Ancient history
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General history
Ancient history is the study of significant cultural and political events from the beginning of human history until the Early Middle Ages. The goal of the modern day critical ancient historian is objectivity.
The term classical antiquity is often used to refer to ancient history since the beginning of ancient Greek history in about 776 BC. This coincides roughly with the traditional date of the founding of Rome in 753 BC, the beginning of the history of ancient Rome.
Although the ending date of ancient history is disputed, currently most Western scholars use the fall of the Western Roman Empire in AD 476 as the end of ancient European history.
The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 – 5,500 years, with Sumerian cuneiform being the oldest form of writing discovered so far. Thus, this is the beginning of history by the definition used by all historians.
The times before writing belong either to protohistory or to prehistory.
The study of ancient history
The fundamental difficulty of studying ancient history is the fact that only a fraction of it has been documented, and only a fraction of those recorded histories have survived into the present day. Literacy was not widespread in any culture until long after the end of ancient history, so there were few people capable of writing histories. Even those written histories which were produced were not widely distributed; the ancients, not having the luxury of a printing press had to make copies of books by hand. The Roman Empire was one of the ancient West's most literate cultures, but many works by its most widely read historians are lost. For example, Livy, a Roman historian who lived in the 1st century BC, wrote a history of Rome called Ab Urbe Condite ("From the Founding of the City") in 142 volumes. Only 35 still survive. Historians have two major avenues which they take to better understand the ancient world: archaeology and the study of primary sources.
Archaeology
Archaeology is the study of material remains in an effort to interpret and reconstruct past human behaviour. In the study of ancient history, archaeologists excavate the ruins of ancient cities looking for clues as to how the people of the time period lived.
Some important discoveries by archaeologists studying ancient history include:
- The Egyptian pyramids - giant tombs built by the ancient Egyptians beginning around 2600 BC as the final resting places of their royalty.
- The study of the ancient cities of Harappa, Mohenjo-daro and Lothal in South Asia.
- The city of Pompeii - an ancient Roman city preserved by the eruption of a volcano in 79 AD. Its state of preservation is so great that it is an invaluable window into Roman culture.
- The Terracotta Army - the mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor in ancient China.
Chronology
Prehistory
- early human migrations
- Lower Paleolithic— Homo erectus spreads across Eurasia. Controlled use of fire from ca. 800 kya.
- c. 200 kya— Homo sapiens evolves in Africa
- c. 80 kya—Modern humans migrate out of Africa to the Near East
- c. 70 kya—Modern humans spread across Asia and reach Australia
- c. 40 kya—Europe first reached by modern humans
- c. 15 kya— Americas first reached by humans
- 10th millennium BC— Invention of agriculture is the earliest given date for the beginning of the ancient era
- 5th millennium BC—late Neolithic civilizations, invention of the wheel and spread of proto-writing.
- 4th millennium BC—First writings in the cities of Uruk and Susa ( cuneiform writings); followed by inscriptions in Harappa and hieroglyphs in Egypt
- 33rd century BC—Oldest historical documents (see history of writing)
History
Some important events:
The older ancient history
Bronze Age through to the Early Iron Age
- 3500 BC—Sumer, arises in Mesopotamia.
- 3100 BC— First dynasty of Egypt
- 3300 BC—Bronze Age begins in the Near East (Sumer and ancient Egypt), Bronze Age slowly begins spreading to the rest of Eurasia
- 3200 BC—Rise of Proto-Elamite Civilization
- 3138 BC— Kurukshetra War, took place between the Kauravas and the Pandavas in ancient Bharat (India) resulting in the death of 1.3 million people
- 3000 BC— Jiroft Civilization Begins
- 3000 BC—Rise of the Nile Valley civilization
- 3000 BC—First known use of papyrus by Egyptians
- 2800 BC—Kot Diji phase of the Indus Valley Civilization begins
- 2700 BC—Rise of Elam in Iran
- 2600 BC—Mature Harappan phase of the Indus Valley civilization (in present-day Pakistan and India) begins
- 2550 BC—Completion of the Great Pyramid of Giza
- 2000 BC— Domestication of the horse
- 1700 BC—Indus Valley Civilization comes to an end but is continued by the Cemetery H culture; The beginning of Poverty Point Civilization in North America
- 1600 BC—The beginning of Shang Dynasty in China, development of first Chinese writing system
- 1600 BC—Beginning of Hittite dominance of the Eastern Mediterranean region
- 1500 BC—Composition of the Rigveda is completed.
