Cricket
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Sports
Cricket is a team sport played between two teams of eleven players each. It is a bat-and-ball game played on a roughly oval grass field, in the centre of which is a flat strip of ground 20.12 m (22 yards) long, called a pitch. At each end of the pitch is a set of wooden stumps, called a wicket. Note that, rather confusingly, the pitch itself is also often referred to as the wicket. A player from the fielding team (the bowler) propels a hard, fist-sized cork-centred leather ball from one wicket towards the other. The ball usually bounces once before reaching a player from the opposing team (the batsman), who defends the wicket from the ball with a wooden cricket bat. The batsman may then run between the wickets, exchanging ends with another batsman (the "non-striker"), who has been standing in an inactive role near the bowler's wicket, to score runs. The remainder of the bowlers' team stand in various positions around the oval as fielders.
Cricket has been an established team sport for several centuries. It originated in its modern form in England and is popular mainly in the present and former members of the Commonwealth. In some countries in South Asia, including India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, cricket is by far the most popular sport. Cricket is also a major sport in England and Wales, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, Zimbabwe and the English-speaking countries of the Caribbean, which are collectively known in cricketing parlance as the West Indies. There are also well established amateur club competitions in countries as diverse as the Netherlands, Kenya, Nepal, and Argentina (see also: International Cricket Council).
The length of the game — certain test matches can last six or more hours a day, for up to five days — the many intervals for lunch and tea and the abundance of specialised terminology are notable aspects that can often confuse those not familiar with the cricket.
The sport is followed with passion in many different parts of the world. It has even occasionally given rise to diplomatic outrage, the most notorious being the Basil D'Oliveira affair which led to the banning of South Africa from sporting events. Other examples include the Bodyline series played between England and Australia in the early 1930s, an event that almost meant diplomatic ties were severed with England or the 1981 underarm bowling incident involving Australia and New Zealand.
Summary
The aim of the batsmen is to score as many runs as possible. A run is scored when both batsmen successfully move to their respective opposite ends of the wicket (the batsmen will usually only attempt to score runs after the striker has hit the ball, but this is not necessary). The aim of the bowler's team is to get each batsman out (this is a wicket, or a dismissal). Dismissals are achieved in a variety of ways. The most direct way is for the bowler to evade the batsman's guard and successfully hit his stumps with the ball, dislodging the bails on top. While the batsmen are attempting a run, the fielders will attempt to knock the bails off either set of stumps with the ball before the batsman nearest to that set of stumps passes the crease with his bat. Other ways for the fielding side to dismiss a batsman include catching a struck ball before it touches the ground. Once the batsmen are not attempting to score any more runs, the ball is "dead" and is bowled again (each attempt at bowling the ball is a ball or a delivery).
Once out, a batsman is replaced by the next batsman in the team's lineup. The innings (singular) of the batting team will end when the tenth batsman is given out, since there always must be two batsmen on the field. When this happens, the team is said to be all out. At the end of an innings, the two teams exchange roles, the fielding team becoming the batting team.
The game is divided into overs of six (legal) balls. At the end of an over, the batting and bowling ends will be swapped, and the bowler replaced by another member of the fielding side. The fielding positions and the two umpires also change positions at this time.
The winning team will be the team that scores the most runs at the end of a match. Different varieties of the game have different restrictions on the number of overs, the number of innings, and the number of balls in each. A draw is not an uncommon result and can occur if the team that is last to bat fails to match the required total of runs, or the bowling team fails to take 10 wickets, before a specified time limit.
Results
If the team that bats last has all of its batsmen dismissed before it can reach the run total of the opposing team, it is said to have lost by (n) runs (where (n) is the difference between the two run totals). If however, the team that bats last exceeds the opposing team's run total before its batsmen are dismissed, it is said to have won by (n) wickets, where (n) is the difference between the number of wickets conceded and 10.
If, in a two-innings-a-side match, one team's combined first and second innings total fails to reach its opponent's first innings total, there is no need for the opposing team to bat again and it is said to have won by an innings and (n) runs, where (n) is the difference between the two teams' totals.
