-8.
- Reminiscences of the Cuban Revolutionary War, Monthly Review Press, paperback, 1998
- Self-Portrait: Che Guevara, Ocean Press, 320pp, paperback, 2005
- Socialism and Man in Cuba: Also Fidel Castro on the Twentieth Anniversary of Guevara's Death, Monad, paperback
- The African Dream: The Diaries of the Revolutionary War in the Congo, Grove Press, paperback.
- The Diary of Che Guevara, Amereon Ltd,
- The Motorcycle Diaries: Notes on a Latin American Journey, Perennial Press, ISBN 0-00-718222-8.
In Spanish
-
 Cuadernos de Praga – Guevara's notebooks written during his clandestine stay in Prague in 1966 ( PDF)
Cuadernos de Praga – Guevara's notebooks written during his clandestine stay in Prague in 1966 ( PDF) -
 Diario del Che en Bolivia – Guevara's diary of the guerrilla war in Bolivia
Diario del Che en Bolivia – Guevara's diary of the guerrilla war in Bolivia -
 Obras Escogidas – Guevara's selected works in Spanish, including his most important speeches ( PDF)
Obras Escogidas – Guevara's selected works in Spanish, including his most important speeches ( PDF) -
 Pasajes de la Guerra Revolucionaria: Congo – Guevara's complete Congo Diary in Spanish, ( PDF)
Pasajes de la Guerra Revolucionaria: Congo – Guevara's complete Congo Diary in Spanish, ( PDF) -
 Pensamiento y acción – A selection of Guevara's writings in Spanish, including El socialismo y el hombre nuevo ( PDF)
Pensamiento y acción – A selection of Guevara's writings in Spanish, including El socialismo y el hombre nuevo ( PDF)


](../../images/29/2924.jpg)





