Battle of Grunwald
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Pre 1900 Military
- For the World War I battle in 1914 at the same location, refer to Battle of Tannenberg (1914)
| Battle of Grunwald | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Polish-Lithuanian-Teutonic War | |||||||
 Battle of Grunwald, by Jan Matejko, 1878. Oil on canvas. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Combatants | |||||||
| Kingdom of Poland Grand Duchy of Lithuania |
Teutonic Order and Mercenaries and Various Knights from the rest of Europe | ||||||
| Commanders | |||||||
| Władysław II Jagiełło, Vytautas the Great, Jan Sokol of Lamberk | Ulrich von Jungingen† | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 39,000 | 27,000 | ||||||
| Casualties | |||||||
| Unknown | 8,000 dead 2,000 captured |
||||||
| Polish-Lithuanian-Teutonic War |
|---|
| Bydgoszcz • Dąbrówno • Kurzętnik • Grunwald • Marienburg • Radzyń • Koronowo • Działdowo • Tuchola • Golub |
The Battle of Grunwald or Battle of Tannenberg took place on July 15, 1410 between the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and their allies on one side, and the Knights of the Teutonic Order on the other. It was the decisive battle of the Polish-Lithuanian-Teutonic War (1409-1411) and one of the greatest battles of medieval Europe.
The Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights was defeated in the battle and never recovered its former influence. The few eyewitness accounts of the battle are contradictory. It took place in the area of several smaller villages, and different names in various languages are attributed to it.
Names and Locations
The battle was fought in the plains between the villages of
- Grunwald (Žalgiris in Lithuanian),
- Stębark (Tannenberg in German) and
- Łodwigowo (Ludwigsdorf in German)
in what was then territory of the Order, and is now part of Poland. The nearest city of any size was Dąbrówno (Gilgenburg in German). The names Žalgiris (from the Lithuanian žalia giria) and Grunwald (from the German grüner Wald) both translate as "Green Forest." It was also called Zielone Pole ("Green Field") in Old Polish, and, in German, Grunenfelde or Grunefeld ("Green field") in the oldest texts.
The battle is called
- Schlacht bei Tannenberg (Battle of Tannenberg) by Germans,
- Žalgirio mūšis (Battle of Žalgiris) by Lithuanians,
- Bitwa pod Grunwaldem (Battle of Grunwald) by Poles,
- Гру́нвальдзкая бі́тва (Battle of Grunwald) by Belarusians,
- Ґрю́нвальдська би́тва (Battle of Grunwald) by Ukrainians and
- Grünwald suğışı by Tatars.
Eve of the battle
In the 13th century, the Teutonic Knights had been invited to the lands surrounding Chełmno to assist in the expulsion of the ( pagan) Prussians. They stayed on, and, under a papal edict which gave them effective carte blanche to act as they wished, established a power base in the region, occupying the Baltic coastal regions of what are now Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia, and showed every sign of further expansion. Their incursions into Poland in the 14th century gave them control of major towns such as Chełmno (Kulm) and Pomorze (Pommern) region. In order to further their war efforts against the (pagan) Lithuanian state, the Teutonic Knights instituted a series of crusades, enlisting support from other European countries.
In 1385 the Union of Kreva joined the crown of Poland and Lithuania, and the subsequent marriage of Grand Duke Jogaila of Lithuania and King Jadwiga of Poland (there was no title "Queen of Poland") was to shift the balance of power; both nations were more than aware that only by acting together could the expansion plans of the Teutonic Order be thwarted. Jogaila accepted Christianity and became the King of Poland as Władysław Jagiełło. Lithuania's conversion to Christianity removed much of the rationale of the Teutonic Knights' anti-pagan crusades. It can be said the Ordenstaat lost its raison d'etre.
The Knights, however, invaded again in 1398 what were now Christian states of Poland and Lithuania. At this time, the Poles and the Lithuanians had little option but to suffer in silence, for they were still not prepared militarily to confront the power of the Knights.