- c. 1200 BC—Theorized time of the Trojan War
- c. 1180 BC—Disintegration of Hittite Empire
- 1122 BC—The Zhou people overthrow the last king of Shang Dynasty; Zhou Dynasty established in China
- 1000 BC— Mannaeans Kingdom Begins
- 800 BC—Rise of Greek city-states
- 776 BC—First recorded Olympic Games. The history of the Games is believed to reach as far back as the 13th century BC but no older written record survives.
The latter ancient history
- 753 BC—Founding of Rome (traditional date)
- 751 BC—The Rise of LeChe
- 745 BC— Tiglath-Pileser III becomes the new king of Assyria. With time he conquers neighboring countries and turns Assyria into an empire
- 728 BC—Rise of the Iranian Median Empire
- 722 BC— Spring and Autumn Period begins in China; Zhou Dynasty's power is diminishing; the era of the Hundred Schools of Thought
- 700 BC the construction of Marib Dam in Arabia Felix
- 653 BC—Rise of first Persian state of Iran
- 612 BC—Attributed date of the destruction of Nineveh and subsequent fall of Assyria.
- 600 BC—Sixteen Maha Janapadas ("Great Realms" or "Great Kingdoms") emerge. A number of these Maha Janapadas are semi- democratic republics.
- c 600 BC— Pandyan kingdom in South India
- 563 BC— Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha), founder of Buddhism is born as a prince of the Shakya tribe, which ruled parts of Magadha, one of the Maha Janapadas
- 551 BC—Confucius, founder of Confucianism, is born
- 549 BC— Mahavira, founder of Jainism is born
- 546 BC—Foundation of the Persian Empire and unification of Iran by Cyrus the Great
- 546 BC—Cyrus the Great overthrows the Lydian kingdom
- 544 BC—Rise of Magadha as the dominant power under Bimbisara.
- 539 BC—The Fall of the Babylonian Empire and liberation of the Jews by Cyrus the Great
- 525 BC— Cambyses II of Persia conquers Egypt
- c. 512 BC— Darius I (Darius the Great) of Persia, subjugates eastern Thrace, Macedonia submits voluntarily, and annexes Libya, Persian Empire at largest extent
- 509 BC—Expulsion of the last King of Rome, founding of Roman Republic (traditional date)
- 500 BC— Panini standardizes the grammar and morphology of Sanskrit in the text Ashtadhyayi. Panini's standardized Sanskrit is known as Classical Sanskrit
- 500 BC— Pingala uses zero and binary numeral system.
- 490 BC—Greek city-states defeat Persian invasion at Battle of Marathon
- 475 BC— Warring States Period begins in China as the Zhou king became a mere figurehead; China is annexed by regional warlords
- 424 BC— Nanda dynasty comes to power.
- 404 BC—End of Peloponnesian War between the Greek city-states
- 331 BC—Alexander the Great defeats Darius III of Persia in the Battle of Gaugamela
- 326 BC—Alexander the Great defeats Indian king Porus ( Purushottama) in the Battle of the Hydaspes River.
- 321 BC— Chandragupta Maurya overthrows the Nanda Dynasty of Magadha
- 323 BC—Death of Alexander the Great
- 305 BC— Chandragupta Maurya seizes the satrapies of Paropanisadai (Kabul), Aria (Herat), Arachosia (Qanadahar) and Gedrosia (Baluchistan)from Seleucus I Nicator, the Macedonian satrap of Babylonia, in return for 500 elephants.
