Washington, D.C.
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: North American Geography
| Washington, D.C. | |||||
|
|||||
| Nickname: "DC", "The District" | |||||
| Motto: Justitia Omnibus (Justice for All) | |||||
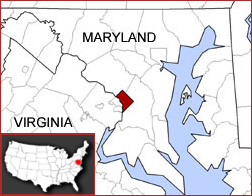
| Location of Washington, D.C., in relation to the states Maryland and Virginia. | |||||
| Coordinates: | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal District | District of Columbia | ||||
| Mayor | Anthony A. Williams (D) | ||||
| City Council | Chairperson: Linda W. Cropp ( D) Ward 1: Jim Graham ( D) |
||||
| Area | |||||
| - City | 177.0 km² (68.3 sq mi) | ||||
| - Land | 159.0 km² (61.4 sq mi) | ||||
| - Water | 18.0 km² (6.9 sq mi) | ||||
| Elevation | 0-410 ft / 0-125 m | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - City (2005) | 582,049 | ||||
| - Density | 3,481/km² (9,015/sq mi) | ||||
| - Urban | 5,214,666 | ||||
| - Metro | 8,026,807 | ||||
| Time zone | EST ( UTC-5) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | EDT ( UTC-4) | ||||
| Website: http://www.dc.gov/ | |||||
Washington, D.C., is the capital city of the United States of America. "D.C." is an abbreviation for the District of Columbia, the federal district coextensive with the city of Washington. The city is named after George Washington, military leader of the American Revolution and the first President of the United States.
The District of Columbia and the city of Washington are coextensive and are governed by a single municipal government, so for most practical purposes they are considered to be the same entity, though this was not always the case. As late as 1871, when Georgetown ceased to be a separate city, there were multiple jurisdictions within the District. Although there is a municipal government and a mayor, Congress has the supreme authority over the city and district, which results in citizens having a different status and less representation in government than residents of the states.
The centers of all three branches of the U.S. federal government are in the District as well as the headquarters of most independent agencies. It serves as the headquarters for the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, and the Organization of American States, and other national and international institutions. Washington is the frequent location of large political demonstrations and protests, particularly on the National Mall. Washington is the site of numerous national landmarks, monuments, and museums, and is a popular destination for tourists.
It is commonly known as D.C., The District, or simply Washington. Historically, it was called the Federal City or Washington City. It is easily confused with the state of Washington, located in the Pacific Northwest — to avoid this, the capital city is often called simply D.C., and the state referred to as "Washington State." The population of the District of Columbia, as of 2005 U.S. Census Bureau estimates, is 582,049 persons. The Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area surpasses 8 million persons. If Washington, D.C. were a state, it would rank last in area behind Rhode Island, 50th in population ahead of Wyoming, first in population density ahead of New Jersey, and 35th in Gross State Product.
History
The District of Columbia, founded on July 16, 1790, is a federal district as specified by the United States Constitution. The U.S. Congress has ultimate authority over the District of Columbia, though it has delegated limited local rule to the municipal government. The land forming the original District came from the states of Maryland and Virginia. However, the area south of the Potomac River (39 square miles or about 100 km²) was returned, or " retroceded", to Virginia in 1847 and now is incorporated into Arlington County and the City of Alexandria. After 1847, the remaining land that formed the area now known as the District of Columbia was formed exclusively from land that once belonged to Maryland.
Planning
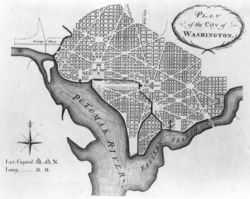
A Southern site for the new country's capital was agreed upon at a dinner between James Madison and Alexander Hamilton, hosted by Thomas Jefferson. The city was designed by Pierre Charles L'Enfant, a Major in the United States Army. The initial plan for the "Federal District" was a diamond, measuring 10 miles (16 km) on each side, totaling 100 square miles (256 km²). The actual site on the Potomac River was chosen by President Washington. Washington may have chosen the site for its natural scenery, believing the Potomac would become a great navigable waterway. The city was officially named "Washington" on September 9, 1791. Out of modesty, George Washington never referred to it as such, preferring to call it "the Federal City." Despite choosing the site and living nearby at Mount Vernon, he rarely visited the city. The federal district was named the District of Columbia because Columbia was a poetic name for the United States used at the time.