If all the batsmen of the team batting last are dismissed with the scores exactly equal then the match is a tie; ties are very rare in cricket, particularly in matches of two innings a side. If the time allotted for the match expires before either side can win, then the game is a draw.
If the match has only a single innings per side, then a maximum number of deliveries for each innings is often imposed. In this case the side scoring more runs wins regardless of the number of wickets lost, so that a draw cannot occur. If this kind of match is temporarily interrupted by bad weather, then a complex mathematical formula known as the Duckworth-Lewis method is often used to recalculate a new target score. A one-day match can be declared a No-Result if fewer than a previously agreed number of overs have been bowled by either team, in circumstances that make normal resumption of play impossible - for example, an extended period of bad weather.
Laws of cricket
The game is played in accordance with 42 laws of cricket, which have been developed by the Marylebone Cricket Club in discussion with the main cricketing nations. Teams may agree to alter some of the rules for particular games. Other rules supplement the main laws and change them to deal with different circumstances. In particular, there are a number of modifications to the playing structure and fielding position rules that apply to one innings games that are restricted to a set number of fair deliveries.
Players and officials
Players
A team consists of eleven players. Depending on his primary skills, a player may be classified as a specialist batsman or bowler. A balanced team usually has five or six specialist batsmen and four or five specialist bowlers. Teams nearly always include a specialist wicket-keeper because of the importance of this fielding position.
A player who excels in both batting and bowling is known as an all-rounder. One who excels as a batsman and wicket-keeper is known as a wicket-keeper/batsman, sometimes regarded as a type of all-rounder. True all-rounders are rare and valuable players; most players focus on either their batting or their bowling.
Umpires
Two on-field umpires preside over a match. One umpire (the field umpire) will stand behind the wicket at the end from which the ball is bowled, and adjudicate on most decisions. The other (the square leg umpire) will stand near the fielding position called square leg, which offers a side view of the batsman, and assist on decisions for which he has a better view. In some professional matches, they may refer a decision to an off-field third umpire, who has the assistance of television replays. In international matches an off-field match referee ensures that play is within the laws of cricket and the spirit of the game.
Scorers
Two scorers are appointed, and most often one scorer is provided by each team. The laws of cricket specify that the official scorers are to record all runs scored, wickets taken and (where appropriate) overs bowled. They are to acknowledge signals from the umpire, and to check the accuracy of the score regularly both with each other and, at playing intervals, with the umpires. In practice scorers also keep track of other matters, such as bowlers' analyses, the rate at which the teams bowl their overs, and team statistics such as averages and records. In international and national cricket competitions, the media often require notification of records and statistics, so unofficial scorers often keep tally for broadcast commentators and newspaper journalists. The official scorers occasionally make mistakes, but unlike umpires' mistakes these can be corrected after the event.
The playing field
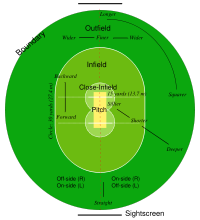
The cricket field consists of a large circular or oval-shaped grassy ground. There are no fixed dimensions for the field but its diameter usually varies between 450 feet (137 m) to 500 feet (150 m). On most grounds, a rope demarcates the perimeter of the field and is known as the boundary.
The pitch
Most of the action takes place in the centre of this ground, on a rectangular clay strip usually with short grass called the pitch. The pitch measures 10 × 66 feet (3.05 × 20.12 m).
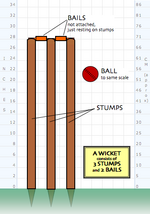
At each end of the pitch three upright wooden stakes, called the stumps, are hammered into the ground. Two wooden crosspieces, known as the bails, sit in grooves atop the stumps, linking each to its neighbour. Each set of three stumps and two bails is collectively known as a wicket. One end of the pitch is designated the batting end where the batsman stands and the other is designated the bowling end where the bowler runs in to bowl. The area of the field on the side of the line joining the wickets where the batsman holds his bat (the right-hand side for a right-handed batsman, the left for a left-hander) is known as the off side, the other as the leg side or on side.
