South Korea
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Asian Countries; Countries
| 대한민국 大韓民國 Daehan Minguk Republic of Korea |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: 널리 인간을 이롭게 하라 弘益人間 "Broadly bring benefit to humanity"
|
|||||
| Anthem: Aegukga | |||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Seoul |
||||
| Official languages | Korean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Republic | ||||
| - President | Roh Moo-hyun | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Han Myung-sook | ||||
| Establishment | |||||
| - Gojoseon | October 3, 2333 BCEa | ||||
| - Republic declared | March 1, 1919 ( de jure) | ||||
| - Liberation | August 15, 1945 | ||||
| - First Republic | August 15, 1948 | ||||
| - [ Nations Recognition] | December 12, 1948 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 99,646 km² ( 108th) 38,492 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 0.3 | ||||
| Population | |||||
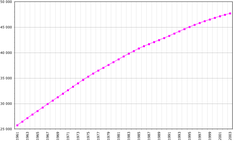
| - July 2006 estimate | 48,846,823 ( 25th) | ||||
| - Density | 480/km² ( 19th) 1,274/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $994.4 billion ( 14th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $20,590 ( 33rd) | ||||
| HDI (2004) | 0.912 (high) ( 26th) | ||||
| Currency | South Korean won ( KRW) |
||||
| Time zone | Korea Standard Time ( UTC+9) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | not observed ( UTC+9) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .kr | ||||
| Calling code | +82 | ||||
| a Legendary. | |||||
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea ( Korean: 대한민국, IPA: [tɛ.ɦan.min.guk̚], listen ), is an East Asian state on the southern half of the Korean Peninsula. To the north, it is bordered by North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea), with which it was a single country called Korea until 1945. To the west, across the Yellow Sea, lies China, and to the southeast, across the Korea Strait, lies Japan. Approximately one-half of South Korea's population lives in or near the capital and largest city, Seoul, the second largest metropolitan area in the world.
Since its founding in 1948, the country has struggled with the aftermath of 35 years of Japanese annexation, the Korean War, and decades of military rule, seeing five major constitutional changes. Pro-democracy demonstrations during the 1980s led to free elections in 1987. South Korea is now a multi-party democracy.
The South Korean economy has advanced rapidly since the 1950s and is now the 10th largest (nominal value) economy in the world. South Korea is also one of the world's most technologically advanced and digitally-connected countries. It has the second highest broadband Internet connections per capita among OECD countries and is a global leader in electronics, digital displays, shipbuilding and mobile phones.
South Korea's entertainment industry has grown explosively since the 1990s, producing Asia-wide successes in music, television, and film in a phenomenon known as Hallyu, or the "Korean wave." However, the country still retains centuries-old customs and traditions, such as its unique cuisine and ancestor worship.
Names
In the Korean language, South Korea is called Daehan Min-guk ( 대한민국 listen , 大韓民國, literally "Great People's Nation"), or Hanguk for short (한국, "Han Nation," usually referring to Korea as a whole) or Namhan (남한, "South Han", referring to South Korea specifically). North Koreans refer to the South as Namjosŏn (남조선, "South Chosŏn").
The name Han dates back to the ancient Samhan Confederacies of the Proto-Three Kingdoms era of Korea.
In English, the nation is often referred to simply as "Korea", a corruption of the name of the Goryeo Dynasty (sometimes spelled Koryo), which in turn derived its name from the more ancient Kingdom of Goguryeo.
History
At the end of World War II, American and Soviet troops had occupied the southern and northern halves of Korea, respectively, dividing the peninsula at the 38th parallel. Despite promises of an independent and unified Korea in the 1943 Cairo Declaration, the United States and Soviet Union helped establish two separate governments in 1948; the communist North and the capitalist South.
On June 25, 1950, the North invaded the South, beginning a civil war that caused the deaths of more than 4 million civilians and soldiers alike, now referred to as the Korean War. The United Nations backed South Korea and the Soviet Union and China backed North Korea. The war eventually reached a stalemate. The 1953 armistice split the peninsula along the demilitarised zone at about the original demarcation line. No peace treaty was ever signed, however, and therefore the two countries are technically still at war.
In 1960, a student uprising overthrew the autocratic government of Syngman Rhee and South Korea saw a brief period of democratic reforms. However, General Park Chung-hee led a military coup (the "5.16 Revolution") against the weak government the following year. Park took over as president from 1961 until his assassination in 1979, overseeing rapid export-led economic growth as well as severe political repression.