Initially, the District of Columbia included four distinct sections, of which the city of Washington was only one. The others were Alexandria County, Georgetown, and the County of Washington. Georgetown occupied its current boundaries. Alexandria County included parts of the present-day City of Alexandria, as well as the current Arlington County, Virginia. Washington City occupied much of its current area but ended at present-day Rock Creek Park on the west and Florida Avenue and Benning Road on the north. Florida Avenue was then called "Boundary Street." The remainder of the district was Washington County.
In 1791–92, Andrew Ellicott and the free African-American Benjamin Banneker surveyed the border of the District with both Maryland and Virginia, placing boundary stones at every mile point; many of these still stand.
The cornerstone of the White House, the first newly constructed building of the new capital, was laid on October 13, 1792. That was the day after the first solemn celebrations of Columbus Day, marking its 300th anniversary.
19th century
On August 24, 1814, British forces burned the capital during the most notable raid of the War of 1812 in retaliation for the sacking and burning of York (modern-day Toronto) during the winter months, which had left many Canadians homeless. President James Madison and U.S. forces fled before the British forces arrived and burned public buildings, including the Capitol and the Treasury building. The White House was burned and gutted. The Navy Yard was also burned—by American sailors. The home of the Commandant of the Marine Corps, located at the Marine Barracks, was one of the few government buildings not burned by the raiding British soldiers out of a sign of respect and is now the oldest public building in continuous use in the nation's capital. Civilians were not directly targeted and, initially, the British had approached the city hoping to secure a truce. However, they were fired upon, triggering frustration and anger among the British, which ultimately led to the sacking of government buildings.
During the 1830s the District was home to one of the largest slave trading operations in the country (see Alexandria, Virginia).
In 1846, the populace of Alexandria County, who resented the loss of business with the competing port of Georgetown and feared greater impact if slavery were outlawed in the capital, voted in a referendum to ask Congress to retrocede Alexandria back to the state of Virginia. Congress agreed to do so on July 9 of that year.
Washington remained a small city—the 1860 Census put the population at just over 75,000 persons—until the outbreak of the Civil War in 1861. The significant expansion of the federal government to administer the war and its legacies such as veterans' pensions led to notable growth in the city's population. By 1870, the District population had grown to nearly 132,000.
In July 1864, Confederate forces under Jubal Anderson Early made a brief raid into Washington, culminating in the Battle of Fort Stevens. The Confederates were repulsed, and Early eventually returned to the Shenandoah Valley. The fort is located near present day Walter Reed Army Medical Centre in northwest Washington. The battle was the only battle where a U.S. president, Abraham Lincoln, was present and under enemy fire while in office.
In the early 1870s, Washington was given a territorial government, but Governor Alexander Robey Shepherd's reputation for extravagance resulted in Congress abolishing his office in favour of direct rule. Congressional governance of the District would continue for a century.
In 1878, Congress passed an Organic Act that made the boundaries of the city of Washington coterminous with those of the District of Columbia. This effectively eliminated Washington County; Georgetown, technically made a part of the city, was allowed to remain nominally separate until 1895 when it was formally combined with Washington.
The Washington Monument opened in 1888. Plans were laid to further develop the monumental aspects of the city, with work contributed by such noted figures as Frederick Law Olmsted and Daniel Burnham. However, development of the Lincoln Memorial and other structures on the National Mall did not begin until the early 20th century.
20th century
The District's population peaked in 1950, when the census for that year recorded a record population of 802,178 people. At the time, the city was the ninth-largest in the country, ahead of Boston and behind St. Louis. The population declined in the following decades, mirroring the suburban emigration of many of the nation's older urban centers following World War II.
The Twenty-third Amendment to the United States Constitution was ratified on March 29, 1961, allowing residents of Washington, D.C. to vote for president and have their votes count in the Electoral College as long as Washington, D.C. does not have more electoral votes than the least populous state.
After the assassination of civil rights activist Martin Luther King, Jr., in Memphis, Tennessee, on April 4, 1968, riots broke out in some sections of the city. The violence raged for four days, and buildings were burned. At one point, the rioters came within two blocks of the White House. President Lyndon Johnson ordered over 13,000 federal troops to occupy the city--the largest occupation of an American city since the Civil War. It took years for the city to recover.
One of the most important developments in bringing people back downtown was the building of the subway system. The first 4.6 miles (7.4 km) of the Washington Metro subway system opened on March 27, 1976.