In 1409, an uprising in Teutonic-held Samogitia started. The king of Poland and Lithuania announced that he would stand by his promises in case the Teutons invaded Lithuania. This was used as a pretext, and on August 14, 1409 the Teutonic Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen declared war on the Polish-Lithuanian union. The forces of the Teutonic Order initially invaded Greater Poland and Kuyavia, but the Poles repelled the invasion and reconquered Bydgoszcz (Bromberg), which led to a subsequent armistice agreement that was to last until June 24, 1410. The Lithuanians and Poles used this time in preparations to remove the Teutonic threat once and for all.
The forces of the Teutonic Knights were aware of the Polish-Lithuanian build-up and expected a dual attack, by the Poles towards Danzig ( Gdańsk) and by the Lithuanians towards Samogitia. To counter this threat, Ulrich von Jungingen concentrated part of his forces in Schwetz ( Świecie) while leaving the large part of his army in the eastern castles of Ragneta/ Ragainė, Rhein ( Ryn) near Lötzen ( Giżycko), and Memel ( Klaipėda). Poles and Lithuanians continued to screen their intentions by organising several raids deep into enemy territory. Ulrich von Jungingen asked for the armistice to be extended to July 4 in order to let the mercenaries from western Europe arrive. Enough time had already been given for the Polish-Lithuanian forces to gather in strength.
On June 30, 1410, the forces of Greater Poland and Lesser Poland crossed the Vistula over a pontoon bridge and joined with the forces of Masovia and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Jagiełło's Polish forces and the Lithuanian soldiers of his cousin Vytautas the Great (to whom Jagiełło had ceded power in Lithuania in the wake of his marriage to the Polish queen) assembled on July 2, 1410. A week later they crossed into the territory of the Teutonic Knights, heading for the enemy headquarters at the castle of Marienburg ( Malbork). The Teutonic Knights were caught by surprise.
Ulrich von Jungingen withdrew his forces from the area of Schwetz ( Świecie) and decided to organise a line of defence on the river Drewenz ( Drwęca). The river crossings were fortified with stockades and the castles nearby reinforced. After meeting with his War Council, Jagiełło decided to out flank the enemy forces from the East and continue the march towards Marienburg through Soldau ( Działdowo) and Gilgenburg ( Dąbrówno). On July 13, these two castles were captured and the way towards Marienburg was opened.
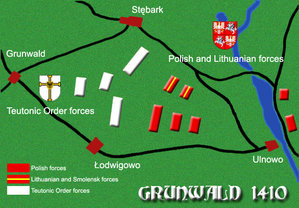
Opposing forces
In the early morning of July 15, 1410, both armies met in the fields near the villages of Grunwald, Tannenberg and Łodwigowo (Ludwigsdorf). Both armies were dislocated in line formations. The Polish-Lithuanian army was set up in front of the villages of Łodwigowo/Ludwigsdorf and Stębark/Tannenberg. The left flank was guarded by the Polish forces of king Władysław Jagiełło and composed mostly of heavy cavalry. The right flank of the allied forces was guarded by the army of Grand Duke Vytautas, and composed mostly of light cavalry. Among the forces on the right flank were banners from all over the Grand Duchy, as well as Tatar skirmishers and (probably) Moldavian mercenaries. The opposing forces of the Teutonic Order were composed mostly of heavy cavalry and infantry. They were aided by mercenaries from Western Europe called "the guests of the Order," and some other Knights including those of the Knights Templar who had been summoned to participate by a Papal Bull.
The exact number of soldiers on both sides is hard to estimate. There are only two reliable sources describing the battle. The best-preserved and most complete was written by Ioannes Longinus but does not mention the exact numbers. The other is incomplete and preserved only in a brief 16th century document. Months after the battle, in December 1410, the Order's new Grand Master Heinrich von Plauen the Elder sent letters to Western European monarchs in which he described the battle as a war against the forces of evil pagans. This view was shared by many chronicle writers. Since the outcome of the battle was subject to propaganda campaigns on both sides, many foreign authors frequently overestimated the Polish-Lithuanian forces in an attempt to explain the dramatic result.
