Costa Rica
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Central & South American Countries; Countries
| República de Costa Rica Republic of Costa Rica |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: ¡Vivan siempre el trabajo y la paz! | |||||
| Anthem: Noble patria, tu hermosa bandera | |||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
San José |
||||
| Official languages | Spanish | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Democratic Republic | ||||
| - President | Óscar Arias | ||||
| Independence | From Spain | ||||
| - Date | 15 September 1821 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 51,100 km² ( 129th) 19,725 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 0.7% | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - 2005 estimate | 4,327,000 ( 119th) | ||||
| - Density | 85/km² ( 107th) 220/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $45.14 billion ( 79th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $10,434 ( 63rd) | ||||
| HDI (2006) | 0.841 (high) ( 48th) | ||||
| Currency | Costa Rican colón ( CRC) |
||||
| Time zone | ( UTC-6) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .cr | ||||
| Calling code | +506 | ||||
Costa Rica, officially the Republic of Costa Rica (Spanish: Costa Rica or República de Costa Rica, IPA: [re'puβlika ðe 'kosta 'rika]), is a country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the south-southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, and the Caribbean Sea to the east. Costa Rica was the first country in the world to constitutionally abolish its army.
History
In Pre-Columbian times the Indigenous people, in what is now known as Costa Rica, were part of the Intermediate Area located between the Mesoamerican and Andean cultural regions. This has recently been updated to include the influence of the Isthmo-Colombian area in the South-Atlantic region of the country, defined by the presence of groups that spoke Chibchan languages. It is still unknown if any of these groups created the famous stone spheres of Costa Rica, between 200 BC and AD 1600. Costa Rica is also justly famous for its beautiful jade artifacts.
There is evidence of human habitation in Costa Rica as early as 10,000 BC in the southern Turrialba Valley. Ceramic artifacts have been dated to 1500 BC, although they are not abundant and are widely scattered. After 400 BC, there was a dramatic increase in population, trade, agricultural sophistication, and social complexity. Three distinct cultural zones also emerge around 400 BC: Guanacaste-Nicoya in the drier northwest, the Central Highlands Region, and Diquis in the southwest. The culture of Guanacaste-Nicoya is related to that of the Greater Nicoya Region extending into modern Nicaragua while Diquis was closely tied to the Greater Chiriqui Region in what is now Panama.
After 400 AD population centers divided into relatively small, rudimentary settlements accompanied by a gradual degradation of the quality of ceramics. Later artifacts point to a strong southern influence, as sculpture, house forms, and burial practices shift drastically to southern styles.
Conquest
The country was visited by Christopher Columbus in 1502, during his fourth expedition. He arrived at Cariay, in front of the Quiribrí island (present day Isla Uvita). The subsequent conquest and colonization of the area was complicated by its distance and the fierce indigenous resistance, however it paled in comparison to the Spanish conquest of Mexico.
During the 16th century, the area found itself with a quickly diminishing workforce. The indigenous population, slaves at the time, were falling ill to many of the diseases brought by the colonists, or dying in resistance battles. Also, the lack of abundant mineral resources and the fact that the richest soils were found deep in the heart of the country (the Central Valley), severely hindered the colonization effort. All these circumstances made Costa Rica, the southernmost province in the Captaincy General of Guatemala, the poorest and most irrelevant region. However, the colonists that braved the hard trip in the Central Valley had established a provincial capital Cartago.
Independence
In 1821, the winds of independence had blown in from the north. The United States of America and Mexico had won their independence recently and in the capital of the Captaincy General of Guatemala, Guatemala City, protests broke out demanding independence. On September 15th, 1821 they declared their independence from the Spanish Empire. At the time, several present-day Mexican states and most of the Central American countries belonged to the Captaincy, in order to send the news to all the states, a horse messenger was sent down through Central America.
Because Costa Rica was the southernmost province, it finally received the news of its independence on October 13th, 1821. The fact that not a single gunshot was fired to obtain its independence marked Costa Rica as a peace-loving nation. Among the independence documents received from Guatemala there was a document prepared in Nicaragua. This document is called "Los Nublados del Dia" which, in Spanish, means the "Clouds of the Day". In this document the Nicaraguan government, which was far more developed at the time and therefore closer to colonial rule, insisted that the states should not jump into independence and should wait for the "clouds of the day" to disperse before the states should make a final decision. However, because this document only reached Costa Rica, it had little effect.