- 273 BC— Ashoka the Great becomes the emperor of the Mauryan Empire
- 250 BC—Rise of Parthia (Ashkâniân), the second native dynasty of ancient Iran
- 232 BC—Death of Emperor Ashoka the Great; Decline of the Mauryan Empire
- 230 BC—Emergence of Satavahanas in South India
- 221 BC—Qin Shi Huang unifies China, end of Warring States Period; beginning of Imperial rule in China which lasts until 1912
- 202 BC— Han Dynasty established in China, after the death of Qin Shi Huang; China in this period officially becomes a Confucian state and opens trading connections with the West, i.e. the Silk Road
- 202 BC— Scipio Africanus defeats Hannibal at Battle of Zama
- c 200 BC— Chera dynasty in South India
- 185 BC— Sunga Empire founded.
- 149 BC- 146—Third and final Punic War; destruction of Carthage by Rome
- 146 BC—Roman conquest of Greece, see Roman Greece
- 110 BC— First Chinese domination of Vietnam in the form of the Nanyue Kingdom.
- c 100 BC—Chola dynasty rises in prominence.
- 49 BC—Roman Civil War between Julius Caesar and Pompey the Great
- 44 BC—Julius Caesar murdered by Marcus Brutus and others; End of Roman Republic; beginning of Roman Empire
- 6 BC—Earliest theorized date for birth of Jesus of Nazareth
- 4 BC—Widely accepted date (Ussher) for birth of Jesus Christ
- 9— Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, the Roman Army's bloodiest defeat
- 14—Death of Emperor Augustus (Octavian), ascension of his adopted son Tiberius to the throne
- 29—Crucifixtion of Jesus Christ.
- 68— Year of the four emperors in Rome
- 70—Destruction of Jerusalem by the armies of Titus.
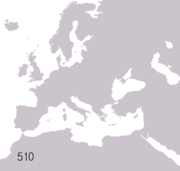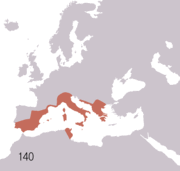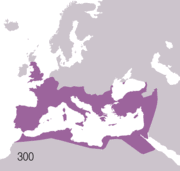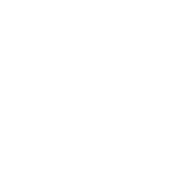
- 117—Roman Empire at largest extent under Emperor Trajan
- 200s—The Hindu Srivijaya Empire established in the Malay Archipelago.
- 220— Three Kingdoms period begins in China after the fall of Han Dynasty
- 226—Fall of the Parthian Empire and Rise of the Sassanian Empire
- 238—Defeat of Gordian III (238–244), Philip the Arab (244–249), and Valerian (253–260), by Shapur I of Persia, (Valerian was captured by the Persians).
- 285— Emperor Diocletian splits the Roman Empire into Eastern and Western Empires
- 313— Edict of Milan declared that the Roman Empire would be neutral toward religious worship
- 335— Samudragupta becomes the emperor of the Gupta empire
- 378— Battle of Adrianople, Roman army is defeated by the Germanic tribes
- 395— Roman Emperor Theodosius I outlaws all pagan religions in favour of Christianity
- 410— Alaric sacks Rome for the first time since 390 BC
- c. 455— Skandagupta repels an Indo-Hephthalite attack on India.
- 476—Romulus Augustus, last Western Roman Emperor is forced to abdicate by Odoacer, a half Hunnish and half Scirian chieftain of the Germanic Heruli; Odoacer returns the imperial regalia to Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno in Constantinople in return for the title of dux of Italy; most frequently cited date for the end of ancient history
End of ancient history in Europe
The date used as the end of the ancient era is entirely arbitrary and is a matter of some dispute amongst historians. Some other dates that are given for the end of antiquity are:
- 293—reforms of Roman Emperor Diocletian
- 395—the division of Roman Empire into the Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire
- 476—the fall of Western Roman Empire
- 529—closure of Platon Academy in Athens by Byzantine Emperor Justinian I
Some prominent civilizations of ancient history
Europe and the Mediterranean
- Carthage
- Etruscans
- Hittites
- Phoenicia
- Scythians
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, which begins roughly with the earliest-recorded Greek poetry of Homer (7th century BC), and continues through the rise of Christianity and the fall of the Western Roman Empire (5th century AD), ending in the dissolution of classical culture with the close of Late Antiquity.