In one of the Prussian chronicles it is mentioned that "the forces of the Polish king were so numerous that there is no number high enough in the human language". One of the anonymous chronicles from the German Hanseatic city of Lübeck mentions that the forces of Jagiello numbered some 1,700,000 soldiers, the forces of Vytautas with 2,700,000 (as well as a great number of Ruthenians), in addition to 1,500,000 Tatars. Among the forces supposedly aiding the Polish-Lithuanian army were " Saracens, Turks, pagans of Damascus, Persia and other lands". According to Enguerrand de Monstrelet, the Teutons fielded some 300,000 men, while their enemies under the kings of "Lithuania, Poland and Sarmatia" fielded 600,000. Andrew of Regensburg estimated the Polish-Lithuanian forces at 1,200,000 men-at-arms.
More recent historians estimate the strength of the opposing forces at a much lower level. Ludwik Kolankowski estimated the Polish-Lithuanian forces at 16,000-18,000 Polish cavalry and 6,000-8,000 Lithuanian light cavalry, with the Teutonic Knights fielding 13,000-15,000 heavy cavalry. Jerzy Dąbrowski estimated the overall strength of the allied forces at 18,000 Polish cavalry and 11,000 Lithuanians and Ruthenians, with the opposing forces bringing 16,000 soldiers.
| Historian | Poland | Lithuania | Others | Teutonic Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lübeck Chronicle | 1 700 000 | 2 700 000 | 1 500 000 | |
| Enguerrand de Monstrelet | 600 000 | 300 000 | ||
| Andrew of Regensburg | 1 200 000 | |||
| Ludwik Kolankowski | 18 000 heavy cavalry | 8 000 light cavalry | 15 000 heavy cavalry | |
| Jerzy Dąbrowski | 18 000 | 11 000 | 16 000 + 3 000 guests | |
| Henryk Łowmiański | 12 000 heavy cavalry | 7 200 light cavalry | 11 000 heavy cavalry | |
| Andrzej Nadolski | 20 000 | 10 000 | 1000 |
Regardless of such estimates, most of the modern historians count only the cavalry units. Apart from 16,000 cavalry, the Teutonic Order also fielded some 9,000 infantry, archers and crossbow troops. Both armies also had large military camps, tabors and other units, which made up some 10% of their total strength.
Both armies were organised in banners. Each heavy cavalry banner was composed of approximately 240 mounted knights as well as their squires and armour-bearers. Each banner flew its own standard and fought independently. Lithuanian banners were usually weaker and composed of approximately 180 light cavalry soldiers. The structure of foot units ( pikemen, archers, crossbowmen) and the artillery is unknown.
The forces on both sides were composed of troops coming from a variety of countries and lands. Apart from units fielded by lands of Poland, Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Teutonic Order, there were also mercenaries from Western Europe (most notably Alsace, Lorraine, German Countries, Moravia, Bohemia and probably Moldavia. Historians of the Soviet Union attempted to overemphasize the Russian role in the battle. For example, they included some Lithuanian banners, such as Smolensk, into the Russian list. They also phrased the desciption of the battle to make it appear that the support from Russian lands was decisive. In fact there was a joke that "the battle with the fascist Teutons was won by joint Polish-Soviet forces" (most of the territory of the Grand Duchy was part of the Soviet Union in the 20th century).
The overall commander of the joint Polish-Lithuanian forces was king Władysław Jagiełło, with the Polish units subordinated to Marshal of the Crown Zbigniew of Brzezie and Lithuanian units under the immediate command of Grand Duke of Lithuania Vytautas. Until recently it was believed that the Sword Bearer of the Crown Zyndram of Maszkowice was the commander in chief of the joint army, but this idea was based on a false translation of the description of the battle by Ioannes Longinus. The Teutonic Forces were commanded directly by the Grand Master of the Order Ulrich von Jungingen.