After gaining independence, Costa Rica, along with the other provinces of the Captaincy, briefly joined the Mexican Empire of Agustín de Iturbide. But because of the distance to the Mexican capital and other underlying conflicts, the Central American states including Costa Rica became federal states of the United Provinces of Central America (see: History of Central America) from 1823 to 1839. In 1838 Costa Rica proclaimed itself a sovereign and independent nation, under the rule of Braulio Carrillo Colina.
In 1856 the Costa Rican army, commanded by Juan Rafael Mora Porras joined forces with the other Central American nations to expel a filibuster invasion, commanded by William Walker. In the battles of Santa Rosa, Rivas and the San Juan campaign, the filibuster army was deterred from invading Costa Rica. In the Battle of Rivas, Juan Santamaría bravely set the place where the invaders had taken refuge on fire and thus became Costa Rica's National Hero.
20th century
Costa Rica has avoided the violence that has plagued Central America; it is seen as an example of political stability in the region. Since the late 19th century, only two brief periods of violence have marred its democratic development.
In 1949, José Figueres Ferrer abolished the army; making Costa Rica the first country ever to operate within the democratic system without the assistance of a military (an example that was later followed by other nations such as Panama after the American invasion of 1989 to oust General Manuel Noriega).
Costa Rica (Spanish for "Rich Coast") was a largely agricultural country. However, during the last few decades, Costa Rica has achieved a relatively high standard of living. Electronics and Software Development are rapidly expanding industries, and along with tourism, serve as the major industries of the country thanks to its social stability and rich natural environment*.
Geography
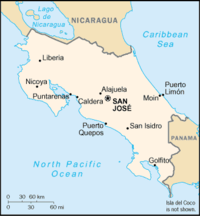
Costa Rica is located on the Central American isthmus, 10° North of the equator and 84° West of the Prime Meridian. It borders both the Caribbean Sea (to the east) and the North Pacific Ocean (to the west), with a total of 1,290 kilometres (802 mi) of coastline (212 km / 132 mi on the Caribbean coast and 1,016 km / 631 mi on the Pacific).
Costa Rica also borders Nicaragua to the north (309 km / 192 mi of border) and Panama to the south-southeast (639 km / 397 mi of border). In total, Costa Rica comprises 51,100 square kilometers (19,730 sq. mi) plus 589.000 square kilometers of territorial waters.
The highest point in the country is Cerro Chirripó, with 3,810 metres (12,500 ft), and is the fifth highest peak in Central America. The highest volcano in the country is the Irazú Volcano (3,431 m or 11,257 ft). The largest lake in Costa Rica is Lake Arenal.
Costa Rica also comprises several islands. Cocos Island stands out because of its distance from continental landmass (24 km² or 9.25 sq mi, 500 km or 310 mi from Puntarenas coast), but Calero Island is the biggest island of the country (151.6 km² or 58.5 sq mi).
Costa Rica protects over 25% of its national territory within national parks. It also possesses the greatest density of species in the world. *
Politics
Costa Rica is a democratic republic with more than 115 years of democracy and a strong constitution. It is seen as one of the most stable countries in Latin America. Costa Rica has avoided the violence that has plagued Central America; it is seen as an example of political stability in the region, and is referred to as the "Switzerland of the Americas" . Executive responsibilities are vested in a president, who is the country's centre of power. There also are two vice presidents and a cabinet designated by the president. The president, vice presidents, and 57 Legislative Assembly assembly delegates are elected for 4-year terms. A constitutional amendment approved in 1969 limited presidents and delegates to one term, although delegates were allowed to run again for an Assembly seat after sitting out a term. In April 2003 the constitutional ban on presidential re-election was reversed, allowing Óscar Arias (Nobel Peace Prize, 1987) to run for President for a second term. In 2006 Óscar Arias was re-elected in tight elections, running on a platform of promoting free trade.