Lines drawn or painted on the pitch are known as creases. Creases are used to adjudicate the dismissals of batsmen and to determine whether a delivery is legal.
Parts of the field
For a one-innings match played over a set number of fair deliveries, there are two additional field markings. A painted oval is made by drawing a semicircle of 30 yards (27.4 m) radius from the centre of each wicket with respect to the breadth of the pitch and joining them with lines parallel, 30 yards (27.4 m) to the length of the pitch. This line, commonly known as the circle, divides the field into an infield and outfield. Two circles of radius 15 yards (13.7 m), centred on each wicket and often marked by dots, define the close-infield. The infield, outfield, and the close-infield are used to enforce fielding restrictions.
Placements of players
The team batting always has two batsmen on the field. One batsman, known as the striker, faces and plays the balls bowled by the bowler. His partner stands at the bowling end and is known as the non-striker.
The fielding team has all eleven of its players on the ground, and at any particular time, one of these will be the bowler. The player designated as bowler must change after every over. The wicket-keeper, who generally acts in that role for the whole match, stands or crouches behind the wicket at the batting end. The captain of the fielding team spreads his remaining nine players — the fielders — around the ground to cover most of the area. Their placement may vary dramatically depending on strategy. Each position on the field has a unique label.
Match structure
The toss
The two opposing captains toss a coin before the match, and the captain winning the toss chooses either to bat or bowl first. This decision will be based on whether the team's bowlers are likely to gain immediate advantage from the pitch and weather conditions (these can vary significantly), or whether it is more likely that the pitch will deteriorate and make batting more difficult later in the game.
Overs
Each innings is divided into overs, each consisting of six consecutive legal (see "Extras" for details) deliveries bowled by the same bowler. After completing an over, the bowler must take up a fielding position and let another player take over the bowling.
After every over, the batting and bowling ends are swapped, and the field positions are adjusted. The umpires swap so the umpire at the bowler's end moves to square leg, and the umpire at square leg moves to the new bowler's end.
End of an innings
An innings is completed if:
- Ten out of eleven batsmen are 'out' (dismissed) — the team are all out.
- The team has only one batsman left who can bat (the others being incapacitated either through injury, illness or absence) — again, the team are all out.
- The team batting last reaches the score required to win the match.
- The predetermined number of overs are bowled (in a one-day match only, usually 50 overs).
- A captain declares his team's innings closed (this does not apply to one-day limited over matches).
Playing time
Typically, two innings matches are played over three to five days with at least six hours of cricket being played each day. One innings matches are usually played over one day for six hours or more. There are formal intervals on each day for lunch and tea, and shorter breaks for drinks, where necessary. There is also a short interval between innings.
The game is only played in dry weather. Additionally, as in professional cricket it is common for balls to be bowled at over 90 mph (144 km/h), the game needs to be played in daylight that is good enough for a batsman to be able to see the ball. Play is therefore halted during rain (but not usually drizzle) and when there is bad light. Some one-day games are now played under floodlights, but, apart from a few experimental games in Australia, floodlights are not used in longer games. Professional cricket is usually played outdoors. These requirements mean that in England, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa and Zimbabwe the game is usually played in the summer. In the West Indies, India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka and Bangladesh games are played in the winter. In these countries the hurricane and monsoon season coincides with their summers.
Batting and scoring runs
Batting
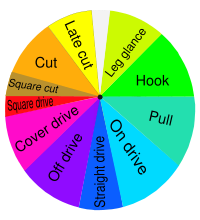
Batsmen strike the ball from the batting crease, with the flat surface of a wooden bat. If the batsman hits the ball with his bat, it is called a shot (or stroke). If the ball brushes the side of the bat it is called an edge or snick. Shots are named according to the style of swing and the direction aimed. As part of the team's strategy, he may bat defensively, blocking the ball downwards, or aggressively, hitting the ball hard to empty spaces in order to score runs. There is no requirement to run if the ball is struck.