Such a wide sampling of history and territory covers many rather disparate cultures and periods. "Classical antiquity" typically refers to an idealized vision of later people, of what was, in Edgar Allan Poe's words, "the glory that was Greece, the grandeur that was Rome!"
In the 18th and 19th centuries reverence for classical antiquity was much greater in Western Europe and the United States than it is today. Respect for the ancients of Greece and Rome affected politics, philosophy, sculpture, literature, theatre, education, and even architecture and sexuality.
In politics, the presence of a Roman Emperor was felt to be desirable long after the empire fell. This tendency reached its peak when Charlemagne was crowned "Roman Emperor" in the year 800, an act which led to the formation of the Holy Roman Empire. The notion that an emperor is a monarch who outranks a mere king dates from this period. In this political ideal, there would always be a Roman Empire, a state whose jurisdiction extended to the entire civilised world.
Epic poetry in Latin continued to be written and circulated well into the nineteenth century. John Milton and even Arthur Rimbaud got their first poetic educations in Latin. Genres like epic poetry, pastoral verse, and the endless use of characters and themes from Greek mythology left a deep mark on Western literature.
In architecture, there have been several Greek Revivals, (though while apparrently more inspired in retrospect by Roman architecture than Greek). Still, one needs only to look at Washington, DC to see a city filled with large marble buildings with façades made out to look like Roman temples, with columns constructed in the classical orders of architecture.
In philosophy, the efforts of St Thomas Aquinas were derived largely from the thought of Aristotle, despite the intervening change in religion from paganism to Christianity. Greek and Roman authorities such as Hippocrates and Galen formed the foundation of the practice of medicine even longer than Greek thought prevailed in philosophy. In the French theatre, tragedians such as Molière and Racine wrote plays on mythological or classical historical subjects and subjected them to the strict rules of the classical unities derived from Aristotle's Poetics. The desire to dance like a latter-day vision of how the ancient Greeks did it moved Isadora Duncan to create her brand of ballet.
The Renaissance discovery of Classical Antiquity is a book by Roberto Weiss on how the renaissance was partly caused by the rediscovery of classic antiquity.
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is the period in Greek history lasting for close to a millennium, until the rise of Christianity. It is considered by most historians to be the foundational culture of Western Civilization. Greek culture was a powerful influence in the Roman Empire, which carried a version of it to many parts of Europe.
The civilization of the ancient Greeks has been immensely influential on the language, politics, educational systems, philosophy, science, art, and architecture of the modern world, fueling the Renaissance in Western Europe and again resurgent during various neo-Classical revivals in 18th and 19th century Europe and The Americas.
"Ancient Greece" is the term used to describe the Greek-speaking world in ancient times. It refers not only to the geographical peninsula of modern Greece, but also to areas of Hellenic culture that were settled in ancient times by Greeks: Cyprus and the Aegean islands, the Aegean coast of Anatolia (then known as Ionia), Sicily and southern Italy (known as Magna Graecia), and the scattered Greek settlements on the coasts of Colchis, Illyria, Thrace, Egypt, Cyrenaica, southern Gaul, east and northeast of the Iberian peninsula, Iberia and Taurica.
During its twelve-century existence, the Roman civilization shifted from a monarchy to an oligarchic republic to a vast empire. It came to dominate Western Europe and the entire area surrounding the Mediterranean Sea through conquest
and assimilation. However, a number of factors led to the eventual decline of the Roman Empire. The western half of the empire, including Hispania, Gaul, and Italy, eventually broke into independent kingdoms in the 5th century; the eastern empire, governed from Constantinople, is referred to as the Byzantine Empire after AD 476, the traditional date for the "fall of Rome" and subsequent onset of the Middle Ages.
Roman civilization is often grouped into " classical antiquity" with ancient Greece, a civilization that inspired much of the culture of ancient Rome. Ancient Rome contributed greatly to the development of law, war, art, literature, architecture, and language in the Western world, and its history continues to have a major influence on the world today.
