Trigonometry
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Mathematics
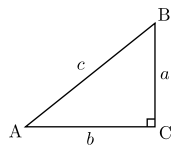
Trigonometry (from the Greek trigonon = three angles and metron = measure ) is a branch of mathematics which deals with triangles, particularly triangles in a plane where one angle of the triangle is 90 degrees ( right triangles). Triangles on a sphere are also studied, in spherical trigonometry. Trigonometry specifically deals with the relationships between the sides and the angles of triangles, that is, the trigonometric functions, and with calculations based on these functions.
Trigonometry has important applications in many branches of pure mathematics as well as of applied mathematics and, consequently, much of science.
Overview
Basic definitions
The shape of a right triangle is completely determined, up to similarity, by the value of either of the other two angles. This means that once one of the other angles is known, the ratios of the various sides are always the same regardless of the size of the triangle. These ratios are traditionally described by the following trigonometric functions of the known angle:
- The sine function (sin), defined as the ratio of the leg opposite the angle to the hypotenuse.
- The cosine function (cos), defined as the ratio of the adjacent leg to the hypotenuse.
- The tangent function (tan), defined as the ratio of the opposite leg to the adjacent leg.
The adjacent leg is the side of the angle that is not the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is the side opposite to the 90 degree angle in a right triangle; it is the longest side of the triangle.
The reciprocals of these functions are named the cosecant (csc), secant (sec) and cotangent (cot), respectively. The inverse functions are called the arcsine, arccosine, and arctangent, respectively. There are arithmetic relations between these functions, which are known as trigonometric identities.
With these functions one can answer virtually all questions about arbitrary triangles by using the law of sines and the law of cosines. These laws can be used to compute the remaining angles and sides of any triangle as soon as two sides and an angle or two angles and a side or three sides are known. These laws are useful in all branches of geometry since every polygon may be described as a finite combination of triangles.
Extending the definitions
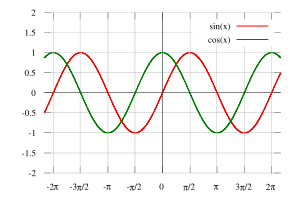
The above definitions apply to angles between 0 and 90 degrees (0 and π/2 radians) only. Using the unit circle, one may extend them to all positive and negative arguments (see trigonometric function). The trigonometric functions are periodic, with a period of 360 degrees or 2π radians. That means their values repeat at those intervals.
The trigonometric functions can be defined in other ways besides the geometrical definitions above, using tools from calculus and infinite series. With these definitions the trigonometric functions can be defined for complex numbers. The complex function cis is particularly useful
See Euler's formula.
Mnemonics
The sine, cosine and tangent ratios in right triangles can be remembered by SOH CAH TOA (sine-opposite-hypotenuse cosine-adjacent-hypotenuse tangent-opposite-adjacent). It is commonly referred to as "Sohcahtoa" by some American mathematics teachers, who liken it to a (nonexistent) Native American girl's name. See trigonometry mnemonics for other memory aids. Also another way to remember is "Some Old Hags, Cant Always Hide, Their Old Age"
Calculating trigonometric functions
Trigonometric functions were among the earliest uses for mathematical tables. Such tables were incorporated into mathematics textbooks and students were taught to look up values and how to interpolate between the values listed to get higher accuracy. Slide rules had special scales for trigonometric functions.
Today scientific calculators have buttons for calculating the main trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan and sometimes cis) and their inverses. Most allow a choice of angle measurement methods, degrees, radians and, sometimes, grad. Most computer programming languages provide function libraries that include the trigonometric functions. The floating point unit hardware incorporated into the microprocessor chips used in most personal computers have built in instructions for calculating trigonometric functions.
Early history of trigonometry
Trigonometry was probably invented for the purposes of astronomy. The origins of trigonometry can be traced to the civilizations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley, more than 4000 years ago. The common practice of measuring angles in degrees, minutes and seconds comes from the Babylonian's base sixty system of numeration.
The first recorded use of trigonometry came from the Hellenistic mathematician Hipparchus circa 150 BC, who compiled a trigonometric table using the sine for solving triangles. Ptolemy further developed trigonometric calculations circa 100 AD.
The Sulba Sutras written in India, between 800 BC and 500 BC, correctly compute the sine of π/4 (45 °) as 1/√2 in a procedure for circling the square (the opposite of squaring the circle).
The ancient Sinhalese, when constructing reservoirs in the Anuradhapura kingdom, used trigonometry to calculate the gradient of the water flow.
The Indian mathematician Aryabhata in 499, gave tables of half chords which are now known as sine tables, along with cosine tables. He used zya for sine, kotizya for cosine, and otkram zya for inverse sine, and also introduced the versine.
Another Indian mathematician, Brahmagupta in 628, used an interpolation formula to compute values of sines, up to the second order of the Newton- Stirling interpolation formula.