If the batsman manages to hit the ball over the boundary ropes, he automatically scores runs. A ball that crosses the boundary on the full (without touching the ground) automatically scores six runs. A ball that crosses the boundary after having touched the ground automatically scores four runs.
Batsmen come in to bat in a batting order, decided by the team captain. The first two positions, the "openers", face the most hostile bowling, from fast bowlers at their freshest and with a new ball. After that, the team typically bats in descending order of batting skill, the first five or six batsmen usually being the best in the team. Then follow the all-rounders—bowlers or wicket-keepers who can bat decently—and finally the pure bowlers who rarely score well. This order may be changed at any time during the course of the game for strategic reasons.
Run scoring
To score a run, a striker must hit the ball and run to the opposite end of the pitch, while his non-striking partner runs to his end. To register a run, both runners must touch the ground behind the popping crease with either their bats or their bodies (the batsmen carry their bats as they run). If the striker hits the ball well enough, the batsmen may double back to score two or more runs. This is known as running between wickets. However, no rule requires the batsman to run upon striking the ball. If the batsmen score an odd number of runs, then they will have swapped ends and their roles as striker and non-striker will be reversed for the next ball, unless the most recent ball marks the end of an over.
If a fielder knocks the bails off the stumps with the ball while no batsman is grounded behind the nearest popping crease, the nearest batsman is run out. If the ball goes over the boundary, then four runs are scored, or six if the ball has not bounced.
Extras
Every run scored by the batsmen contributes to the team's total. A team's total also includes a number of runs which are unaccredited to any batsmen. These runs are known as extras, apart from in Australia where they are also called sundries. Extras consist of byes, leg byes, no balls, wides and penalty runs. The former two are runs that can be scored if the batsman misses making contact with bat and ball, and the latter two are types of fouls committed by the bowler. For serious infractions such as tampering with the ball, deliberate time-wasting, and damaging the pitch, the umpires may award penalty extras to the opposition; in each case five runs. Five penalty runs are also awarded if a fielder uses anything other than his body to field the ball, or if the ball hits a protective helmet left on the field by the fielding team. A team need not be batting in order to receive penalty extras.
Bowling and dismissals
Bowling
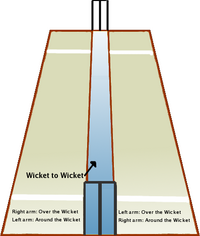
A bowler delivers the ball toward the batsmen, using what is known as a bowling action: the elbow may be held at any angle and may bend further, but may not straighten out during the action. If the elbow straightens, it is an illegal throw and the delivery is called a no-ball. Under new cricketing law, after consultation with health experts, the bowler is allowed to straighten his arm 15 degrees or less; if the bowler straightens his arm more than 15 degrees it is called a "no ball". This new law came in to prevent injury to bowlers.
Usually, the bowler pitches the ball so that it bounces before reaching the batsman. Some part of the bowler's front foot in the delivery stride (that is, the stride when the ball is released) must be behind the popping crease to avoid a no-ball (although the bowler's front foot does not have to be grounded). The ball must also be delivered so it is within the batsman's reach; otherwise it is termed a wide. A wide cannot be called if the batsman hits the ball. A wide or no-ball results in an extra run being added to the batting team's score, and an extra ball being bowled in the over.
The bowler's primary goal is to take wickets; that is, to get a batsman out or dismissed. If a bowler can dismiss the more accomplished batsmen on the opposing team he reduces the opportunity for them to score, as it exposes the less skilful non-specialist batsmen. The bowler's next task is to limit the numbers of runs scored per over bowled. This is known as the Economy rate. There are two main kinds of bowlers: pace bowlers, who attempt to bowl the ball too quickly for the batsman to properly react, and spin bowlers who bowl slower balls that bounce and curve in unpredictable ways.
Dismissal of a batsman
There are ten ways for a batsman to be dismissed. Once a batsman is dismissed, he leaves the field to be replaced by another player from the batting team until ten batsmen are out and the innings is over.