Course of the battle
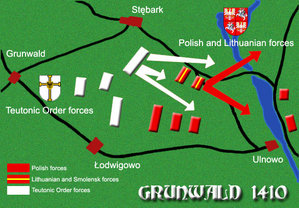
The opposing forces formed their lines at dawn. At noon the forces of Grand Duke of Lithuania Vytautas started an all-out assault on the left flank of the Teutonic forces, near the village of Tannenberg ( Stębark). The Lithuanian cavalry was supported by a cavalry charge of several Polish banners on the right flank of the enemy forces. The enemy heavy cavalry counter-attacked on both flanks and fierce fighting occurred.
After more than an hour, the Lithuanian light cavalry started a planned retreat maneuver towards marshes and woods. This maneuver was often used in the east of Grand Duchy of Lithuania by Mongols. Vytautas, who had experience in battles against Mongols, used it in this battle. Only three banners of Smolensk commanded by Lengvenis (Simon Lingwen), son of Algirdas, brother of Jagiełło and a cousin of Vytautas, remained on the right flank after the retreat of Vytautas and his troops. One of the banners was totally destroyed, while the remaining two were backed up by the Polish cavalry held in reserve and broke through the enemy lines to the Polish positions.
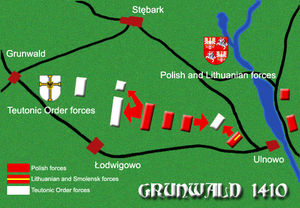
Heavy cavalry of the Order started a disorganised pursuit after the retreating Lithuanians, which might have been a fatal mistake. The Knights entered the marshes, where Vytautas reorganized his forces to return to battle.
At the same time heavy fighting continued on the left flank of the Polish forces. After several hours of massed battle, the Teutonic cavalry started to gain the upper hand. According to Ioannes Longinus the Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen personally led a cavalry charge on the strongest Polish unit — the Banner of the Land of Kraków. The Polish ranks started to waver and the flag of the banner was lost. However, it was soon recaptured by the Polish knights, and king Władysław Jagiełło ordered most of his reserves to enter combat.
The arrival of fresh troops allowed the Poles to repel the enemy assault and the forces of Ulrich von Jungingen were weakened. At the same time his reserves were still busy pursuing the evading Lithuanian cavalry. When they finally returned to the battlefield, it was already too late for the Teutonic charge to succeed and the forces of the Order started the withdrawal.
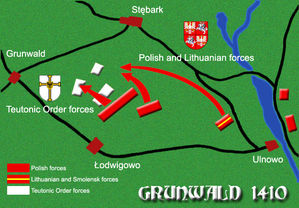
After several hours of fighting, Ulrich von Jungingen decided to join his embattled forces in the main line of engagement. Vytautas, however, also returned to the battlefield with the reorganized forces of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and joined the fierce fighting. The Teutonic forces were by then becoming outnumbered by the mass of Polish knights and the advancing Lithuanian infantry, which all of a sudden had come pouring on the battlefield from the surrounding forests.
Ulrich von Jungingen personally led the assault with 16 banners of heavy cavalry, which until then were held in reserve. Jagiełło, however, threw in all his remaining reserves, as well as several already tired units. Putting up heavy resistance, the 16 banners of the Great Master were surrounded and began to suffer high losses, including the Grand Master himself, who was probably killed by Polish peasantry. Seeing the fall of their Grand Master, the rest of the Teutonic forces started to withdraw towards their camp.
Part of the routed units retreated to the forests where they were pursued by the Lithuanian and Polish cavalry, while the rest retreated to the camp near the village of Grunwald, where they tried to organise the defence by using the tabor tactics: the camp was surrounded by wagons tied up with chains, serving as a mobile fortification. However, the defences were soon broken and the camp was looted. According to the anonymous author of the Chronicle of the Conflict of Ladislaus King of Poland with the Teutons Anno Domini 1410, there were more bodies in and around the camp than on the rest of the battlefield. The pursuit after the fleeing Teutonic cavalry lasted until the dusk.