In 1973, Congress enacted the District of Columbia Self-Rule and Governmental Reorganization Act, providing for an elected mayor and city council for the District. As a result, Walter Washington became the first elected mayor of the District in 1975. Marion Barry became mayor in 1979, but was arrested for drug use in an FBI sting operation on January 18, 1990, and served a six-month jail term. His successor, Sharon Pratt Kelly, became the first black woman to lead a city of that size and importance in the U.S. Barry, however, defeated her in the 1994 primary and was once again elected mayor for his fourth term, during which time the city nearly became insolvent and was forced to give up some home rule to a congressionally-appointed financial control board. In 1998, Anthony A. Williams was elected the city's mayor and led the city into a fiscal recovery, which made him a popular figure. Williams was reelected in 2002.
21st century
On September 29, 2004, Major League Baseball officially relocated the Montreal Expos to Washington for the 2005 season, despite opposition from Baltimore Orioles owner Peter Angelos. The new team was christened the Washington Nationals. Controversy between the city council and MLB threatened to scuttle the agreement until December 21, when a plan for a new stadium in Southeast D.C. was finalized. The Nationals will play at R.F.K. Stadium until the new stadium is ready on the Anacostia River waterfront in 2008.
Geography
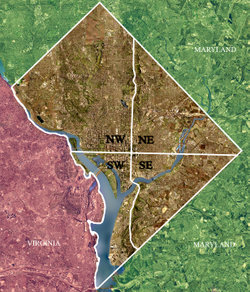
Washington, D.C. is located at (the coordinates of the Zero Milestone, on The Ellipse). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 68.3 square miles (177.0 km²). 61.4 square miles (159.0 km²) of it is land and 6.9 square miles (18.0 km²) of it (10.16%) is water.
Washington is surrounded by the states of Maryland (on its southeast, northeast, and northwest sides) and Virginia (on its western side); it interrupts those states' common border, which is the Potomac River's southern shore both upstream and downstream from the District. The Potomac River as it passes Washington is virtually entirely within the District of Columbia border because of colonial riparian rights between Maryland and Virginia.
The District has three major natural flowing streams: the Potomac River, the Anacostia River, and Rock Creek. The Anacostia River and Rock Creek are tributaries of the Potomac River. There are also three man-made reservoirs: Dalecarlia Reservoir, which crosses over the northwest border of the District from Maryland; McMillan Reservoir near Howard University; and Georgetown Reservoir upstream of Georgetown.
The highest point in the District of Columbia is 410 feet (125 m) above sea level at Tenleytown. The lowest point is sea level, which occurs along all of the Anacostia shore and all of the Potomac shore except the uppermost portion (the Little Falls - Chain Bridge area). The sea level Tidal Basin rose eleven feet during Hurricane Isabel on September 18, 2003.
The geographic centre of the District of Columbia is located near 4th Street NW, L Street NW, and New York Avenue NW (not under the Capitol Dome, as is sometimes said.)
Geographical features of Washington, D.C. include Theodore Roosevelt Island, Columbia Island, the Three Sisters, and Hains Point.
Climate
Washington has a humid subtropical climate typical of the Mid-Atlantic U.S., with four distinct seasons. Summer tends to be hot and humid with daily high temperatures in July and August averaging in the high 80s° to low 90s° F (about 30° to 33° C). The combination of heat and humidity makes thunderstorms very frequent in the summer, some of which occasionally produce tornadoes in the area. Spring and fall are mild with high temperatures in April and October averaging in the high 60s° Fahrenheit (about 20 °C). Winter brings cool temperatures and occasional snowfall. Average highs tend to be in the 40s (4 to 8 °C) and lows in the 20s (-6 to -2 °C) from mid December to mid February. While hurricanes (or the remnants of them) occasionally track through the area in the late summer and early fall, they have often weakened by the time they reach Washington. Spring is generally the most favorable time of year, with low humidity, mild temperatures and blooming foliage. This period generally lasts from late March until mid May.
The average annual snowfall is 15 inches (381 mm) and the average high temperature in January is 43 °F (6 °C); the average low for January is 27 °F (-3 °C). The highest recorded temperature was 106 °F (41 °C) on July 20, 1930 and August 6, 1918 and the lowest recorded temperature was -15 °F (-26 °C) on February 11, 1899.
Demographics
The 2005 Census estimate of the city's population was 582,049, After the city government questioned the original results—an estimate of 550,521—the Census admitted it had made a mistake. The corrected figure marked the biggest increase in the city's population since 1950.