Many modes of dismissal require the wicket to be "put down". The wicket is put down if a bail is dislodged from the top of the stumps; or if a stump is struck out of the ground either by the ball, or by a fielder using his hand which is holding the ball. Of the following ten modes of dismissal, the first six are common, while the last four are technicalities which rarely occur. Briefly, the ten modes are:
- Caught — When a fielder catches the ball before the ball bounces and after the batsman has struck it with the bat or it has come into contact with the batsman's glove while it is in contact with the bat handle. The bowler and catcher are both credited with the dismissal. ( Law 32)
- Bowled — When a delivered ball hits the stumps at the batsman's end, and dislodges one or both of the bails. This happens regardless of whether the batsman has edged the ball onto the stumps or not. The bowler is credited with the dismissal. ( Law 30)
- Leg before wicket (LBW) — When a delivered ball misses the bat and strikes the batsman's leg or pad, and the umpire judges that the ball would otherwise have struck the stumps. The laws of cricket stipulate certain exceptions in favour of the batsman; for instance, a batsman should not be given out LBW if the place where the ball bounced on the pitch is to the leg-side of the area strictly between the two wickets. The purpose of this rule is to prevent the batsman from unfairly using his pads to obstruct the passage of the ball without striking it. The bowler is credited with the dismissal.
- Run out — When a fielder, bowler or wicket-keeper removes one or both of the bails with the ball by hitting the stumps whilst a batsman is still running between the two ends. The ball can either hit the stumps directly or the fielder's hand with the ball inside it can be used to dislodge the bails. Such a dismissal is not officially credited to any player, although the identities of the fielder or fielders involved is often noted in brackets on the scorecard.
- Stumped — When the batsman leaves his crease in playing a delivery, voluntarily or involuntarily, but the ball goes to the wicket-keeper who uses it to remove one or both of the bails through hitting the bail(s) or the wicket before the batsman has remade his ground. The bowler and wicket-keeper are both credited. This generally requires the keeper to be standing within arm's length of the wicket, which is done mainly to spin bowling. ( Law 39)
- Hit wicket — When the batsman accidentally knocks the stumps with either the body or the bat, causing one or both of the bails to be dislodged, either in playing a shot or in taking off for the first run. The bowler is credited with the dismissal. ( Law 35)
- Handled the ball — When the batsman deliberately handles the ball without the permission of the fielding team. No player is credited with the dismissal. ( Law 33)
- Hit the ball twice — When the batsman deliberately strikes the ball a second time, except for the sole purpose of guarding his wicket. No player is credited with the dismissal. ( Law 34)
- Obstructing the field — When a batsman deliberately hinders a fielder from attempting to field the ball. No player is credited with the dismissal. ( Law 37)
- Timed out — When a new batsman takes more than three minutes to take his position in the field to replace a dismissed batsman (If the delay is protracted, the umpires may cause the match to be forfeited). This rule prevents the batting team using time limits of the game to unfair advantage. No player is credited with the dismissal. ( Law 31)
Additionally, a batsman may leave the field without being dismissed. For instance, if he is injured or taken ill, this is known as retired hurt or retired ill. The batsman is not out; he may return to bat later in the same innings if sufficiently recovered. Also, an unimpaired batsman may retire, in which case he is treated as being dismissed retired out; no player is credited with the dismissal.
An individual cannot be out — 'bowled', 'caught', 'leg before wicket', 'stumped', or 'hit wicket' off a no ball. He cannot be out — 'bowled', 'caught', 'leg before wicket', or 'hit the ball twice' off a wide.
Some of these modes of dismissal can take place without the bowler bowling a delivery. The batsman who is not on strike may be run out by the bowler if he leaves his crease before the bowler bowls, and a batsman can be out obstructing the field or retired out at any time. Timed out by its nature is a dismissal without a delivery. With all other modes of dismissal, only one batsman can be dismissed per ball bowled. Obstructing the field, Handled the ball, Timed Out and Hit the ball twice dismissals are extremely rare.
Fielding and wicket-keeping
Fielders assist the bowlers in preventing batsmen from scoring too many runs. They do this in two ways: by taking catches to dismiss a batsman, and by intercepting hit balls and returning them to the pitch to attempt run-outs to restrict the scoring of runs.
