Guangzhou
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Geography of Asia
| Guangzhou (Canton) | |
| Pearl River at night | |
| Nickname: "The Flower City" | |
| Location within China | |
| Coordinates: | |
|---|---|
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Guangdong |
| Officiated | 1918 |
| Mayor | Zhang Guangning |
| Area | |
| - City | 3718.8 km² (1436.1 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 8 m (26 ft) |
| Population | |
| - City () | |
| - Urban | 6,560,500 |
| - Metro | 12 600 000 |
| Time zone | UTC ( UTC+8) |
| Website: http://www.guangzhou.gov.cn/ | |
| Guangzhou | ||
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Chinese: | 廣州 | |
| Simplified Chinese: | 广州 | |
| Mandarin | ||
| Hanyu Pinyin: | Guǎngzhōu | |
| Wade-Giles: | Kuang-chou [Listen] |
|
| Cantonese | ||
| Jyutping: | Gwong2 zau1 | |
| Min Nan | Pe̍h-ōe-jī: | kńg-chiu |
| Hakka | romanization: | [gong31 zu24] |
| Postal map spelling: | Canton | |
Guangzhou is the capital and the sub-provincial city of Guangdong Province in southern mainland China. The city was formerly known internationally as Canton City or simply Canton, after a French language transliteration of the name of the province in Cantonese. It is a port on the Pearl River, navigable to the South China Sea. As of the 2000 census, the city has a population of 6 million, and a metropolitan population of 12.6 million, making it the most populous city in the province and the fifth most populous in China.
Name
The Chinese abbreviation of Guangzhou is Sui (穗; pinyin: sùi; Jyutping: seoi6; Yale: seuīh) or sometimes GZ. The city has the nicknames of Wuyangcheng (City of Five Rams), Yangcheng (City of Rams), Huacheng (City of Flowers), or Suicheng (City of Wheats). The city can also be referred to as the MuMengCheng (City of Wood Wools), a reference to a tall, native tree that produces wool fibre in its gorgeous red blossoms.
"Canton" was the convenient Portuguese romanisation of "Guangdong" Province, and the city Guangzhou is the capital of the province and frequently referred as 廣東省城 ("the Canton Province Capital City") or simply 省城 ("the Province City") by Cantonese people. The city naturally represents the province and thus was erroneously used as the city's name. It was more convenient for Europeans who during the colonial period generally did not understand ideographic characters (see exonym and endonym). When the term "Canton" is pronounced in Portuguese it provides a closer oral rendering of the name in its original Cantonese. Guangzhou is a Mandarin pronunciation of the Han ideographs.
Geography
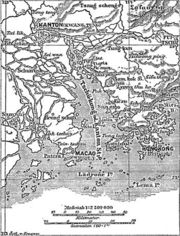
Guangzhou is located at 112°57'E to 114°3'E and 22°26'N to 23°56'N. The city is part of the Pearl River Delta.
Administrative divisions
Guangzhou is a sub-provincial city. It has direct jurisdiction over ten districts and two county-level cities.
- Districts
- Yuexiu District
- Liwan District
- Haizhu District
- Tianhe District
- Baiyun District
- Huangpu District
- Huadu District
- Panyu District
- Nansha District
- Luogang District
- County-level cities
- Zengcheng City
- Conghua City
As of April 28, 2005, the districts of Dongshan and Fangcun have been abolished and merged into Yuexiu and Liwan respectively; at the same time the district of Nansha is established out of parts of Panyu, and the district of Luogang is established out of parts of Baiyun, Tianhe, Huangpu, and Zengcheng.
History
It is believed that the first city built at the site of Guangzhou was Panyu (蕃禺, later simplifed to 番禺; the locals pronounced this in Cantonese as Poon Yu) founded in 214 BC. The city has been continuously occupied since that time. Panyu was expanded when it became the capital of the Nanyue Kingdom (南越) in 206 BC.
Recent archaeological founding of her palace suggests that the city might have traded frequently with foreigners by the sea routes. The foreign trade continued every dynasty and the city remains a major international trading port to this day.