As of the 2000 census, there were 572,059 people, 248,338 households, and 114,235 families residing in the city. The population density was 9,316.4 per square mile (3,597.3/km²). There were 274,845 housing units at an average density of 1,728.3/km² (4,476.1/mi²).
|
|
| Demographics of District of Columbia (csv) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By race | White | Black | AIAN | Asian | NHPI |
| AIAN is American Indian or Alaskan Native - NHPI is Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander | |||||
| 2000 (total population) | 35.34% | 61.96% | 0.86% | 3.17% | 0.14% |
| 2000 (Hispanic only) | 6.43% | 1.34% | 0.17% | 0.09% | 0.03% |
| 2005 (total population) | 39.02% | 58.04% | 0.92% | 3.59% | 0.14% |
| 2005 (Hispanic only) | 7.05% | 1.48% | 0.17% | 0.10% | 0.02% |
| Growth 2000-2005 (total population) | 6.25% | -9.85% | 2.84% | 9.05% | -2.22% |
| Growth 2000-2005 (non-Hispanic only) | 6.41% | -10.22% | 4.41% | 9.25% | 6.78% |
| Growth 2000-2005 (Hispanic only) | 5.52% | 6.98% | -3.49% | 2.58% | -34.66% |
The largest Hispanic group is Salvadoran, and a plurality of whites are of British ancestry.
There were 248,338 households, out of which 19.8% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 22.8% were married couples living together, 18.9% had a female householder with no husband present, and 54.0% were non-families. 43.8% of all households were made up of individuals and 10.0% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.16 and the average family size was 3.07.
In the city, the population was spread out with 20.1% under the age of 18, 12.7% from 18 to 24, 33.1% from 25 to 44, 21.9% from 45 to 64, and 12.2% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 35 years. For every 100 females there were 89.0 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 86.1 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $40,127, and the median income for a family was $46,283. Males had a median income of $40,513 versus $36,361 for females. The per capita income for the city was $28,659. About 16.7% of families and 20.2% of the population were below the poverty line, including 31.1% of those under age 18 and 16.4% of those over age 65.
As of 2000, 83.2% of Washington, D.C. residents age 5 and older speak only English at home and 9.2% speak Spanish. French is the third most spoken language at 1.8%, followed by African languages at 1.0% and Chinese at 0.5%.
According to the 2001 American Religious Identification Survey, nearly three out of four District residents identified themselves as Christian. This breaks down to 72% Christian (27% Catholic, 19% Baptist, and 26% other Protestant churches), 13% stating no religion, 4% Buddhist, 2% Muslim, and 1% Jewish.
According to the Census Bureau, the District's daytime population is estimated at 982,853. The influx of over 410,000 workers into Washington on a normal business day comprises a 72% increase of the capital's normal population. That is the largest increase percentage-wise of any city studied and the second-largest net increase, behind only New York City.
The Greater Washington metropolitan area, including contiguous areas of Maryland and Virginia, had an estimated population of 5.8 million in 2003, according to the estimates of the Greater Washington Initiative.
As host to over 180 embassies and hundreds of international organizations, Washington, D.C. has a substantial population of foreign residents. There are also many students from abroad studying at the local universities and colleges. This adds a cosmopolitan flavor to the city.
Landmarks and museums
Washington is home to numerous national landmarks and is one of the most popular tourist destinations in the United States. The National Mall is a large, open area in the center of the city featuring many monuments to American leaders; it also serves to connect the White House and the United States Capitol buildings. Located prominently in the centre of the Mall is the Washington Monument. Other notable points of interest near the Mall include the Jefferson Memorial (see right), Lincoln Memorial, Franklin Delano Roosevelt Memorial, National World War II Memorial, Korean War Veterans Memorial, Vietnam Veterans Memorial, the District of Columbia War Memorial and the Albert Einstein Memorial.
The world famous Smithsonian Institution is located in the District. The Smithsonian today is a collection of museums that includes the Anacostia Museum, Arthur M. Sackler Gallery, Hirshhorn Museum, National Air and Space Museum, National Museum of American History, National Museum of the American Indian, National Museum of Natural History, National Portrait Gallery, National Postal Museum, Smithsonian American Art Museum, Renwick Gallery, and the National Zoo.
There are many art museums in D.C., in addition to those that are part of the Smithsonian, including the National Gallery of Art, National Museum of Women in the Arts, the Corcoran Gallery of Art, and the Phillips Collection.