The wicket-keeper is a specialist fielder who stands behind the batsman's wicket throughout the game. His primary job is to gather deliveries that the batsman fails to hit, to prevent them running into the outfield, which would enable batsmen to score byes. To this end, he wears special gloves (he is the only fielder allowed to do so) and pads to cover his lower legs. Due to his position directly behind the striker, the wicket-keeper has a good chance of getting a batsman out caught off a fine edge from the bat; thicker edges are typically handled by the "slips" fieldsmen. The wicket-keeper is also the only person who can get a batsman out stumped. The umpire may call no-ball if the wicket-keeper positions any part of his body or equipment in front of the line of the popping crease before the ball is bowled.
Other roles
Captain
The captain's acumen in deciding the strategy is crucial to the team's success. The captain makes a number of important decisions, including setting field positions, alternating the bowlers and taking the toss. The captain's job on the team is very important but can be rather stressful at times. Much blame is placed on a captain when his team loses. However, it is considered an honour to be in such a privileged position and much praise is given to the captain when his team wins. The burden of the captain's duties can interfere with his quality of play considerably, slightly, or not at all, depending on how well he deals with the stress of his position.
A runner
In the event of a batsman being fit to bat but too injured to run, he may ask the umpire and the fielding captain for a runner. The runner chosen must, if possible, be a player who has already been given out. After a batsman hits the ball, the runner's only task is to run between the wickets in place of the injured batsman. The runner is required to wear and carry exactly the same equipment as the batsman he is running for.
Substitutes
In all forms of cricket, if a player gets injured or becomes ill during a match, a substitute is allowed to field instead of him; though he cannot bowl, bat, or act as a captain or wicket-keeper. Here the substitute is a temporary role and leaves the field once the injured player is fit to return.
For 9 months from July 2005, the ICC trialled the concept of a Super Sub in One-day International (ODI) cricket and some other limited overs competitions. A single full substitution was allowed, with the replaced player not allowed to return to the game. It was discontinued from March 2006.
History

A basic form of cricket can be traced back to the 13th century, but it may have existed even earlier than that. The game seems to have originated among children of the farming and metalworking communities in the Weald between Kent and Sussex. Written evidence exists of a game known as creag being played by Prince Edward, the son of Edward I (Longshanks), at Newenden, Kent in 1300.
In 1598, a court case referred to a sport called kreckett being played at the Royal Grammar School, Guildford around 1550. The Oxford English Dictionary gives this as the first recorded instance of cricket in the English language.
A number of words are thought to be possible sources for the term cricket. The name may derive from a term for the cricket bat: old French criquet (meaning a kind of club) or Flemish krick(e) (meaning a stick) or in Old English crycc (meaning a crutch or staff). (The latter is problematic, since Old English 'cc' was palatal in pronunciation in the south and the west midlands, roughly ch, which is how crycc leads to crych and thence crutch; the 'k' sound would be possible in the north, however.) Alternatively, the French criquet apparently derives from the Flemish word krickstoel, which is a long low stool on which one kneels in church and which resembles the long low wicket with two stumps used in early cricket.
During the 17th century, numerous references indicate the growth of cricket in the south-east of England. By the end of the century, it had become an organised activity being played for high stakes and it is likely that the first professionals appeared in that period. We know that a great cricket match with eleven players a side was played for high stakes in Sussex in 1697 and this is the earliest reference we have to cricket in terms of such importance.
The game underwent major development in the 18th Century and had become the national sport of England by the end of the century. Betting played a major part in that development and rich patrons began forming their own "select XIs". Cricket was prominent in London as early as 1707 and large crowds flocked to matches on the Artillery Ground in Finsbury. The Hambledon Club was founded in the 1760s but its team was already playing first-class matches in 1756. For the next 20 years until the formation of MCC and the opening of Lord's in 1787, Hambledon was the game's greatest club and its focal point. MCC quickly became the sport's premier club and the custodian of the Laws of Cricket.