Governors appointed by the president head the country's seven provinces, but they exercise little power. There are no provincial legislatures. Autonomous state agencies enjoy considerable operational independence; they include the telecommunications and electrical power monopoly, the nationalized commercial banks, the state insurance monopoly, and the social security agency. Costa Rica has no military by constitution but maintains domestic Police and armed National Guard forces for internal security. See also: Military of Costa Rica
Famous Costa Ricans
- Óscar Arias Sánchez, Nobel Peace Prize winner (1987) and President of the Republic (1986–1990, 2006-current).
- José Figueres Ferrer, National caudillo and President of the Republic (1948–1949, 1953–1958, and 1970–1974).
- Rafael Ángel Calderón Guardia, politician and social reformer. President of the Republic (1940–1944).
- Franklin Chang-Díaz, Astronaut.
- Clodomiro Picado Twight, Toxicologist.
- Claudia Poll Olympic gold medalist.
- Juan Santamaría The official National Hero.
Administrative divisions
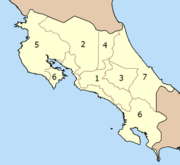
Costa Rica is divided into 7 provinces:
- San José (Capital) (political, technological and economical centre of Costa Rica)
- Alajuela (central; north of capital San José, agriculture and industrial manufacturing)
- Cartago (former Costa Rican Provincial capital during colonial times)
- Heredia (central; north of capital, industrial manufacturing)
- Guanacaste (north-west, important touristic and agricultural area)
- Puntarenas (along most of the Pacific coast, with a large bulge in the south-west and a smaller one at the northern end at both sides of the Golfo de Nicoya, where the eponymous capital is located)
- Limón (Caribbean coast, agricultural and eco-tourism area)
Economy
Historically, Costa Rica's economy has been based on agriculture, including the production of coffee, bananas, pineapples, and ornamentals, but in recent times ecotourism, electronics, pharmaceuticals, financial outsourcing and software development have become the prime industries. Costa Rica's location in the Central American isthmus provides easy access to American markets as it has the same time zone as the central part of the United States and direct ocean access to Europe and Asia.
The economy has been expanding for Costa Rica in part because the Government had implemented a seven year plan of expansion in the high tech industry. The central government offers tax exemptions for those who are willing to invest in the country. High levels of education among its residents make the country an attractive investing location. Several global high tech corporations have already started developing in the area exporting goods including chip manufacturer Intel and pharmaceutical company Glaxo Smith Kline and consumer products company Procter & Gamble. Trade with South East Asia and Russia has boomed during 2004 and 2005, and the country is expected to obtain full Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Forum (APEC) membership by 2007 (the country became an observer in 2004).
For the fiscal year 2005 the country showed a government deficit of 2.1%, internal revenue increased an 18%, exports increased a 12.8% and the number of visiting tourists increased a 19%, reaching 1.5 million people. Revised economic figures released by the Central Bank indicate that economic growth stood at 5 %, nevertheless the country faced high inflation (14%) and a trade deficit of 5.2%. For 2006 the economy is expected to grow a 6.8%
The unit of currency is the colón ( CRC), which trades around 500 to the U.S. dollar; currently about 600 to the euro. For 2007 a new currency exchange system will allow the value of the CRC colón to float between two bands as done previously by Chile. The idea is that by doing so the Central Bank will be able to better tackle inflation and discourage the use of US dollars.
Foreign affairs
Costa Rica is an active member of the United Nations, the Organization of the American States and many international organizations related to human rights and democracy.
Costa Rica's main foreign policy objective is to foster human rights and sustainable development as a way to secure stability and growth.
Costa Rica is also a member of the International Criminal Court, without a Bilateral Immunity Agreement of protection for the US-military (as covered under Article 98)
Flora and fauna
Costa Rica is home to a rich variety of plants and animals. While the country has only about 0.1% of the world's land mass, it contains 5% of the world's biodiversity. Over 25% of Costa Rica is composed of protected forests and reserves.
One national park that is internationally renowned among ecologists for its biodiversity (including big cats and tapirs) and where visitors can expect to see an abundance of wildlife is the Corcovado National Park.