The Library of Congress and the National Archives house thousands of documents covering every period in American history. Some of the more notable documents in the National Archives include the Declaration of Independence, Constitution and Bill of Rights.
The District of Columbia operates its own public library system with 27 branches throughout the city. The main branch — which occupies a multi-story glass and steel-framed building at the intersection of 9th and G Streets, N.W., designed by modernist architect Ludwig Mies van der Rohe — is known as the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial Library. It has a large mural in its mail hall depicting the civil rights leader.
Other points of interest in the District include Arena Stage, Chinatown, Basilica of the National Shrine of the Immaculate Conception, Blair House, Cathedral of St. Matthew the Apostle, Folger Shakespeare Library, Ford's Theatre, Frederick Douglass National Historic Site, International Spy Museum, National Building Museum, the Awakening at Hains Point, Old Post Office Building, Theodore Roosevelt Island, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, and the Washington National Cathedral. —
Economy
As of 2002, the federal government accounts for 27% of Washington, D.C.'s jobs. The presence of many major government agencies, including the Department of Defense, National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration, has led to business development both in the District itself as well as in the National Capital Region of Maryland and northern Virginia. These businesses include federal contractors (defense and civilian), numerous nonprofit organizations, law firms and lobbying firms, catering and administrative services companies, and several other industries that are sustained by the economic presence of the federal government. This arrangement makes the Washington economy virtually recession-proof relative to the rest of the country, because the federal government will still operate no matter the state of the general economy, and it often grows during recessions.
The gross state product of the District in 2004 was $75.264 billion, ranking it #36 when compared with the fifty states. In 2006, Expansion Magazine ranked DC among the top 10 metropolitan areas in the nation for climates favorable to business expansion. In terms of commercial office space, Washington, D.C. has the 3rd largest downtown in America behind New York and Chicago.
Of non-government employers, Washington, D.C.'s major universities and hospitals are among the top employers with George Washington University, Georgetown University and Washington Hospital Centre as the top three. Howard University and Fannie Mae round out the top five employers in Washington, D.C.
Washington is also a global media centre. Most major news outlets have bureaus in the city and Washington is home to Black Entertainment Television, C-SPAN, the Washington Post Company, and XM Satellite Radio. Washington's unique scenery makes it a popular location for film and television production.
Law and government
Local government
The city is run by an elected mayor (currently Anthony A. Williams, Adrian Fenty will take over when inaugurated in January) and a city council. The city council is composed of 13 members — a representative elected from each of the eight wards and five members, including the chairman, elected at large. The council conducts its work through standing committees and special committees established as needed. District schools are administered by a school board that has both elected and appointed members. There are 37 elected Advisory Neighbourhood Commissions that provide the most direct access for residents to their local government. The commissions serve as local councils, and their suggestions are required to be given "great weight" by the D.C. Council. However, the U.S. Congress has the ultimate plenary power over the district. It has the right to review and overrule laws created locally and has often done so. The Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution does not apply to the District of Columbia.
D.C. residents pay federal taxes, such as income tax, as well as local taxes. The mayor and council adopt a budget of local money with Congress reserving the right to make any changes. Much of the valuable property in the District is federally owned and hence exempt from local property taxes; at the same time, the city is burdened with the extraordinary expenses related to its role as the capital, such as police overtime and street cleaning for D.C.'s frequent parades and festivals. These factors are often used to explain why the city's budget is frequently overstretched. However, the federal government also appropriates funds for the city. For instance, according to Public Law 108-7, the federal government provided, among other funds, an estimated 25% of the District's operating budget in 2003.
Historically, the city's local government has earned somewhat of a reputation for mismanagement and waste, particularly during the mayoralty of Marion Barry, who was re-elected despite serving jail time for smoking crack cocaine. A front page story in the July 21, 1997 Washington Post reported that Washington had some of the highest cost, lowest quality services in the region. Prosperity in the late 1990s and early 2000s has lessened public pressure on Mayor Williams, who still faces daunting urban renewal, public health, and public education challenges.
Representation in federal government
The U.S. Constitution gives Congress direct jurisdiction for Washington, D.C. While Congress has delegated various amounts of this authority to local government, including an elected mayor and city council, Congress still intervenes, from time to time, in local affairs relating to schools, gun control policy, and other issues.