The Han Dynasty annexed Nanyue in 111 BC, and Panyu became a provincial capital and remains so until this day. In 226 AD, the city became the seat of the Guang Prefecture (廣州; Guangzhou). Therefore, "Guangzhou" was the name of the prefecture, not of the city. However, people grew accustomed to calling the city Guangzhou, instead of Panyu.
Although the Chinese name of Guangzhou replaced Panyu as the name of the walled city, Panyu was still the name of the area surrounding the walled city until the end of Qing era.
Arabs and Persians sacked Guangzhou (known to them as Sin-Kalan) in AD 758, ² according to a local Guangzhou government report on October 30, 758, which corresponded to the day of Guisi (癸巳) of the ninth lunar month in the first year of the Qianyuan era of Emperor Suzong of the Tang Dynasty.
During the Northern Song Dynasty, a celebrated poet called Su Shi visited Guangzhou's Baozhuangyan Temple and wrote the inscription "Liu Rong" (Six Banyan Trees) because of the six banyan trees he saw there. It has since been called the Temple of the Six Banyan Trees.
The Portuguese were the first Europeans to arrive to the city by sea, obtaining the monopoly for external trade with its harbour by 1511. They were later expelled from their settlements in Guangzhou (in Portuguese Canton or Cantao), but instead granted use of Macao (first occupied in 1511) as a trade base with the city in 1557. They would keep a near monopoly of foreign trade in the region until the arrival of the Dutch in the early XVII century.
After China brought Taiwan under its control in 1683, the Qing government became open to encouraging foreign trade. Guangzhou quickly emerged as one of the most adaptable ports for negotiating commerce and before long, many foreign ships were going there to procure cargos. Portuguese in Macao, Spanish in Manila, and Armenians and Muslims from India were already actively trading in the port by the 1690s, when the French and English East India companies' ships began frequenting the port. Other companies were soon to follow: the Ostend General India Company in 1717; Dutch East India Company in 1729; the first Danish ship in 1731, which was followed by a Danish Asiatic Company ship in 1734; the Swedish East India Company in 1732; followed by an occasional Prussian and Trieste Company ship; the Americans in 1784; and the first ships from Australia in 1788. By the middle of the 18th century, Guangzhou had emerged as one of the world's great trading ports, which was a distinction it maintained until the outbreak of the Opium War in 1839 and the opening of other ports in China in 1842.
Guangzhou was one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened by the Treaty of Nanking (signed in 1842) at the end of the First Opium War between Britain and China. The other ports were Fuzhou, Xiamen, Ningbo, and Shanghai.
In 1918, "Guangzhou" became the official name of the city, when an urban council was established in Guangzhou. Panyu became a county's name south of Guangzhou. In both 1930 and 1953, Guangzhou was promoted to the status of a Municipality, but each promotion was cancelled within the year.
Japanese troops occupied Guangzhou from 1938- 10-12 to 1945- 09-16.
After the communist take-over, urban renewal projects in the city improved the lives of many residents. New housing on the shores of the Pearl River provided homes for the poor boat people. Reforms by Deng Xiaoping, who came to power in the late 1970s, led to rapid economic growth due to the city's close proximity to Hong Kong and access to the Pearl River.
As labor costs increased in Hong Kong, manufacturers opened new plants in the cities of Guangdong including Guangzhou. As the largest city in one of China's wealthiest provinces, Guangzhou attracts farmers from the countryside looking for factory work. Cantonese links to overseas Chinese and beneficial tax reforms of the 1990s have aided the city's rapid growth.
In 2000, Huadu and Panyu were merged into Guangzhou as districts, and Conghua and Zengcheng became county-level cities of Guangzhou.
Modern Guangzhou
Economy
Guangzhou is the economic centre of the Pearl River Delta, placing it in the heart of one of mainland China's leading commercial and manufacturing regions.
In 2005, the GDP per capita was ¥58,000 (about US $7,000), ranking the city third among 659 Chinese cities.
The Chinese Export Commodities Fair, also called "Canton Fair", is held each spring and autumn by Bo Liu. Inaugurated in the spring of 1957, the Fair is a major event for the city.