Despite the technological superiority of the Teutonic Knights, to the point of this being believed to be the first battle in this part of Europe in which field-artillery was deployed, the numbers and tactical superiority of the Polish Lithuanian alliance were to prove overwhelming.
Jan Žižka of Trocnov lost his first eye in the battle, fighting for the Lithuanians.
After the Battle
The defeat of the Teutonic Order was resounding. According to Andrzej Nadolski about 8,000 Teuton soldiers were killed in the battle, and an additional 14,000 taken captive. Most of the approximately 250 members of the Order were also killed, including much of the Teutonic leadership. Apart from Ulrich von Jungingen himself, the Polish and Lithuanian forces killed also the Grand Marshal Friedrich von Wallenrode, Grand Komtur Kuno von Lichtenstein and Albrecht von Schwartzburg, the Grand Treasurer Thomas von Merheim.
Markward von Salzbach, the Komtur of Brandenburg, and mayor Schaumburg of Sambia were executed by order of Vytautas after the battle. The only higher officials to escape from the battle were Grand Hospital Master and Komtur of Elbing Werner von Tettinger. Such a slaughter of noble knights and personalities was quite unusual in Mediæval Europe. This was possible mostly due to the participation of the peasantry who joined latter stages of the battle, and took part in destruction of the surrounded Teutonic troops. Unlike the noblemen, the peasants did not receive any ransom for taking captives; they thus had less of an incentive to keep them alive. Among those taken captive were Kasimir V, duke of Stettin ( Szczecin), and Konrad the White, duke of Oels ( Oleśnica).
After the battle Polish and Lithuanian forces stayed on the battlefield for three days. All notable officials were interred in separate graves, while the body of Ulrich von Jungingen was covered with royal coat and transported to Marienburg. The rest of the dead were gathered in several mass graves. There are different speculations as to why Jagiello decided to wait that long. After three days, the Polish-Lithuanian forces moved on to Marienburg and laid siege upon the castle, but the three days time was enough for the Teutons to organise the defence. After several weeks of siege, the Lithuanian Grand Duke withdrew from the war and it became clear that the siege would not be effective. The nobility from Lesser Poland also wanted to end the war before the harvest and the siege was lifted.
In the battle, both Polish and Lithuanian forces took several thousand captives. Most of the mercenaries were released shortly after the battle on the condition that they will return to Krakow on 29 September 1410. After that move, the king held most of the Teutonic officials, while the rest returned to Prussia to beg the Teutonic Order officials for their liberation and ransom payment. This proved to be a major drain of the Teutonic budget as an average rate for a knight was quite high. For instance, one of the mercenaries named Holbracht von Loym had to pay sixty times the number of 150 Prague groszes, that is almost 300 kilograms of pure silver, a value uncommon even in modern times. With his army defeated and the remnants of it composed mostly of ill-paid mercenaries, Heinrich von Plauen the Elder had little incentive to continue the fight, especially that most of the cities owned by the Teutons sworn their loyalty to the Polish king. Thus, after retaking Danzig from rebellious burghers, the peace negotiations were started.
The Peace of Thorn ( Peace of Torun) was concluded as a result of the Battle of Grunwald, in which Poland annexed the Dobriner Land ( Dobrzyń Land) and Lithuania recovered Samogitia. This is thought to be a diplomatic defeat for Poland and Lithuania as they pushed for attempts to dismantle the Teutonic Knights state altogether. However, while the Poles and Lithuanians were unable to translate their military victory to greater political gains, the indirect results of the battle were much worse for the Teutons. The massacre of Teutonic troops left them with few forces to defend their remaining territories. The Grand Masters from then on had to rely on mercenary troops, which proved too expensive for the Teutons' budget to sustain. Although Heinrich von Plauen the Elder, the successor to Ulrich von Jungingen, managed to save his state from complete breakdown, the opposition to his rule among the burghers, the knights and within the Order itself forced his ouster.
The Teutons' lost support due to their internal conflicts and constant tax increases, which decades later was manifested in the foundation of the Prussian Confederation, or Alliance against Lordship. This led to a series of conflicts that culminated in the Thirteen Years' War, ending with another defeat of the victorious order.
