Tonga
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Countries; Geography of Oceania (Australasia)
| Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga KINGDOM OF TONGA |
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: Ko e ʻOtua mo Tonga ko hoku tofiʻa ("God and Tonga are my Inheritance") |
|||||
| Anthem: Ko e fasi ʻo e tuʻi ʻo e ʻOtu Tonga | |||||
| Capital | Nukuʻalofa |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Largest city | Nukuʻalofa | ||||
| Official languages | Tongan, English | ||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||
| - King | George Tupou V | ||||
| - Prime Minister | Dr. Feleti Sevele | ||||
| Monarchy | |||||
| - Independence | 4 June 1970, from British protectorate status | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 748 km² ( 186th) 289 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 4 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - July 2005 estimate | 102,000 ( 194th) | ||||
| - Density | 153/km² ( 67th1) 396/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2005 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $817 million ( 167th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $7,984 ( 76th) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | 0.810 (high) ( 54th) | ||||
| Currency | Paʻanga ( TOP) |
||||
| Time zone | ( UTC+13) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | ( UTC+13) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .to | ||||
| Calling code | +676 | ||||
| 1 based on 2005 figures. | |||||
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( Tongan for "south"), is an independent archipelago in the southern Pacific Ocean. It lies about a third of the way between New Zealand and Hawaii, south of Samoa and east of Fiji.
The islands are also known as the Friendly Islands, the name given by Captain Cook because of the friendly reception he received. He happened to arrive at the time of ʻinasi festival, the yearly donation of the first fruits to the Tuʻi Tonga and was invited to the festivities. According to the writer William Mariner, in reality the chiefs had wanted to kill Cook during the gathering, but had been unable to agree on a plan.
History
Archaeological evidence shows that the first settlers in Tonga sailed from the Santa Cruz Islands, as part of the original Austronesian-speakers' ( Lapita) migration which originated out of S.E. Asia some 6000 years ago. Archaeological dating places Tonga as the oldest known site in Polynesia for the distinctive Lapita ceramic ware, at 2800–2750 years ago. The " Lapita" people lived and sailed, traded, warred, and intermarried in the islands now known as Tonga, Samoa, and Fiji for 1000 years, before more explorers set off to the east to discover the Marquesas, Tahiti, and eventually the rest of the Pacific Ocean islands. For this reason, Tonga, Samoa, and Fiji are described by anthropologists as the cradle of Polynesian culture and civilization.
By the 12th century, Tongans, and the Tongan paramount chief, the Tuʻi Tonga, were known across the Pacific, from Niue to Tikopia, sparking some historians to refer to a ' Tongan Empire'. A network of interacting navigators, chiefs, and adventurers might be a better term although the empire did have its own dynasties. In the 15th century and again in the 17th, civil war erupted. It was in this context that the first Europeans arrived, beginning with Dutch explorers Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire in 1616, who called on the northern island of Niuatoputapu, and Abel Tasman, who visited Tongatapu and Haʻapai in 1643. Later noteworthy European visits were by Captain Cook in 1773, 1774, and 1777, the first London missionaries in 1797, and the Wesleyan Methodist Walter Lawry Buller in 1822.
Tonga was united into a Polynesian kingdom in 1845 by the ambitious young warrior, strategist, and orator Tāufaʻāhau. He held the chiefly title of Tuʻi Kanokupolu, but was baptised with the name King George. In 1875, with the help of missionary Shirley Baker, he declared Tonga a constitutional monarchy, formally adopted the western royal style, emancipated the 'serfs', enshrined a code of law, land tenure, and freedom of the press, and limited the power of the chiefs.
Tonga became a British protected state under a Treaty of Friendship on 18 May 1900, when European settlers and rival Tongan chiefs tried to oust the second king. Within the British Empire, which posted no higher permanent representative on Tonga than a British Consul (1901-1970), it was part of the British Western Pacific Territories (under a colonial High Commissioner, then residing on Fiji) from 1901 until 1952.