In 1980, General Chun Doo-hwan launched a coup d'etat against a short-lived civilian administration to assume the presidency. Chun's seizure of power was greeted by widespread protests, culminating in the 1980 Gwangju Massacre. The movement for democracy gained strength in its aftermath, ultimately forcing Chun to allow free elections and a change to civilian democratic rule in 1988. That year, Seoul hosted the 1988 Summer Olympics.
In 1996, South Korea became a member of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development. Despite a severe setback caused by the Asian financial crisis in 1997, the country soon emerged as a major economic power. In 2004, South Korea joined the "trillion dollar club" of world economies and, today, its standard of living is equal to that of many countries in Western Europe.
In June 2000, as a part of South Korean president Kim Dae Jung's Sunshine Policy of engagement, a historic first North-South summit took place in North Korea's capital Pyongyang. That year, Kim won the Nobel Peace Prize for his work for democracy and human rights and efforts at reconciliation between the two Koreas. Since then, trade and investment between the two Koreas have increased dramatically as a result of regular contacts in relations and economic ties.
Government and politics
South Korea is a liberal democracy based on a presidential republican system with powers shared between the president, legislature, and judiciary. Since 1948, the constitution has undergone five major revisions, with each signifying a new Republic. The current Sixth Republic began with the last major constitutional revision in 1988.
The head of state and head of government is the President, who is elected by direct popular vote for a single five-year term. In addition to being the commander-in-chief of the armed forces, the president also has considerable executive powers. The president appoints the Prime Minister with the approval of the National Assembly, as well as appointing and presiding over the State Council of chief ministers.
The South Korean legislature is the National Assembly, unicameral body in which members serve a four-year term of office. This legislature currently has 299 seats, of which 243 are elected by regional vote. The remainder are distributed by proportional representation.
The South Korean judiciary is largely independent of the other two branches. The highest judiciary body is the Supreme Court, whose justices are appointed by the president with the consent of the National Assembly. In addition, the independent Constitutional Court oversees questions of constitutionality.
Several changes have been unsuccessfully attempted, including a direct vote for all seats of the National Assembly, coordination of legislative and presidential election periods, a semi-presidential system, and a shortening of the presidential term.
The main political parties in South Korea as of 2006 are the Uri Party, the Grand National Party (GNP), the Democratic Labor Party (DLP), and the Democratic Party (DP). The Uri Party was formed in late 2003 from a liberal faction of the DP (then the Millennium Democratic Party). It gained a slim majority in the National Assembly after the April 2004 legislative elections, but lost it in subsequent by-elections. The conservative GNP and centrist DP form the dominant political opposition. The progressive DLP is aligned with labour unions and farmers' groups, and constitutes the left-wing opposition.
Geography and climate
South Korea occupies the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula, which extends some 680 miles (1,100 km) from the Asian mainland. This mountainous peninsula is flanked by the Yellow Sea to the west, and the Sea of Japan to the east. Its southern tip lies on the Korea Strait and the East China Sea. The country's total area is 38,462.49 square miles or 99,617.38 square kilometres.
South Korea's land is mountainous, and most of it is not arable. Lowlands, located primarily in the west and southeast, constitute only 30% of the total land area. South Korea can be divided into four general regions: an eastern region of high mountain ranges and narrow coastal plains; a western region of broad coastal plains, river basins, and rolling hills; a southwestern region of mountains and valleys and a southeastern region dominated by the broad basin of the Nakdong River.
About three thousand islands, mostly small and uninhabited, lie off the western and southern coasts. Jeju Island is located about 100 kilometres (about 60 mi) off the southern coast of South Korea. It is the country's largest island, with an area of 1,845 square kilometres (712 sq mi). Jeju is also the site of South Korea's highest point: Halla-san, an extinct volcano on Jeju, reaches 1,950 metres (6,398 ft) above sea level.
The local climate is relatively temperate, with precipitation heavier in summer during a short rainy season called jangma, and winters that can be bitterly cold. In Seoul the average January temperature range is -7° C to 1°C (19° F to 33°F), and the average July temperature range is 22°C to 29°C (71°F to 83°F). Winter temperatures are higher along the southern coast and considerably lower in the mountainous interior. Rainfall is concentrated in the summer months of June through September. The southern coast is subject to late summer typhoons that bring strong winds and heavy rains. The average annual precipitation varies from 1,370 millimetres (54 in) in Seoul to 1,470 millimetres (58 in) in Busan.