The 19th Century saw underarm replaced by first roundarm and then overarm bowling. Both developments were accompanied by major controversy. The concept of a "champion county" arose in the 1820s and then, starting with Sussex CCC in 1839, county clubs were founded and these ultimately formed a County Championship.
In 1859, a team of England players went on the first overseas tour (to North America) and 18 years later another England team took part in the first-ever Test match at the Melbourne Cricket Ground against Australia.
The legendary W G Grace started his long career in 1864. It can fairly be said that he revolutionised the sport and did much to ensure its massive popularity.
The last two decades before the First World War have been called the "Golden Age of Cricket". It is almost certainly a nostalgic idea based on the sense of loss brought about by the war, but even so the period did produce some great players and memorable matches, especially as organised competition at county and Test level developed.
The inter-war years were dominated by one player: Don Bradman, statistically the greatest batsman of all time. It was the determination of the England team to overcome his incredible skill that brought about the infamous Bodyline series in 1932/33.
Cricket entered an epochal era in 1963, when English counties modified the rules to provide a variant match form that produced a certain result: games with a restricted number of overs per side. This gained widespread popularity and resulted in the birth of One-day International (ODI) matches in 1971. The governing International Cricket Council quickly adopted the new form and held the first ODI Cricket World Cup in 1975. Since then, ODI matches have gained mass spectatorship, at the expense of the longer form of the game and to the consternation of fans who prefer the longer form of the game.
As of the early 2000s, however, the longer form of cricket is experiencing a growing resurgence in popularity but a new limited overs phenomenon, Twenty20, has made an immediate impact.
Forms of cricket
There are many different types and grades of cricket; those played professionally at an international level are Test cricket, one-day cricket and Twenty20.
Test cricket
Test cricket is a form of international cricket started in 1877 during the 1876/77 English cricket team's tour of Australia. The first Test match began on 15 March 1877 and had a timeless format with four balls per over. It ended on 19 March 1877 with Australia winning by 45 runs.
The Test cricket series between England and Australia is called The Ashes, with the titular trophy being a tiny fragile urn, reputed to hold the ashes of a bail or cricket ball used during the second Test series between the two countries. The tiny urn was presented to the English Cricket Captain, Ivo Bligh, by a group of Melbourne women, following the Test Series win by the England Cricket Team, during the England Cricket Team's Tour of Australia in 1882/83. The actual trophy is a cut glass replica. The original urn is considered priceless and remains in England, except for special occasions when it may travel on display for promotional purposes, as is the case with the 2006 Ashes Series where it toured Australia's capital city museums.
Other trophies contested in Test Cricket are the Basil D'Oliveira trophy (for a series between England and South Africa played in South Africa), the Wisden trophy (England - West Indies), The Frank Worrell trophy (Australia - West Indies), the Trans-Tasman trophy (Australia - New Zealand), the Border- Gavaskar trophy (Australia - India) and the Sir Vivian Richards trophy (South Africa - West Indies).
Since then, over 1,800 Test matches have been played and the number of Test playing nations has increased to ten with Bangladesh, the most recent nation elevated to Test status, making its debut in 2000. Test matches are two innings per side, usually played over five consecutive days. Tests that are not finished within the allotted time are drawn.
One-day cricket
Limited overs matches, also known as one day cricket or instant cricket, were introduced in the English domestic season of 1963 due to the growing demands for a shorter and more dramatic form of cricket to stem the decline in attendances. One-day, single-innings, matches often took place before this, but the innovation was the limiting of each side's innings to an agreed number of overs (nowadays usually 50). The idea was taken up in the international arena in 1971, during England's tour of Australia, when a match was played on the scheduled fifth day of the rained-off third Test. The one-day game has since become a crowd-pleaser and TV-audience-generator across the globe, hastened in part by the success of the inaugural World Cup in 1975. The abbreviations ODI (One-day International) or sometimes LOI (Limited Overs International) are used for international matches of this type. Important one-day matches, international and domestic, often have two days set aside, the second day being a "reserve" day to allow more chance of the game being completed if a result is not possible on the first day (for instance if play is prevented or interrupted by rain). Innovations have included the introduction of coloured clothing, distinct tournaments, and "day-night" matches (where play extends into the night under floodlights); together with frequent nail-biting finishes and the impossibility of either side opting to play for a draw, these have seen ODI cricket gain many supporters.