Citizens of the District have no voting representation in Congress. They are represented in the House of Representatives by a non-voting delegate (currently Eleanor Holmes Norton (D- DC At-Large)) who sits on committees and participates in debate but cannot vote. D.C. has no representation at all in the Senate. Attempts to change this situation, including the proposed District of Columbia Voting Rights Amendment, have been unsuccessful.
Citizens of Washington, D.C. are not unique in having diminished representation in their federal legislature, although they are unique in having no voting representation at all. Some nations that have built capital cities from scratch, including Nigeria, have diminished representation for a federal district. Washington's situation can also be compared to the historical status of U.S. territories, which had only non-voting delegates to the House. However, unlike U.S. territories today (such as American Samoa and Guam), citizens of the District of Columbia are fully taxed and subject to all U.S. laws, just as the citizens of the fifty states. In recent years, "Taxation Without Representation" has been the ironic motto featured on D.C. license plates.
With the passage of the 23rd Amendment in 1961, citizens of the District became eligible to vote for President. The District has three electoral votes--the same number as states with the smallest populations, such as Montana, Wyoming, and the Dakotas.
Education
Public schools
The public school system in the city is operated by District of Columbia Public Schools and consists of 167 schools and learning centers, which consist of 101 elementary schools, 11 middle schools, 9 junior high schools, 20 senior high schools, 6 education centers, and 20 special schools. The District of Columbia Public Charter School Board monitors 34 charter schools in Washington, D.C.
Private schools
Private schools in the city include the British School of Washington, Emerson Preparatory School, Georgetown Day School, St. Patrick's Episcopal Day School, Holy Trinity School, Georgetown Visitation Preparatory School, Gonzaga College High School, Edmund Burke School, Field School, German School, The Maret School, The Model Secondary School, National Cathedral School, Our Lady of Victory, Sheridan School, Sidwell Friends School, St. Albans School, St. Anselm's Abbey School, St. John's College High School, Archbishop Carroll High School, St.Augustine Catholic School, Parkmont School and the Washington International School. Many DC students attend nearby schools in Virginia and Maryland, these schools include The Potomac School, Landon School, Holton-Arms School, The St. Andrew's Episcopal School, and The Bullis School.
Colleges and universities
The city is home to several universities, colleges, and other institutes of higher education, both public and private. The University of the District of Columbia is the city's public university; it is the nation's only urban land-grant university and is counted among the historically black colleges. The Department of Agriculture's Graduate School offers continuing education and graduate-level classes in many disciplines. The Department of Defense maintains the National Defense University at Fort McNair.
Among private institutions, Georgetown University is older than the District itself, having been founded in 1789 by John Carroll. It is the nation's oldest Roman Catholic affiliated body of higher education. The nation's first African-American university president was at Georgetown. The university is especially well-known for the Edmund Walsh School of Foreign Service and the Georgetown University Law Centre. It also is home to a medical school.
The George Washington University, founded by an act of Congress in 1821, is the largest institution of higher education in the nation's capital with its main campus in Foggy Bottom and its Mount Vernon campus in the Foxhall neighbourhood of Northwest Washington. It is the second-largest landholder and employer in the District, second only to the Federal government.
The Catholic University of America (CUA), in the Northeast quadrant of the District is unique as the national university of the Roman Catholic Church and as the only higher education institution founded by U.S. Roman Catholic bishops. Established in 1887 following approval by Pope Leo XIII as a graduate and research centre, the university began offering undergraduate education in 1904. In April of 2004, CUA purchased 49 acres (20 ha) of land from the Armed Forces Retirement Home. The parcel is the largest plot of open space in the District and makes CUA the largest university in D.C. by land area. Trinity University, a female-only Roman Catholic affiliated institution, is located near CUA.
American University, a private institution chartered by an act of Congress in 1893, is situated on an 84 acre (34 ha) campus in upper Northwest Washington and is well known for the Washington College of Law, the Kogod School of Business, the School of International Service, the School of Public Affairs, and the School of Communication.
Other notable private colleges in the District include Gallaudet University, the first liberal arts college for the deaf and hard-of-hearing; Howard University, a historically black university dating to the nineteenth century; and Southeastern University. Both were signed into being by Lincoln.
Furthermore, The Johns Hopkins University's Paul H. Nitze School of Advanced International Studies (SAIS), dedicated to the graduate study of international relations and international economics, is located near Dupont Circle, on Massachusetts Avenue's Embassy Row.