In the 10th century, the Persian mathematician and astronomer Abul Wáfa introduced the tangent function and improved methods of calculating trigonometry tables. He established the angle addition identities, e.g. sin (a + b), and discovered the sine formula for spherical geometry:
Also in the late 10th and early 11th centuries, the Egyptian astronomer Ibn Yunus performed many careful trigonometric calculations and demonstrated the formula cos(a)cos(b) = (1 / 2)[cos(a + b) + cos(a − b)].
Indian mathematicians were the pioneers of variable computations algebra for use in astronomical calculations along with trigonometry. Lagadha (circa 1350- 1200 BC) is the first person thought to have used geometry and trigonometry for astronomy, in his Vedanga Jyotisha.
Persian mathematician Omar Khayyám ( 1048- 1131) combined trigonometry and approximation theory to provide methods of solving algebraic equations by geometrical means. Khayyam solved the cubic equation x3 + 200x = 20x2 + 2000 and found a positive root of this cubic by considering the intersection of a rectangular hyperbola and a circle. An approximate numerical solution was then found by interpolation in trigonometric tables.
Detailed methods for constructing a table of sines for any angle were given by the Indian mathematician Bhaskara in 1150, along with some sine and cosine formulae. Bhaskara also developed spherical trigonometry.
The 13th century Persian mathematician Nasir al-Din Tusi, along with Bhaskara, was probably the first to treat trigonometry as a distinct mathematical discipline. Nasir al-Din Tusi in his Treatise on the Quadrilateral was the first to list the six distinct cases of a right angled triangle in spherical trigonometry.
In the 14th century, Persian mathematician al-Kashi and Timurid mathematician Ulugh Beg (grandson of Timur) produced tables of trigonometric functions as part of their studies of astronomy.
The mathematician Bartholemaeus Pitiscus published an influential work on trigonometry in 1595 which may have coined the word "trigonometry".
Applications of trigonometry
There are an enormous number of applications of trigonometry and trigonometric functions. For instance, the technique of triangulation is used in astronomy to measure the distance to nearby stars, in geography to measure distances between landmarks, and in satellite navigation systems. The sine and cosine functions are fundamental to the theory of periodic functions such as those that describe sound and light waves.
Fields which make use of trigonometry or trigonometric functions include astronomy (especially, for locating the apparent positions of celestial objects, in which spherical trigonometry is essential) and hence navigation (on the oceans, in aircraft, and in space), music theory, acoustics, optics, analysis of financial markets, electronics, probability theory, statistics, biology, medical imaging ( CAT scans and ultrasound), pharmacy, chemistry, number theory (and hence cryptology), seismology, meteorology, oceanography, many physical sciences, land surveying and geodesy, architecture, phonetics, economics, electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, civil engineering, computer graphics, cartography, crystallography and game development.
Common formulae
Certain equations involving trigonometric functions are true for all angles and are known as trigonometric identities. Many express important geometric relationships. For example, the Pythagorean identities are an expression of the Pythagorean Theorem. Here are some of the more commonly used identities, as well as the most important formulae connecting angles and sides of an arbitrary triangle. For more identities see trigonometric identity.
Trigonometric identities
Pythagorean identities
|
|
|
|
Sum and difference identities
Double-angle identities
Half-angle identities
Note that 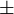 in these formulae does not mean both are correct, it means it may be either one, depending on the value of A/2.
in these formulae does not mean both are correct, it means it may be either one, depending on the value of A/2.
Triangle identities
Law of sines
The law of sines for an arbitrary triangle states:
or equivalently:
Law of cosines
The law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula) is an extension of the Pythagorean theorem to arbitrary triangles:
- c2 = a2 + b2 − 2abcosC,
or equivalently:
Law of tangents
The law of tangents:
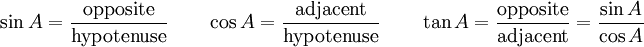
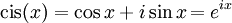
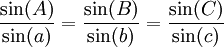

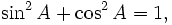
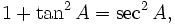
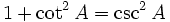
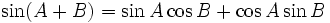
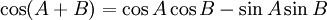
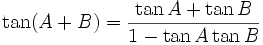
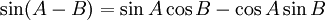
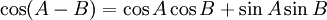
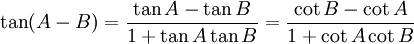
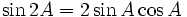
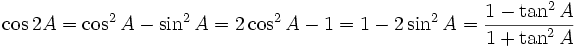
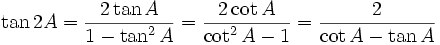
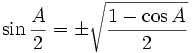
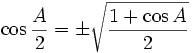
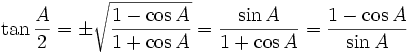
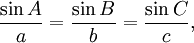
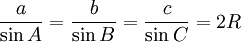
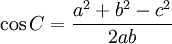
![\frac{a+b}{a-b} = \frac{\tan[\frac{1}{2}(A+B)]}{\tan[\frac{1}{2}(A-B)]}](../../images/379/37973.png)