Administrative divisions
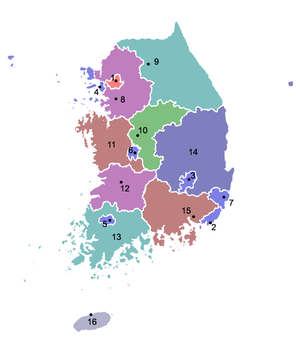
South Korea is divided into eight provinces, one special self-governing province, six metropolitan cities, and one special city. The names below are given in English, Hangul, and Hanja.
| Namea | Hangul | Hanja | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Special cities (Teukbyeolsi a) | |||
| 1 | Seoul | 서울특별시 | 서울特別市 |
| Metropolitan cities (Gwangyeoksi a) | |||
| 2 | Busan | 부산광역시 | 釜山廣域市 |
| 3 | Daegu | 대구광역시 | 大邱廣域市 |
| 4 | Incheon | 인천광역시 | 仁川廣域市 |
| 5 | Gwangju | 광주광역시 | 光州廣域市 |
| 6 | Daejeon | 대전광역시 | 大田廣域市 |
| 7 | Ulsan | 울산광역시 | 蔚山廣域市 |
| Provinces | |||
| 8 | Gyeonggi-do | 경기도 | 京畿道 |
| 9 | Gangwon-do | 강원도 | 江原道 |
| 10 | Chungcheongbuk-do | 충청북도 | 忠淸北道 |
| 11 | Chungcheongnam-do | 충청남도 | 忠淸南道 |
| 12 | Jeollabuk-do | 전라북도 | 全羅北道 |
| 13 | Jeollanam-do | 전라남도 | 全羅南道 |
| 14 | Gyeongsangbuk-do | 경상북도 | 慶尙北道 |
| 15 | Gyeongsangnam-do | 경상남도 | 慶尙南道 |
| Special self-governing province (Teukbyeoljachi-do a) | |||
| 16 | Jeju | 제주특별자치도 | 濟州特別自治道 |
a Revised Romanization.
b See also Special cities of Korea and Provinces of Korea.
Economy
South Korea has the tenth largest economy in the world (fourteenth largest by purchasing power parity), and the third largest in Asia, behind only Japan and China (fourth behind China, Japan, and India by purchasing power parity). As one of the East Asian Tigers, it achieved rapid economic growth through exports of manufactured goods. This is in sharp contrast to the stagnation of North Korea's economy, which has turned for the worse since the disintegration of the Soviet Union. South Korea's per capita GDP is now roughly 12 times that of North Korea.
In the 1950s, South Korea was one of the poorest countries in Asia. At the end of World War II, the country inherited a colonial economic system designed solely for Japan's exploitative needs. Much of the country's infrastructure was destroyed during the Korean War that followed in 1950-1953. After the war, South Korea became heavily dependent on U.S. aid.
Following the military coup led by general Park Chung-hee in 1962, South Korea embarked on a series of ambitious five-year plans for economic development. Emphasis shifted to foreign trade with the normalization of relations with Japan in 1965 and a subsequent boom in trade and investment. Rapid expansion, first into light and then heavy industries, in the 1960s and 1970s followed. During this period, the South Korean economy grew at an average annual rate of 8.6%.
This phenomenal growth is often called the " Miracle on the Han River", the Han River being the main river that runs through the nation's capital and largest city, Seoul. In the 1980s and 1990s, growth continued as South Korea transformed itself from an exporter of mostly textiles and shoes into a major global producer of automobiles, electronics, shipbuilding, and steel and later, high-technology fields such as digital monitors, mobile phones, and semiconductors.
The South Korean model of encouraging the growth of large, internationally competitive companies through easy financing and tax incentives led to the dominance of the family-controlled conglomerates. These companies, known as chaebol, flourished under the support of the Park regime. Some such as Hyundai, Samsung and LG became global corporations. In 2004, through all of this combined, South Korea joined in the trillion dollar club of world economies.