The Treaty of Friendship and Tonga's protectorate status ended in 1970 under arrangements established prior to her death by Queen Salote Tupou III. Tonga joined the Commonwealth of Nations in 1970 (atypically as an autochthonous monarchy, that is one with its own hereditary monarch rather than Elizabeth II), and the United Nations in September 1999. While exposed to colonial forces, Tonga has never lost indigenous governance, a fact that makes Tonga unique in the Pacific and gives Tongans much pride, as well as confidence in their monarchal system. As part of cost cutting measures across the British Foreign Service, the British Government closed the British High Commission in Nukuʻalofa in March 2006, transferring representation of British interests in Tonga to the UK High Commissioner in Fiji. The last resident British High Commissioner was His Excellency Mr. Paul Nessling.
Politics
Tonga is a constitutional monarchy. The reverence for the kingship is likened to that held in prior centuries for the sacred paramount chief, the Tuʻi Tonga. Criticism of the monarch is held to be contrary to Tongan culture and etiquette. A direct descendant of the first monarch, King George Tupou V, his family, some powerful nobles, and a growing non-royal elite caste live in much wealth, with the rest of the country living in relative poverty. The effects of this disparity are mitigated by three factors: education, medicine, and land tenure.
Tonga's education system is free and mandatory for all children up to age twelve, with only nominal fees for secondary education, and foreign-funded scholarships for post-secondary education. Tongans are well-educated, with a 98% literacy rate, and higher education up to and including medical and graduate degrees. Tongans also have universal access to a socialized medicine system. Tongan land is constitutionally protected and cannot be sold to foreigners (although it may be leased). While there is a land shortage on the urbanized main island of Tongatapu (where 60% of the population resides), there is farm land available in the rural islands. The majority of the population engages in some form of subsistence production of food, with approximately half producing almost all of their basic food needs through farming, sea harvesting, and animal husbandry. Women and men have equal access to education and health care, and are fairly equal in employment, but women are discriminated against in land holding, electoral politics, and government ministries.
There is a pro-democracy movement in Tonga, which emphasises reforms including better representation in the Parliament for the majority commoners, and better accountability in matters of state. An overthrow of the monarchy itself is not part of the movement and the institution of monarchy continues to hold popular support, even while reforms are advocated. Until recently, the governance issue was generally ignored by the leaders of other countries, but major aid donors and neighbours New Zealand and Australia are now expressing concerns about some Tongan government actions.
Following the precedents of Queen Sālote, and with numerous international advisors, the government of Tonga under King Tāufaʻāhau Tupou IV has monetized the economy, internationalized the medical and education system, and enabled access by commoners to increasing forms of material wealth (houses, cars, and other commodities), education, and overseas travel. The government has supported Olympic and other international sports competition, and contributed Peacekeepers to the United Nations (notably to Bougainville). The Tongan government also supported the American ' coalition of the willing' action in Iraq, and a small number of Tongan soldiers were deployed, as part of an American force, to Iraq in late 2004. However, the contingent of 40+ troops returned home on 17 December 2004.
The previous king, Tāufaʻāhau and his government have made some problematic economic decisions and are accused of wasting millions of dollars in poor investments. The problems have mostly been driven by attempts to increase national revenue through a variety of schemes, including searching for oil (despite geological reports indicating no possible oil); considering making Tonga a nuclear waste disposal site (an idea floated in the mid-90s by the current crown prince); selling Tongan Protected Persons Passports (which eventually forced Tonga to nationalize the purchasers, sparking ethnicity-based concerns within Tonga); registering foreign ships (which proved to be engaged in illegal activities, including shipments for al-Qaeda); claiming geo-orbital satellite slots (the revenue from which seems to belong to the Princess Royal, not the state); holding a long-term charter on an unusable Boeing 757 that was sidelined in Auckland Airport, leading to the collapse of Royal Tongan Airlines; building an airport hotel and potential casino with an Interpol-accused criminal; and approving a factory for exporting cigarettes to China (against the advice of Tongan medical officials, and decades of health promotion messaging). The king has proved vulnerable to speculators with big promises and lost several million (reportedly 26 million USD) to Jesse Bogdonoff, a financial adviser who called himself the king's Court Jester. The police have imprisoned pro-democracy leaders, and the government repeatedly confiscated the newspaper The Tongan Times (which was printed in New Zealand and sold in Tonga) because the editor had been vocally critical of the king's mistakes. Notably, the Keleʻa, produced specifically to critique the government and printed in Tonga by pro-democracy leader ʻAkilisi Pōhiva, was not banned during that time. Pōhiva, however, had been subjected to harassment in the form of frequent lawsuits.