The US military's National Defense University is located in Washington on Fort McNair. The Corcoran College of Art and Design has an arts program attached to the Corcoran Museum of Art, adjacent to the White House Complex. The Reformed Theological Seminary and the Washington Theological Union have graduate programs in theology. Strayer University, a for-profit career school, has a campus in Washington, D.C.
Sports
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Washington Redskins | Football | National Football League; NFC, East Division | FedExField ( Landover, Maryland) |
| Washington Nationals | Baseball | Major League Baseball; NL, East Division | RFK Stadium |
| Washington Capitals | Ice Hockey | NHL, Eastern Conference, Southeast Division | Verizon Centre |
| D.C. United | Soccer | Major League Soccer, Eastern Conference | RFK Stadium |
| Washington Wizards | Basketball | NBA; Eastern Conference, Southeast Division | Verizon Centre |
| Washington Mystics | Basketball | WNBA, Eastern Conference | Verizon Centre |
Other professional and semi-professional teams based in D.C. include the USAFL Baltimore Washington Eagles, the NWFA D.C. Divas, the Minor League Football D.C. Explosion, the Washington RFC rugby union team of the Rugby Super League, as well as a host of others playing in the Potomac Rugby Union, and the Washington Cricket League. It was also home to the WUSA Washington Freedom, from 1987 to 1989 home of the Major Indoor Lacrosse League's Washington Wave, and during the 2000– 2002 NLL seasons, the Washington Power was based in the city. In rugby league, the Washington D.C. Slayers play in the American National Rugby League.
There were two Major League Baseball teams named the Washington Senators in the early and mid-20th century, which left to become respectively the Minnesota Twins and the Texas Rangers. In the 19th century, the town was home to teams called the Washington Nationals, Washington Statesmen, and Washington Senators on and off from the 1870s to the turn of the century.
Washington was home to several Negro League baseball teams, including the Homestead Grays, Washington Black Senators, Washington Elite Giants, Washington Pilots, and Washington Potomacs.
The Verizon Centre in Chinatown, home to the Capitals, Mystics, Wizards, and the Georgetown Hoyas, is also a major venue for concerts, World Wrestling Entertainment (WWE) professional wrestling, and other events.
Washington hosts the annual Legg Mason Tennis Classic tennis tournament that takes place at the Carter Barron Tennis Centre on 17th Street.
The Marine Corps Marathon and the National Marathon are both held annually in Washington.
Transportation
Pierre L'Enfant's original plan for the city provided for a grid of streets and a diagonal array of avenues, all centered on the Capitol building. The north-south streets are primarily named with numbers and the east-west streets with letters. With the Capitol as the centre, one set of numbered streets sweeps eastward from it (1st Street, 2nd Street, etc.) and another set sweeps westward (1st Street, 2nd Street, etc.) Similarly, sets of lettered streets sweep northward from the Capitol (A Street, C Street, etc.) and southward. The diagonal avenues in L'Enfant's plan are chiefly named after states (e.g., Pennsylvania Avenue). Street addresses are identified by their location in one of the four quadrants of the city, centered on the Capitol building: Northeast (NE), Northwest (NW), Southeast (SE), and Southwest (SW). Addresses end with a quadrant suffix to indicate whether the location is, for example, on 4th Street NE, 4th Street NW, 4th Street SE or 4th Street SW. Outside the original city boundaries, street layout and naming practices are less regular. However, the alphabetic order of east-west streets, ending with W Street, is in some areas succeeded by an alphabetic progression of two-syllable names (e.g., Adams, Bryant, Channing), followed by a three-syllable progression (e.g., Allison, Buchanan, Crittenden)
Major interstates running through the area include the Capital Beltway (I-495), I-66, I-95, I-395, I-295, and I-270 (which does not reach D.C., terminating at I-495). Other major highways include the Whitehurst Freeway, and Anacostia Freeway in D.C., the George Washington Parkway in D.C. and Virginia, the Suitland Parkway in D.C. and Maryland, US Route 50, the Clara Barton Parkway, and the Baltimore-Washington Parkway in Maryland, and the Dulles Toll Road in Virginia.

The Washington area is served by the Washington Metro public transportation system, which operates public buses ( Metrobus) and the region's subway system ( Metrorail). A public-private partnership operates the DC Circulator buses downtown. Many of the jurisdictions around the region run public buses that interconnect with the Metrobus/Metrorail system. Union Station is served by MARC and Virginia Railway Express commuter trains, and Amtrak intercity rail. Intercity bus service is available from the Greyhound Bus Terminal in Northeast and from dragon buses leaving from Chinatown.