Influences of the Battle of Grunwald on modern culture
Poland
The battle of Grunwald is regarded as one of the most important battles in Polish history. It is often depicted by an ideogram of two swords, which were supposedly given to king Jagiello before the battle by the Teutonic envoys to "raise Polish desire for battle".
In 1914, on the eve of World War I, during the celebrations marking the 500-year anniversary of the battle a monument was erected in Kraków. The ceremony spawned demonstrations of outrage within Polish society against the aggressive politics of the German Empire, including the forcible Germanization of Poles after the partitions of Poland. Polish poet Maria Konopnicka wrote the fiercely Polish-patriotic and anti-German poem Rota. About the same time, Henryk Sienkiewicz wrote his novel The Teutonic Knights (Polish: Krzyżacy) , one of his series of books designed to increase the patriotic spirit among the Poles. The book was eventually depicted in the film The Teutonic Knights by Aleksander Ford. Today, a festival is held every year to commemorate this medieval battle. Thousands of medieval reenactors, many of them in knight's armor, from all across Europe gather every year in July at the Grunwald fields to reconstruct the battle again. Great care is put to the historical details of the armour, weapons and the conduct of the battle.
Order Krzyża Grunwaldu (The Cross of Grunwald medal) was a Polish military decoration created in 1943 by the commander of the Gwardia Ludowa (confirmed in 1944 by the Krajowa Rada Narodowa) which was awarded for heroism in World War II.
In Poland there are sport teams named "Grunwald"' like Grunwald Poznań.
Belarus
The victory in the Battle of Grunwald is widely respected and commemorated in Belarus. In 15th century the lands of modern-day Belarus were a part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Many of cities from what is today Belarus sent their troops to the battle to fight on the Grand Duchy's side.
Lithuania
The victory at the Battle of Grunwald or Žalgirio mūšis in 1410 is synonymous to the peak of the political and military power of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The demise of the Teutonic order ended the period of German expansion and created preconditions for the political stability, economic growth and relative cultural prosperity that lasted until the rise of Muscovy in the late 16th century. In the Lithuanian historical discourse regarding the battle there is a lasting debate and controversy over the role played by the Lithuanian-born king of Poland Jogaila, and his cousin, the Grand Duke of Lithuania, Vytautas, the latter usually being favoured as a national hero.
Leading Lithuanian basketball and football teams are both called "Žalgiris" to commemorate the victorious battle BC Žalgiris and FK Žalgiris.
The term Žalgiris became a symbol of the resistance to the foreign domination over Lithuania. The victories of the basketball club BC Žalgiris Kaunas against the Soviet Army sports club CSKA Moscow (in the late 1980s) served as a major emotional inspiration for the Lithuanian national revival, and the consequent emergence of the Sąjūdis movement that led to the collapse of the USSR.
Germany
In Germany the battle was known as the Battle of Tannenberg. In 1914 yet another Battle of Tannenberg took place between Germany and Russia, ending with a Russian defeat. In German propaganda during the WWI / WWII period the 1914 battle was put forth as a revenge for the Polish - Lithuanian victory 504 years earlier, and the battle itself was purposefully named to suit this agenda.
Russia and Soviet Union
Due to participation of Smolensk regiment in the battle, Soviet propaganda depicted the battle as Polish-Lithuanian-Russian coalition against invading Germans.
Banners
Poland
The exact Order of Battle of the Polish forces is unknown. However, Ioannes Longinus in his Historiæ Polonicæ written after 1455 recorded 51 Polish banners, together with their descriptions, blazoning and commanders. It is not certain whether the list is complete.