In mid-2003, the government passed a radical constitutional amendment to "Tonganize" the press, by licensing and limiting freedom of the press, so as to protect the image of the monarchy. The amendment was defended by the government and by royalists on the basis of traditional cultural values. Licensure criteria include 80% ownership by Tongans living in the country. As of February 2004, those papers denied licenses under the new act included the Taimi ʻo Tonga (Tongan Times), the Keleʻa and the Matangi Tonga, while those which were permitted licenses were uniformly church-based or pro-government. The bill was opposed in the form of a several-thousand-strong protest march in the capital, a call by the Tuʻi Pelehake (a prince, nephew of the king and elected member of parliament) for Australia and other nations to pressure the Tongan government to democratize the electoral system, and a legal writ calling for a judicial investigation of the bill. The latter was supported by some 160 signatories, including seven of the nine elected "People's Representatives". The strong-arm tactics and gaffes have overshadowed the good that the aged king had done in his lifetime, as well as the many beneficial reforms of his son, ʻAhoʻeitu ʻUnuakiʻotonga Tukuʻaho (Lavaka Ata ʻUlukālala), who was Prime Minister from 3 January 2000 to 11 February 2006. The former Crown Prince and current monarch, Tupoutoʻa, and Pilolevu, the Princess Royal, remained generally silent on the issue. In total, the changes threatened to destabilize the polity, fraction support for the status quo, and place further pressure on the monarchy.
In 2005 the government spent several weeks negotiating with striking civil service workers before reaching a settlement. The civil unrest that ensued was not limited to just Tonga; protests outside the king's New Zealand residence made headlines, too. A constitutional commission is currently (2005-06) studying proposals to update the constitution.
Prime Minister Prince ʻAhoʻeitu ʻUnuakiʻotonga Tukuʻaho (Lavaka Ata ʻUlukālala) resigned suddenly on 11 February 2006, and also gave up his other cabinet portfolios. He was replaced in the interim by the elected Minister of Labour, Dr Feleti Sevele.
The co-chairman of the constitutional reform commission His Royal Highness ʻUluvalu (Prince Tuipelehake), 55, who was a nephew of the King, and his wife, Kaimana Aleamotuʻa, 45, were killed by Edith Delgado, an 18-year old reckless teenager driving a Ford Mustang as she was racing in a California freeway near Menlo Park about 30 miles south of San Francisco, California on 5 July 2006. The teenager was reported to have been travelling around 100mph upon hitting the red Ford Explorer carrying the two and also instantly killing the driver of the Explorer. Delgado was not hurt in the accident. .
The Tongan government formally announced Monday, 11 September 2006 that King Tupou IV died late Sunday night in Middlemore Hospital in Auckland, New Zealand where he had been receiving treatment for much of the past year. He was 88 and had reigned for 41 years.
He was succeeded by his eldest son, Tupoutoʻa, now ruling under the title Siaosi Tupou V.
The public expected some changes under the new monarch. On November 16, 2006, rioting broke out in the capital city of Nuku'alofa when it seemed that the parliament would adjourn for the year without having made any advances in increasing democracy in government. Government buildings, offices, and shops were looted and burned.
Kings and queens of modern Tonga
- King George Tupou I (1875-1893)
- King George Tupou II (1893-1918)
- Queen Salote Tupou III (1918-1965)
- King Taufa'ahau Tupou IV (1965-2006)
- King George Tupou V (2006-present)
Geography
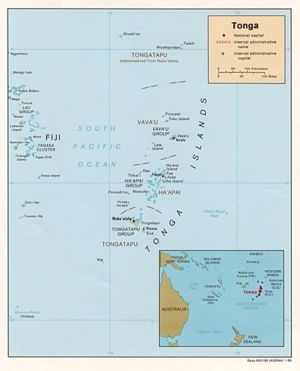
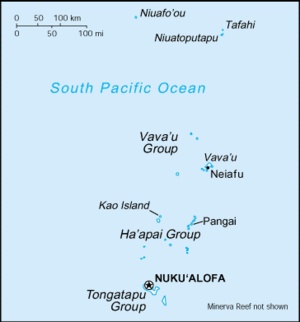
Tonga is an archipelago in the South Pacific consisting of 169 islands, 36 of them inhabited, and is divided into three main groups – Vavaʻu, Haʻapai, and Tongatapu, which together cover an 800 kilometre (500 mi) long north–south line. The largest island, Tongatapu, on which the capital city of Nukuʻalofa is located, covers 257 square kilometres (99 sq mi). Geologically, the Tongan islands generally comprise two types: volcanic islands rising directly from the ocean floor (e.g. Kao and Tofua in the Haʻapai group), and seismically uplifted coral limestone islands overlaying an older volcanic base (e.g. Tongatapu). The active volcanic islands are situated in an approximate north-south line located west of the more populated islands. A new volcanic island broke the ocean's surface in the Haʻapai group during the 1990s.