Since the Asian financial crisis of 1997, however, the corporate landscape has changed considerably as a result of massive bankruptcies and government reforms. The crisis exposed longstanding weaknesses in South Korea's economy, including high debt/equity ratios, massive foreign borrowing, and an undisciplined financial sector. This led to two rounds of financial and industrial restructuring, in 1997 and again following the collapse of Daewoo in 1999. Daewoo's collapse has been recorded as one of the world's largest bankruptcies in history. By 2003, just over one-half of the 30 largest chaebol from 1995 remained.
Between 2003 and 2005, economic growth has moderated to about 4% per year. A downturn in consumer spending, attributed to massive personal credit card debt, was offset by rapid export growth especially to China. In 2005, the government proposed labor reform legislation and a corporate pension scheme to help make the labor market more flexible, and new real estate policies to cool property speculation.
Moderate inflation, low unemployment, an export surplus, and fairly equal distribution of income characterize this economy.
Transportation
Transportation in South Korea is provided by extensive networks of railways, highways, bus routes, ferry services, and air routes that criss-cross the country.
Korail provides frequent service to all major South Korean cities. Two rail lines to North Korea are now being reconnected. The Korean high-speed railway system is known as Korea Train Express (KTX).
Major cities have subway systems, including the popular Seoul Metropolitan Subway. Virtually all towns in South Korea are served by regional bus service.
Highways in South Korea are classified into freeways (expressways/motorways), national highways, and various classifications below the national level. Korea Highway Corporation operates the toll highways and service amenities en route.
The main international airport is Incheon International Airport. South Korea's national air carriers are Korean Air and Asiana Airlines.
Demographics
Most South Koreans live in urban areas, due to rapid migration from the countryside during the country's rapid economic expansion in the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s. The capital city of Seoul is also the country's largest city and chief industrial centre. It had 10.3 million inhabitants in 2006, making Seoul one of the most populated single cities in the world. Other major cities include Busan (3.65 million), Incheon (2.63 million), Daegu (2.53 million), Daejeon (1.46 million), Gwangju (1.41 million) and Ulsan (1.10 million).
The population has also been shaped by international migration. Following the division of the Korean peninsula after World War II, about four million people from North Korea crossed the border to South Korea. This trend of net entry reversed over the next forty years due to emigration, especially to the United States and Canada. However, South Korea's burgeoning economy and improved political climate in the early and mid-1990s slowed the high emigration rates typical of the previous decade. Many of those who left the country chose to return.
Although small, the percentage of non-Koreans in South Korea has risen rapidly in the early twenty-first century. Officially, as of April 2005, the total number of known foreign labourers in South Korea stood at 378,000, 52% of whom were in the country without authorization. This foreign workforce mainly comes from South Asian and Southeast Asian nations. There are also many workers from the former Soviet Union countries and Nigeria. In addition to these workers, there are about 11,000 expat English teachers and around 31,000 US military personnel.
As of 2005, approximately 25 million or 46.5% of the South Korean population express no religious preference. Of the remainder, 13.7 million are Christian, 10.7 million are Buddhist, and small numbers belong to various minor religions including Jeungsando and Wonbuddhism. The largest Christian church in the world, Yoido Full Gospel Church, is located in Seoul and has approximately 780,000 members (2003 estimate). Including Yoido Full Gospel, 11 of the world's 12 largest churches are located in Seoul (see Korean Christianity). South Korea is also the second largest missionary sending nation on earth, after the U.S.
Foreign relations and the military
In its foreign relations, South Korea is primarily concerned with North Korea and the neighboring countries of China, Japan, and Russia, as well as its main ally, the United States. The US was the primary driver in the establishment and initial sustenance of the South Korean government before the Korean War of 1950-1953; however, since the 1990s the two nations have often been at odds with regard to their policies towards North Korea.
South Korea and China established formal diplomatic relations on August 24, 1992, despite previous hostility dating back to the Korean War.
The South Korea government declared all problems of the Japanese colonization of Korea to have been solved by the National agreement in 1965. However South Korea's relations with Japan continue to be turbulent due to a number of unsettled Korean-Japanese disputes, many of which stemmed from the period of Japanese occupation. During World War II, more than 100,000 Koreans civilians served in the Japanese army as officers and soldiers. However, longstanding issues such as Japanese war atrocities against Korean civilians, the visits by Japanese politicians to the Yasukuni Shrine honoring convicted war criminals, the re-writing of Japanese textbooks to justify Japanese aggression during WWII, and the territorial disputes over the islands of Dokdo (known as "Takeshima" in Japanese) continue to trouble Korean-Japanese relations. In response to then- Prime Minister Junichiro Koizumi's repeated visits to the Yasukuni shrine, the President of South Korea Roh Moo-hyun suspended all summit talks between South Korea and Japan.