East Asia
- Ancient China
- Ancient Japan
- Ancient Korea
- Mongols
- Huns
Ancient China
The earliest written record of China's past dates from the Shang Dynasty (商朝) in perhaps the 13th century BC, and takes the form of inscriptions of divination records on the bones or shells of animals—the so-called oracle bones (甲骨文). Archaeological findings providing evidence for the existence of the Shang Dynasty, c. 1600– 1046 BC is divided into two sets. The first, from the earlier Shang period (c. 1600– 1300) comes from sources at Erligang (二里崗), Zhengzhou (鄭州) and Shangcheng. The second set, from the later Shang or Yin (殷) period, consists of a large body of oracle bone writings. Anyang (安陽) in modern day Henan has been confirmed as the last of the nine capitals of the Shang (c. 1300–1046 BC).
By the end of the 2nd millennium BC, the Zhou Dynasty (周朝) began to emerge in the Yellow River valley, overrunning the Shang. The Zhou appeared to have begun their rule under a semi-feudal system. The ruler of the Zhou, King Wu, with the assistance of his uncle, the Duke of Zhou, as regent managed to defeat the Shang at the Battle of Muye. The king of Zhou at this time invoked the concept of the Mandate of Heaven to legitimize his rule, a concept that would be influential for almost every successive dynasty. The Zhou initially moved their capital west to an area near modern Xi'an, near the Yellow River, but they would preside over a series of expansions into the Yangtze River valley. This would be the first of many population migrations from north to south in Chinese history.
In the 8th century BC, power became decentralized during the Spring and Autumn Period (春秋時代), named after the influential Spring and Autumn Annals. In this period, local military leaders used by the Zhou began to assert their power and vie for hegemony. The situation was aggravated by the invasion of other peoples from the northwest, such as the Qin, forcing the Zhou to move their capital east to Luoyang. This marks the second large phase of the Zhou dynasty: the Eastern Zhou. In each of the hundreds of states that eventually arose, local strongmen held most of the political power and continued their subservience to the Zhou kings in name only. Local leaders for instance started using royal titles for themselves. The Hundred Schools of Thought (諸子百家) of Chinese philosophy blossomed during this period, and such influential intellectual movements as Confucianism (儒家), Taoism (道家), Legalism (法家) and Mohism (墨家) were founded, partly in response to the changing political world. The Spring and Autumn Period is marked by a falling apart of the central Zhou power. China now consists of hundreds of states, some only as large as a village with a fort.
After further political consolidation, seven prominent states remained by the end of 5th century BC, and the years in which these few states battled each other is known as the Warring States Period (戰國時代). Though there remained a nominal Zhou king until 256 BC, he was largely a figurehead and held little real power. As neighboring territories of these warring states, including areas of modern Sichuan (四川) and Liaoning (遼寧), were annexed, they were governed under the new local administrative system of commandery and prefecture (郡縣). This system had been in use since the Spring and Autumn Period and parts can still be seen in the modern system of Sheng & Xian (province and county, 省縣). The final expansion in this period began during the reign of Ying Zheng (嬴政), the king of Qin. His unification of the other six powers, and further annexations in the modern regions of Zhejiang (浙江), Fujian (福建), Guangdong (廣東) and Guangxi (廣西) in 214 BC enabled him to proclaim himself the First Emperor (Qin Shi Huangdi, 始皇帝).
Central and South Asia
Ancient India
In the Indian subcontinent, the Rigveda, in Sanskrit, goes back to about 1500 BCE. The Indian literary tradition has an oral history reaching down into the Vedic period of the later 2nd millennium BC. Ancient India is usually taken to refer to the "golden age" of classical Hindu culture, as reflected in Sanskrit literature, beginning around 500 BCE with the sixteen monarchies and 'republics' known as the Mahajanapadas, stretched across the Indo-Gangetic plains from modern-day Afghanistan to Bangladesh. The largest of these nations were Magadha, Kosala, Kuru and Gandhara. Notably, the great epics of Ramayana and Mahabharata are rooted in this classical period.