On August 12, 2006, the crew of the yacht Maiken reported sighting a new volcanic island breaking the sea after sailing through a pumice raft. There was no official confirmation of a new island, either from Tonga's Ministry of Lands or the Tonga Defense Service. Instead of contacting officials in Tonga, the crew wrote about the experience in their travel blog. Shortly thereafter, NASA contacted the crew to obtain the exact latitude and longitude coordinates of the new island. Links to the blog and NASA images can be found on the Vava'u page.
The 2006 Tonga earthquake was a great earthquake measuring 8.0 on the Richter scale which occurred on 4 May 2006 (Tonga time). The quake was centred about 155 km (95 miles) south of the island of Neiafu and north-east of the capital, Nuku'alofa.
The climate is basically subtropical with a distinct warm period (December–April), during which the temperatures rise above 32 ° C (90 ° F), and a cooler period (May–November), with temperatures rarely rising above 27 °C (80 °F). The temperature increases from 23 °C to 27 °C (74 °F to 80 °F), and the annual rainfall is from 1,700 to 2,970 millimetres (67 to 117 in) as one moves from Tongatapu in the south to the more northerly islands closer to the Equator. The mean daily humidity is 80%. Over the last few years the weather has been warmer and wetter than average in the cooler period (May–November), this has caused some problems with fruiting trees and other crops grown on the island.
Economy
Tonga's economy is characterized by a large non monetary sector and a heavy dependence on remittances from the half of the country's population that lives abroad, chiefly in Australia, New Zealand, and the United States. The monetary sector of the economy is dominated and largely owned by the royal family and nobles. This is particularly true of the telecommunications and satellite services. Much of small business, particularly retail establishments on Tongatapu, is now dominated by recent Chinese immigrants who arrived under a cash-for-passports scheme ended in 1998.
The manufacturing sector consists of handicrafts and a few other very smallscale industries, all of which contribute only about 3% of GDP. Commercial business activities also are inconspicuous and, to a large extent, are dominated by the same large trading companies found throughout the South Pacific. In September 1974, the country's first commercial trading bank, the Bank of Tonga, opened.
Rural Tongans rely on plantation and subsistence agriculture. Coconuts, vanilla beans, and bananas are the major cash crops. The processing of coconuts into copra and desiccated coconut is the only significant industry. Pigs and poultry are the major types of livestock. Horses are kept for draft purposes, primarily by farmers working their api (a plot of bushland). More cattle are being raised, and beef imports are declining.
Tonga's development plans emphasize a growing private sector, upgrading agricultural productivity, revitalizing the squash and vanilla bean industries, developing tourism, and improving the island's communications and transportation systems. Substantial progress has been made, but much work remains to be done. A small but growing construction sector is developing in response to the inflow of aid monies and remittances from Tongans abroad. The copra industry is plagued by world prices that have been depressed for years.
Efforts are being made to discover ways to diversify. One hope is seen in fisheries; tests have shown that sufficient skipjack tuna pass through Tongan waters to support a fishing industry. Another potential development activity is exploitation of forests, which cover 35% of the kingdom's land area but are decreasing as land is cleared. Coconut trees past their prime bearing years also provide a potential source of lumber.
The tourist industry is relatively undeveloped; however, the government recognizes that tourism can play a major role in economic development, and efforts are being made to increase this source of revenue. Cruise ships often stop in Nukuʻalofa and Vavaʻu.
In 2005 the country became a member of the World Trade Organization.