| Banner of | Battle sign | Origin | Remarks | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army of The Crown - Court Banners | |||||||||||||
| Great Banner of Kraków and the Kingdom of Poland | Elite troops, under Zyndram of Maszkowice | ||||||||||||
| "Gończa" Court Banner | under Andrzej of Ochocice of Osorya | ||||||||||||
| Pogoń Court Banner | under Andrzej Ciołek of Żelechów and Jan of Sprowa of Odrowąż | ||||||||||||
| Saint George | Bohemian and Moravian mercenaries, under Sokol and Zbyslavek | ||||||||||||
| Army of The Crown - Regional Banners | |||||||||||||
| Greater Poland | |||||||||||||
| Land of Sandomierz | |||||||||||||
| Kalisz | |||||||||||||
| Land of Sieradz | |||||||||||||
| Land of Lublin | |||||||||||||
| Land of Łęczyca | |||||||||||||
| Land of Cuyavia | |||||||||||||
| Land of Lwów | |||||||||||||
| Land of Wieluń | Reinforced with mercenaries from Silesia | ||||||||||||
| Land of Przemyśl | |||||||||||||
| Dobrzyń | |||||||||||||
| Land of Chełm | |||||||||||||
| Three banners of Podolia | Split up due to large number of knights | ||||||||||||
| Land of Halicz | |||||||||||||
| Army of The Crown - Masovian Banners | |||||||||||||
| Two banners of Duke Siemowit IV of Masovia |
Masovia, mostly Płock area | Dukes of Masovia | |||||||||||
| Duke Janusz I of Masovia | Masovia, mostly Warsaw area | Dukes of Masovia | |||||||||||
| Army of The Crown - Personal Banners | |||||||||||||
| Archbishop of Gniezno Mikołaj Kurowski |
|||||||||||||
| Bishop of Poznań ; Wojciech Jastrzębiec |
under Jarand of Brudzewo | ||||||||||||
| Castellan of Kraków Krystyn of Ostrów |
|||||||||||||
| Voivod of Kraków Jan of Tarnów |
|||||||||||||
| Voivod of Poznań Sędziwój of Ostroróg |
|||||||||||||
| Voivod of Sandomierz Mikołaj of Michałowo |
|||||||||||||
| Voivod of Sieradz Jakub of Koniecpol |
|||||||||||||
| Castellan of Śrem Iwo of Obiechów |
|||||||||||||
| Voivod of Łęczyca Jan Ligęza |
|||||||||||||
| Castellan of Wojnice Andrzej of Tęczyn |
|||||||||||||
| Marshal of The Crown Zbigniew of Brzezie |
|||||||||||||
| Chambelain of Kraków Piotr Szafraniec |
|||||||||||||
| Castellan of Wiślica Klemens of Moskorzów |
|||||||||||||
| Castellan of Śrem and mayor of Greater Poland Wincenty of Granów |
|||||||||||||
| Dobko of Oleśnica | |||||||||||||
| Spytko of Tarnów | |||||||||||||
| Lord High Steward of Kalisz Marcin of Sławsko |
|||||||||||||
| Dobrogost Świdwa of Szamotuły | |||||||||||||
| Krystyn of Koziegłowy | |||||||||||||
| Master King's Cup-Bearer Jan Mężyk |
|||||||||||||
| Deputy Chancellor of the Crown Mikołaj Trąba |
|||||||||||||
| Mikołaj Kmita of Wiśnicz | |||||||||||||
| Gryf Clan | Family of Gryf, under Zygmunt of Bobowa | ||||||||||||
| Zaklika of Korzkiew | |||||||||||||
| Clan of Koźlerogi | Family, under Castellan of Wiślica Florian of Korytnica | ||||||||||||
| Jan of Jičín | Moravia | Volunteers from Moravia, commanded by certain Helm | |||||||||||
| Steward of the Crown and starost of Lwów Gniewosz of Dalewice |
Silesia, Bohemia and Moravia | Only foreign volunteers and mercenaries | |||||||||||
| Duke of Lithuania Sigismund Korybut | |||||||||||||
Lithuania
Due to different system of feudal overlordship, as well as lack of heraldic traditions, the units of Grand Duchy of Lithuania were all grouped under banners of two types: the Vytis and the Columns of Gediminas. The only difference between various lands using the same emblem was the blazon. The hareness and the colour of the horse on the Pahonia differed.