Tortuguero National Park (the name Tortuguero can be translated as turtle catcher or turtle hunter, it is also understood as full of turtles) is home to spider, howler and white-throated Capuchin monkeys, the three-toed sloth, 320 species of birds (including eight species of parrots), a variety of reptiles, but is mostly recognized for the annual nesting of the endangered green turtle and is considered the most important nesting site for this species. Giant leatherback, hawksbill, and loggerhead turtles also nest here.
The Monteverde Cloud Forest Reserve hosts 2,000 plant species including numerous orchids. Over 400 types of birds can be found here, as well as over 100 species of mammals. Costa Rica as a whole has over 800 species of birds. The entity entrusted to do genetic and biochemical prospection on Costa Rica's biological wealth is the INBIO (Instituto Nacional de Biodiversidad), and it is allowed to collect royalties on any biological discoveries of medical importance.
Also see:
- Wildlife of Costa Rica
- List of birds of Costa Rica
- Instituto Nacional de Biodiversidad
Demographics
In 2005, Costa Rica had an estimated population of 4,016,173 persons. The majority of people in Costa Rica are descended from Spanish settlers and Amerindian peoples. In contrast to most neighboring Central American nations, the Spanish component is rather strong in Costa Ricans at approx. 80%, while the indigenous component oscilates at approx. 20% (similar to Chileans). Most Costa Ricans are either primarily Spanish or of mixed heritage (Mestizo). In addition, there are significant numbers of Costa Ricans of Italian, German, Jewish, and Polish descent. Together, Mestizos and European descendants make up a full 94% of the population. Just under 3% of the population is of black African descent who are called Afro-Costa Ricans and are of English-speaking descendants of 19th century black Jamaican immigrant workers. Another 1% is composed of ethnic Chinese.
As of today, the indigenous population numbers around 1.7%, or around 50000 individuals. In Guanacaste Province, a significant portion of the population descends from a mix of local Amerindians, Africans and Spaniards. There is also a expatriate community of American and Canadian retirees.
Christianity is a major religion in Costa Rica. Some 92% of Costa Ricans are Christian . Like many other parts of Latin America, Protestant denominations have been enjoying rapid growth. However 3 in 4 Costa Ricans still adhere to Roman Catholicism. Due to small but recent immigration from Asia, the Middle East, and other places, new religions have sprung up. The most popular being Buddhism (due to a growing Chinese community of 40,000), with even smaller numbers of Jewish, Muslim, and Hindu adherents.
Culture
The locals refer to themselves as tico or tica (female). "Tico" comes from the locally popular usage of "tico" diminutive suffixes (e.g., 'momentico' instead of 'momentito'). The tico ideal is that of a very friendly, helpful, laid back, unhurried, educated and environmentally aware people. Visitors from the United States are often referred to as gringos, which is virtually always congenial in nature. The phrase "Pura Vida" (literally pure life) is a motto ubiquitous in Costa Rica. It encapsulates the pervading ideology of living in peace in a calm, unflustered manner, appreciating a life surrounded by nature and family and friends.
Some folk might use maje or mae (, actually maje means "dumb") to refer to each other although this might be slightly insulting to older folk.
Costa Rican traditions and culture tend to retain a strong degree of Spanish influence. Their spoken accent is rather different than its Central American counterparts.normally -ito or ita is added to many words to sound more polite and courteous. Costa Rica boasts a varied history. Costa Rica was the point where the Mesoamerican and South American native cultures met. The northwest of the country, Nicoya, was the southernmost point of Nahuatl cultural influence when the Spanish conquerors ( conquistadores) came in the 16th century. The centre and southern portions of the country had Chibcha influences. However, the indigenous people have influenced modern Costa Rican culture to a relatively small degree, as most of the Indians died from disease and mistreatment by the Spaniards. The Atlantic coast, meanwhile, was populated with African slaves in the 17th and 18th centuries, although most Caribbean Costa Ricans of African ascent descend from Jamaican workers brought in during the 19th century to work in the construction of railways connecting the urban populations of the Central Plateau to the port of Limon on the Caribbean coast. During the 19th century Chinese and Italian immigrants came to the country to work on the construction of the railroad system as well.