Both North and South Korea continue to officially claim sovereignty over the entire peninsula. Despite longstanding animosity following the Korean War in 1950 (which has still not officially ended), the South and North have in recent times sought to establish a more conciliatory relationship. Events such as family reunifications and the Olympic Games, where the two Koreas entered the opening ceremonies together but still competed as separate teams, promised a gradual thaw in the North-South relationship (see Sunshine policy). However, the progress has been complicated by North Korean missile tests in 1993, 1998 and 2006.
In addition, South Korea maintains diplomatic relations with approximately 170 countries. The country has also been a member of the United Nations since 1991, when it joined at the same time as North Korea. On January 1, 2007, South Korean Foreign Minister Ban Ki-Moon will assume the post of UN Secretary General. It has also developed links with ASEAN as both a member of "ASEAN Plus three" and the East Asia Summit (EAS).
The South Korean military is composed of the Republic of Korea Army (ROKA), Republic of Korea Navy (ROKN), Republic of Korea Air Force (ROKAF), and Republic of Korea Marine Corps (ROKMC), together with reserve forces. Many of these forces are concentrated near the border with North Korea. All South Korean males are constitutionally required to serve in the military, typically for a period of twenty-four months.
From time to time, South Korea has sent its troops overseas to assist American forces. South Korea dispatched 320,000 troops to fight alongside American soldiers in the Vietnam War. Most recently, South Korea sent 3,300 troops in the form of the Zaytun Division to assist with reconstruction efforts in northern Iraq, the largest contributor after the U.S. and Britain.
The United States has stationed a substantial contingent of troops in the ROK since the Korean War. The American Troops are stationed in bases, of which most are camps. They are considered camps not for their lack of buildings or support structure; but, in order to represent a lack of permanence for the ROK Government. (See List of United States Army installations in South Korea and USFK for more information on these military bases.)
Sports
Taekwondo, a popular martial art, originated in Korea. Taekwondo means the way of the foot, the way of the fist, and the way of life. It became standard military training in South Korea, and in 1961 the rules were standardized and taekwondo became an official Olympic sport in 2000. Taekwondo in the military is a integral part in the Korean land forces.Other Korean martial arts include hapkido and taekkyeon.
Baseball was first introduced to Korea in 1905 by an American missionary named Phillip Gillette and has since become the most popular spectator sport in South Korea. The first South Korean professional sports league was the Korea Baseball Association, established in 1982. During the 2006 World Baseball Classic, South Korea reached the final four before losing to Japan. Prior to that final match, the South Korean team was the only undefeated team, and had beaten Japan twice and the United States once.
Other popular sports in South Korea include basketball, football, golf, tennis, and ice hockey. Women's golf is especially strong, with over thirty South Koreans playing on the world's leading women's tour, the U.S. LPGA Tour, including stars such as future Hall of Famer Se Ri Pak. Rising star Michelle Wie is also of Korean heritage, with both parents from South Korea. South Korea's Olympic teams have also traditionally performed strongly in archery, boxing, judo, short track speed skating, taekwondo, and wrestling.
In 1988, South Korea hosted the Summer Olympics in Seoul. There is an ongoing campaign to have a future Winter Olympics held in Pyeongchang County. South Korea has hosted the Asian Games on numerous occasions.
The 2002 FIFA World Cup was jointly hosted by South Korea and Japan, and South Korea became the first Asian team to reach the semi-finals. During the 2006 Winter Olympics in Turin the South Korean short track team dominated their event, taking home six of the eight gold medals available as well as three silvers and one bronze. Skaters Ahn Hyun Soo and Jin Sun-Yu were the second and third persons in the Games to win three gold medals.
The Korea Republic national football team, also known as the " Taeguk Warriors", qualified for the 2006 FIFA World Cup in Germany for their sixth consecutive World Cup.
South Korea is also the cradle of the e-sports (electronic sports) world. Home to KesPA, e-sports has become popular in Korea with two broadcasting stations broadcasting live matches on television. South Korea has been regarded the birthplace of e-sports and also the future of e-sports. The Koreans are widely known for their e-sports, and especially in the WCG, World Cyber Games, where in the RTS game, Starcraft, no non-Korean has ever won.