Note that the number of Lithuanian banners is uncertain. According to Ioannes Longinus there were 40 banners on the right flank of the Polish-Lithuanian forces, 10 flying the Columns of Gediminas and 30 flying the Vytis. However, he also mentions that there might have been 2 additional banners from Smolensk and up to six additional banners of Samogitia. German authors also mention that there were three auxiliary banners of Moldavia flying their own flags. In addition, it is probable that the units from Trakai, Volhynia, Smolensk, Kiev and Nowogrodek used their own emblems.
| Banner of | Battle sign | Origin | Remarks | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Army of the Grand Duchy - Flying the Vytis Banners | |||||||||||||
| Vytautas the Great | |||||||||||||
| Minsk | |||||||||||||
| Polock | |||||||||||||
| Hrodna | |||||||||||||
| Kreva | |||||||||||||
| Krichev | |||||||||||||
| Mahileu | |||||||||||||
| Niasvizh | |||||||||||||
| Novgorod | |||||||||||||
| Nowogrod Siewierski | |||||||||||||
| Orsha | |||||||||||||
| Slonim | |||||||||||||
| Slutsk | |||||||||||||
| Vitsebsk | |||||||||||||
| Vladzimir | |||||||||||||
| Army of the Grand Duchy - Flying the Columns Banners | |||||||||||||
| Sigismund Kestutaitis | |||||||||||||
| Manvydas | |||||||||||||
| Yurij, son of Lengvenis | |||||||||||||
| Trakai | |||||||||||||
| Vilnius | |||||||||||||
| Hrodna | |||||||||||||
| Kaunas | |||||||||||||
| Lida | |||||||||||||
| Medininkai | |||||||||||||
| Three (?) Banners of Smolensk | under Lengvenis (Simon Lingwen) | ||||||||||||
| Vitebsk | |||||||||||||
| Kiev | |||||||||||||
| Pinsk | |||||||||||||
| Navahradak | |||||||||||||
| Brest | |||||||||||||
| Wolkowysk | |||||||||||||
| Drohiczyn | |||||||||||||
| Mielnik | |||||||||||||
| Krzemieniec | |||||||||||||
| Starodub | |||||||||||||
| Auxiliary Units | |||||||||||||
| Lipka Tatars | none | approximately 1000 skirmishers under Jalal ad-Din | |||||||||||
| Three Banners of Moldavia | approximately 900 foot soldiers and 25 knights under Logofat Mihaiu Alexandrel | ||||||||||||
Related reading
Non-fiction
- Stefan Kuczyński, Szymon Kobyliński, Chorągwie grunwaldzkich zwycięzców (The Banners of the Victors of Grunwald); WAiF, Warsaw, 1989. ISBN 83-221-0467-7
- Ioannes Longinus, Annales seu Cronicæ Incliti Regni Poloniæ; PWN, Warsaw, 2000. ISBN 83-01-13301-5
- Ioannes Longinus, Bitwa grunwaldzka; Ossolineum, Wrocław, 2003. ISBN 83-04-04632-6
- Mečislovas Jučas, Žalgirio mūšis (Battle of Grunwald); Mokslas, Vilnius, 1990. ISBN 5-420-00242-6
- Sven Ekdahl, Die Schlacht bei Tannenberg 1410. Quellenkritische Untersuchungen. Bd. 1: Einführung und Quellenlage. ISBN 3-428-05243-9
- Sven Ekdahl Die "Banderia Prutenorum" des Jan Dlugosz: Eine Quelle zur Schlacht bei Tannenberg 1410 : Unters. zu Aufbau, Entstehung u. Quellenwert d. Hs. : mit e. ... Klasse ; Folge 3, Nr. 104). ISBN 3-525-82382-7
Fiction
- Henryk Sienkiewicz, Krzyżacy ( The Teutonic Knights); Tygodnik Ilustrowany, Kraków, 1900. ISBN 0-7818-0433-7
- James A. Michener, Poland; Random House, 1984. ISBN 0-449-20587-8