Twenty20 Cricket
Twenty20 Cricket was first played in English domestic cricket in 2003 to popularise first-class cricket and attract more spectators to the game. Now it has spread to many other countries. A "Twenty20 Game" consists 20 overs per each side, a free-hit after a no-ball is bowled, short boundaries, batting-friendly pitches, and other rules designed to attract crowds that would not usually wish to sit through the slower paced one day games or test matches. The first men's Twenty20 international was between Australia and New Zealand in 2005, the first women's Twenty20 international having been between England and New Zealand in 2004.The ICC announced after its Executive Board meeting in March this year that beginning from 2007 to 2015, the Twenty20 World Championship would be held on an annual basis and the first ever Twenty20 World Championship in South Africa in probably May-June.
First-class matches
A first-class match is generally defined as a high-level international or domestic match that takes place over at least three days on natural (as opposed to artificial) turf. First-class games are two innings per side. Like Test matches, if the game is not completed over the allotted time then it is drawn. Games where the teams have only one innings each are not first-class (including one-day internationals).
A two-innings match of at least three days duration is granted first-class status only if both teams have first-class status. For example, Test matches, other games between two Test nations, games between two domestic teams deemed first-class in countries holding full membership of the ICC, and games between a Test nation's national side (or a team drawn from a national touring squad) and a first-class domestic team from a Test nation, are usually deemed to be first class. Matches between Kenya, one of the leading associate members of the ICC, and another team adjudjed first-class are usually granted first-class status, but domestic matches in Kenya are not.
Among cricket statisticians, first class cricket is variously deemed to have started in 1660, 1772, 1801, 1815 or 1864. This ongoing controversy is described in the main article.
Other forms of cricket
At all levels, the rules of cricket are often modified. At international or first-class levels this is usually in order to make the game more commercially attractive. More or less formal domestic club cricket matches are usually played over one to two days, either two innings per side or one innings per side with limited overs. At lower levels the rules are often changed simply to make the game playable with limited resources, or to render it more convenient and enjoyable for the participants. Variants of the sport are played in areas as diverse as sandy beaches and ice floes. Families and teenagers play backyard cricket in suburban yards or driveways, and the teeming cities of India and Pakistan play host to countless games of 'Gully Cricket' or 'Tapeball' on their streets. Tennis balls and homemade bats are often used, and a variety of objects may serve as wickets. Sometimes the rules are also improvised: for instance it is sometimes agreed that fielders can catch the ball with one hand after one bounce and claim a wicket, or if only a few people are available then everyone may field while the players take it in turns to bat and bowl.
In Kwik cricket, the bowler does not have to wait for the batsman to be ready before a delivery, leading to a faster, more exhausting game designed to appeal to children, which is often used in English schools' PE lessons. Another modification to increase the pace of the game is the "Tipsy Run" rule, in which the batter must run when the ball touches the bat, even if it the contact is unintentional or minor. This rule, seen only in impromptu games, speeds the match up by disable the batsmens ability to block the ball. Indoor cricket is played in a netted, indoor arena.
International structure
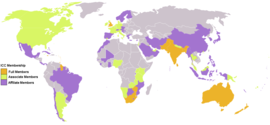
The International Cricket Council (ICC) is the international governing body for cricket. It is headquartered in Dubai and includes representatives of each of the ten Test-playing nations, as well as an elected panel representing non-Test-playing nations.
Each nation has a national cricket board which regulates cricket matches played in their country. The cricket board also selects the national squad and organises home and away tours for the national team.
Nations playing cricket are separated into three tiers depending on the level of cricket infrastructure in that country. At the highest level are the Test-playing nations. They qualify automatically for the quadrennial World Cup matches. A rung lower are the Associate Member nations. The lowermost rung consists of the Affiliate Member nations.
See also: Non-Test teams to have played ODI matches.