Demographics
Almost two-thirds of the population of the Kingdom of Tonga live on its main island, Tongatapu. Although an increasing number of Tongans have moved into the only urban and commercial centre, Nukuʻalofa, where European and indigenous cultural and living patterns have blended, village life and kinship ties continue to be important throughout the country. Everyday life is heavily influenced by Polynesian traditions and especially by the Christian faith; for example, all commerce and entertainment activities cease from midnight Saturday until midnight Sunday, and the constitution declares the Sabbath to be sacred, forever. Tonga is said to have the highest proportion of Latter-day Saints (Mormons) of any state or country outside of Utah.
Tongans, a Polynesian group with a very small mixture of Melanesian, represent more than 98% of the inhabitants. The rest are European, mixed European, and other Pacific Islanders. There also are several hundred Chinese.
Primary education between ages 6 and 14 is compulsory and free in state schools. Mission schools provide about 83% of the primary and 90% of the secondary level education. Higher education includes teacher training, nursing and medical training, a small private university, a women's business college, and a number of private agricultural schools. Most higher education is pursued overseas.
Culture and diaspora
The Tongan archipelago has been inhabited for perhaps 3000 years, since settlement in late Lapita times. The culture of its inhabitants has surely changed greatly over this long time period. Before the arrival of European explorers in the late 1600s and early 1700s, the Tongans were in frequent contact with their nearest Oceanic neighbors, Fiji and Samoa. In the 1800s, with the arrival of Western traders and missionaries, Tongan culture changed dramatically. Some old beliefs and habits were thrown away, and others adopted. Some accommodations made in the 1800s and early 1900s are now being challenged by changing Western civilization. Hence Tongan culture is far from a unified or monolithic affair, and Tongans themselves may differ strongly as to what it is "Tongan" to do, or not do.
Contemporary Tongans often have strong ties to overseas lands. Many Tongans have emigrated to Australia, New Zealand, and the United States to seek employment and a higher standard of living. U.S. cities with significant Tongan American populations include San Mateo, California; East Palo Alto, California; Oakland, California; Los Angeles, California; Salt Lake City, Utah; Honolulu, Hawaii; and Euless, Texas (near the Dallas/Fort Worth metroplex). This Tongan diaspora is still closely tied to relatives at home, and a significant portion of Tonga's income derives from remittances to family members (often aged) who prefer to remain in Tonga.
Tongans, therefore, often have to operate in two different contexts, which they often call anga fakatonga, the traditional Tongan way, and anga fakapãlangi, the Western way. A culturally adept Tongan learns both sets of rules and when to switch between them.
Sport
Rugby union is the most popular sport in Tonga, and the national team (Ikale Tahi) has performed quite well on the international stage. Tonga has competed at four Rugby World Cups, the first being in 1987, and its best result thus far was in 1995 when it reached the first round. Tonga performs the Kailao (Sipi Tau) before its matches. Tonga also competes in the Pacific Tri-Nations and the IRB Pacific 5 Nations. At club level, there are the Datec Cup Provincial Championship and the Pacific Rugby Cup. Rugby union is governed by the Tonga Rugby Football Union, which is also a member of the Pacific Islands Rugby Alliance. Tonga contributes to the Pacific Islanders rugby union team.
Boxer Paea Wolfgram won the silver medal in the Super Heavyweight division (> 91kg) at the 1996 Summer Olympics.
Miscellany
- On either his 1773 or 1777 visit, Captain Cook presented a tortoise to the king. This tortoise, known thereafter as Tuʻi Malila, lived to be either 188 or 192 years old. It is listed in the Guinness Book of World Records as the oldest animal (kingdom Animalia) on record.
- Tonga is famous as the location where Fletcher Christian forced William Bligh into an open boat during the mutiny on HMS Bounty (1789). Bligh briefly went ashore at Tofua, which was then heavily populated, in search of water. The Tongans fought Bligh and killed a member of his crew, forcing Bligh back out into the open ocean. Bligh and his small crew eventually made their way to the Dutch East Indies, setting a record for the longest voyage in an open boat (3618 nautical miles / 6701 km).
- In 1972, the military of Tonga took over the micronation Republic of Minerva, which had created an artificial island on the Minerva reefs.
- In Wil McCarthy's The Queendom of Sol, a series of science fiction novels, the Queen of Sol is said to be a descendant of the Tongan royal family.
- The Walt Disney film The Other Side of Heaven, is based on the real life story of a young (Mormon) missionary in Tonga, though the film was shot on location in the Cook Islands.