Washington, D.C. is served by three major airports, one in Maryland and two in Virginia. Ronald Reagan Washington National Airport ( IATA: DCA, ICAO: KDCA) is the closest — located in Arlington County, Virginia, just across the Potomac River from Hains Point, and accessible via Washington Metro. The airport is conveniently located to the downtown area; however it has somewhat restricted flights to airports within the United States because of noise and security concerns. Most major international flights arrive and depart from Washington Dulles International Airport ( IATA: IAD, ICAO: KIAD), located 26.3 miles (42.3 km) west of the city in Fairfax and Loudoun counties in Virginia. Dulles is the second busiest international gateway on the Eastern Seaboard. Dulles offers service from several low-cost carriers including JetBlue, although the low-cost selection decreased greatly when Independence Air (which was headquartered at Dulles) folded in January 2006. Baltimore-Washington International Thurgood Marshall Airport ( IATA: BWI, ICAO: KBWI), is located 31.7 miles (51.0 km) northeast of the city in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, near Baltimore. BWI has had the highest passenger volume of the three major airports in the Baltimore-Washington Metroplex for several months.
General aviation is additionally available at several smaller airfields, including Montgomery County Airpark ( Gaithersburg, Maryland), College Park Airport ( College Park, Maryland), Potomac Airfield ( Friendly CDP of Prince George's County, Maryland), and Manassas Regional Airport ( Manassas, Virginia). Since 2003, the general aviation airports closest to Washington, D.C. have had their access strictly limited by the implementation of the Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ).
Crime
During the violent crime wave of the early 1990s, Washington, D.C. was known as the murder capital of the United States, and often rivaled New Orleans as the nation's most murderous city. Murders peaked in 1991 at 482, with violence declining drastically since then: murders declined to 198 in 2004, with a slight decline to 195 in 2005. Once plagued with violent crime, many D.C. neighborhoods, such as Columbia Heights, are becoming safe and vibrant areas as a result of gentrification. While not as intensely violent, crime hot spots have since displaced farther into the eastern sections of Washington, D.C. and across the border into Maryland. Although the southeastern side of the city has developed a reputation for being unsafe, these crime hot spots are generally concentrated in very specific areas that are associated with drugs and gangs. Other areas east of the U.S. Capitol, as well as the city's wealthier Northwest neighborhoods, experience low levels of crime. Despite the declining trends, Washington D.C. crime rates (2005) remain among the highest of U.S. cities, and it was most recently ranked as the 13th most dangerous city in the nation. Washington D.C. surpasses L.A. and New York in crime.
On July 11, 2006, Metropolitan Police Chief Charles H. Ramsey declared a "crime emergency" in the city in response to a rising homicide rate (the city had logged 13 murders since July 1st, most notably the killing of a prominent British political activist in Georgetown. While the declaration allowed for more flexible and increased policing in high-crime neighborhoods, it was temporary and scheduled to be revisited following a 30-day trial period.
Nature
DC has many natural areas and birdwatching spots inside the city. DC's parks and natural areas include Anacostia Park, the National Arboretum, Rock Creek Park, The Arlington Cemetery, The National Zoological Park, Langley Oaks Park, Roosevelt Island, the C&O Canal, the Potomac River and Anacostia River. The American Forests Report found that "The region Washington DC Metro area is comprised of 187,767 acres of tree canopy (46%), 110,300 acres of impervious surfaces (27%), 70,747 acres of open space (17%), 27,072 acres of bare soil area (7%), and 11,036 acres of water (3%). The total storm water retention capacity of the urban forest on these lands is 949 million cubic feet in avoided storage of water and is valued at $4.7 billion (based on construction costs estimated at $5 per cubic foot to build equivalent retention facilities). The urban forest provides air quality benefits by removing nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide ozone and particulate matter 10 microns or less. The Metro DC areas urban forest removes 20 million pounds of pollutants from the air each year, a benefit worth $49.8 million annually."
Sister cities
Washington, D.C.'s sister cities are:
|
Ten of these cities are designated by Sister Cities International.
In June, 2006, the city signed an Agreement of Friendship with the British city of Sunderland, signalling the start of increased economic and cultural cooperation between the two cities. Washington Old Hall, on the outskirts of Sunderland, is the ancestral home of George Washington. Both these cities participate in town twinning instead of sister cities.