Transportation
The Guangzhou Metro opened in 1999.
Guangzhou's main airport is the New Baiyun International Airport in Huadu District, that opened on 5 August 2004 replacing old Baiyun International Airport close to the city centre.
Guangzhou is connected to Hong Kong by train, bus and ferry services. Express trains arrive in Hong Kong at the Hung Hom KCR station. They cover the 182 km route in approximately two hours. Daily ferry sailings include an overnight steamer, which takes eight hours, and high-speed catamarans and hydrofoils which take three hours to reach the China Ferry Terminal or Macau Ferry Pier in Hong Kong.
Tourist attractions
- Chenjiaci ( 陈家祠)
- Guangdong Museum of Folk Handcraft
- Shamian Island
- Guangdong Provincial Museum
- Museum of the Tomb of the King of Southern Yue in Western Han Dynasty
- Temple of the Six Banyan Trees
- Shishi Holy Heart Cathedral
- Huaisheng Mosque
Parks
- Baiyun Mountain ( 白云山)
- Lie shi ling yuan ( 烈士陵园)
- Yue Xiu Park ( 越秀公园)
Significant buildings
- Guangdong Olympic Stadium
- CITIC Plaza
- Sky Central Plaza
- Guangdong TV Tower
- Guangzhou TV Tower
- China Hotel
Plans are also underway to build what will become the world's tallest free-standing TV tower.
Culture
- Cantonese (linguistics)
- Cantonese cuisine
- Cantonese opera
Education
Major educational institutions
National
- Sun Yat-sen University (中山大学) (founded 1924)
- South China University of Technology (华南理工大学)
- Jinan University (暨南大学) (founded 1906)
Public
- Guangdong University of Foreign Studies (广东外语外贸大学)
- South China Agricultural University (华南农业大学) (founded 1909)
- Zhongkai Agrotechnical College (仲恺农业技术学院) (founded 1927)
- South China Normal University (华南师范大学)
- Guangzhou Medical College (广州医学院)
- Guangzhou University of TCM (广州中医药大学)
- Guangdong College of Pharmacy (广东药学院)
- Guangdong University of Technology (广东工业大学)
- Guangzhou University (广州大学)
- Guangdong Business College (广东商学院)
- Xinghai Conservatory of Music (星海音乐学院)
- GuangDong Polytechnic Normal University (广东技术师范学院)
- Guangzhou Physical Education Institute (广州体育学院)
Note: Institutions without full-time bachelor programs are not listed.
Sister cities
Guangzhou is twinned with the following cities:
 Fukuoka, Japan (May, 1979)
Fukuoka, Japan (May, 1979) Los Angeles, United States ( March 2, 1982)
Los Angeles, United States ( March 2, 1982) Manila, Philippines (November, 1982)
Manila, Philippines (November, 1982) Vancouver, Canada (March, 1985)
Vancouver, Canada (March, 1985) Sydney, Australia (May, 1986)
Sydney, Australia (May, 1986) Bari, Italy (November, 1986)
Bari, Italy (November, 1986) Frankfurt am Main, Germany ( April 11, 1988)
Frankfurt am Main, Germany ( April 11, 1988) Lyon, France (November, 1988)
Lyon, France (November, 1988) Auckland, New Zealand, (February, 1989)
Auckland, New Zealand, (February, 1989) Gwangju, South Korea (October, 1996)
Gwangju, South Korea (October, 1996) Linköping, Sweden (November, 1997)
Linköping, Sweden (November, 1997) Durban, South Africa (July, 2000)
Durban, South Africa (July, 2000) Bristol, United Kingdom (May, 2001)
Bristol, United Kingdom (May, 2001) Yekaterinburg, Russia ( July 10, 2002)
Yekaterinburg, Russia ( July 10, 2002) Arequipa, Peru ( October 27, 2004)
Arequipa, Peru ( October 27, 2004) Birmingham, United Kingdom (Dec, 2006)
Birmingham, United Kingdom (Dec, 2006)