The births of Mahavira and Buddha in the 6th century BCE mark the beginning of well-recorded Indian history. Around the 5th century BCE, the northern Indian subcontinent was invaded by the Achaemenid Empire and the Greeks of Alexander's army. Amongst the sixteen Mahajanapadas, the kingdom of Magadha rose to prominence under a number of dynasties that peaked in power under the reign of Ashoka Maurya, one of India's most legendary and famous emperors. During the reign of Asoka, the three Tamil dynasties of Chola, Chera and Pandya were ruling in the south. These kingdoms, while not part of Asoka's empire, were in friendly terms with the Maurya Empire. The Satavahanas started out as feudatories to the Mauryan Empire, and declared independence soon after the death of Ashoka (232 BCE). Other notable ancient South Indian dynasties include the Kadambas of Banavasi, western Ganga dynasty, Chalukyas of Badami, Chalukyas, Hoysalas, Kakatiyas, Pallavas, Rashtrakutas of Manyaketha and Satavahanas.
The period between 320CE–550 is known as the Classical Age, when most of North India was reunited under the Gupta Empire (ca. 320CE–550). This was a period of relative peace, law and order, and extensive achievements in religion, education, mathematics, arts, Sanskrit literature and drama. Grammar, composition, logic, metaphysics, mathematics, medicine, and astronomy became increasingly specialized and reached an advanced level. The Gupta Empire was weakened and ultimately ruined by the raids of Hunas (a branch of the White Huns emanating from Central Asia). Under Harsha (r. 606–47), North India was reunited briefly.
The educated speech at that time was Sanskrit, while the dialects of the general population of northern India were referred to as Prakrits. The South Indian coast of Malabar and the Tamil people of the Sangam age traded with the Graeco-Roman world. They were in contact with the Phoenicians, Romans, Greeks, Arabs, Syrians, Jews, and the Chinese.
India is estimated to have had the largest economy of the world between the 1st and 15th centuries CE, controlling between one third and one quarter of the world's wealth up to the time of the Mughals, from whence it rapidly declined during British rule.
Southwest Asia
- Ancient Persia
- Arabia Felix
- Assyria
- Babylonia
- Proto-Elamite
- Elam
- Jiroft Kingdom
- Kingdom of Israel
- Kingdom of Judah
- Medes
- Mesopotamia
- Mitanni
- Sumer
- Urartu
Saharan and Sub-Saharan Africa
Ancient Egypt was a long-lived ancient civilization geographically located in north-eastern Africa. It was concentrated along the middle to lower reaches of the Nile River reaching its greatest extension during the second millennium BC, which is referred to as the New Kingdom period. It reached broadly from the Nile Delta in the north, as far south as Jebel Barkal at the Fourth Cataract of the Nile. Extensions to the geographical range of ancient Egyptian civilisation included, at different times, areas of the southern Levant, the Eastern Desert and the Red Sea coastline, the Sinai Peninsula and the Western Desert (focused on the several oases).
Ancient Egypt developed over at least three and a half millennia. It began with the incipient unification of Nile Valley polities around 3500 BC and is conventionally thought to have ended in 30 BC when the early Roman Empire conquered and absorbed Ptolemaic Egypt as a province. (Though this last did not represent the first period of foreign domination, the Roman period was to witness a marked, if gradual transformation in the political and religious life of the Nile Valley, effectively marking the termination of independent civilisational development).
The civilization of ancient Egypt was based on a finely balanced control of natural and human resources, characterised primarily by controlled irrigation of the fertile Nile Valley; the mineral exploitation of the valley and surrounding desert regions; the early development of an independent writing system and literature; the organisation of collective projects; trade with surrounding regions in east / central Africa and the eastern Mediterranean; finally, military ventures that exhibited strong characteristics of imperial hegemony and territorial domination of neighbouring cultures at different periods. Motivating and organising these activities were a socio-political and economic elite that achieved social consensus by means of an elaborate system of religious belief under the figure of a (semi)-divine ruler (usually male) from a succession of ruling dynasties and which related to the larger world by means of polytheistic beliefs.
- Ancient Egypt
- Axumite Kingdom
- Kush
The Americas
- Adena
- Aztecs
- Incas
- Mayans
- Mississippian culture
- Native America
- Olmecs
- Poverty Point culture