Thomas Pynchon
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Writers and critics
Thomas Ruggles Pynchon, Jr. (born May 8, 1937) is an American writer based in New York City. He is noted for his dense and complex works of fiction. Hailing from Long Island, Pynchon spent two years in the United States Navy and earned an English degree from Cornell University. After publishing several short stories in the late 1950s and early 1960s, he began composing the novels for which he is best known today: V. (1963), The Crying of Lot 49 (1966), Gravity's Rainbow (1973), Vineland (1990), Mason & Dixon (1997), and Against the Day (2006).
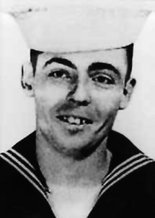
Pynchon is regarded by many readers and critics as one of the finest contemporary authors. He is a MacArthur Fellow and a recipient of the National Book Award, and is regularly cited as a contender for the Nobel Prize in Literature. Both his fiction and non-fiction writings encompass a vast array of subject matter, styles and themes, including (but not limited to) the fields of history, science and mathematics. Pynchon is also known for his avoidance of personal publicity: very few photographs of him have ever been published, and rumors about his location and identity have been circulated since the 1960s.
Biography
Thomas Pynchon was born in 1937 in Glen Cove, Long Island, New York, one of three children of Thomas Ruggles Pynchon, Sr. (1907-1995) and Katherine Frances Bennett (1909-1996). His earliest American ancestor, William Pynchon, emigrated to the Massachusetts Bay Colony with the Winthrop Fleet in 1630, and thereafter a long line of Pynchon descendants found wealth and repute on American soil. Pynchon's family background and aspects of his ancestry have provided source material for his fictions, particularly in the Slothrop family histories related in "The Secret Integration" (1964) and Gravity's Rainbow.
Childhood and education
Pynchon attended Oyster Bay High School, where he wrote for the school newspaper and excelled in his studies. After graduating in 1953, he studied engineering physics at Cornell University, but left at the end of his second year to serve in the U.S. Navy. In 1957, Pynchon returned to Cornell to pursue a degree in English. His first published story, "The Small Rain", appeared in the Cornell Writer in May 1959, and narrates an actual experience of a friend who had served in the army; subsequently, however, episodes and characters throughout Pynchon's fiction draw freely upon his own experiences in the navy.
While at Cornell, Pynchon became a friend of Richard Fariña, and both briefly led what Pynchon has called a "micro-cult" around Oakley Hall's 1958 novel Warlock. (He later reminisced about his college days in the introduction he wrote in 1983 for Fariña's novel Been Down So Long It Looks Like Up to Me, first published in 1966.) Pynchon also reportedly attended lectures given by Vladimir Nabokov, who then taught literature at Cornell. While Nabokov later said that he had no memory of Pynchon (although Nabokov's wife, Vera, who graded her husband's class papers, commented that she remembered his distinctive handwriting, his later handwriting appears unexceptional), other teachers at Cornell, like the novelist James McConkey, recall him as being a gifted and exceptional student. Pynchon received his BA in June 1959.
Early career
After leaving Cornell, Pynchon began to work on his first novel. From February 1960 to September 1962, he was employed as a technical writer at Boeing in Seattle, where he compiled safety articles for the Bomarc Service News (see Wisnicki 2000-1), a support newsletter for the BOMARC surface-to-air missile deployed by the U.S. Air Force. Pynchon's experiences at Boeing inspired his depictions of the " Yoyodyne" corporation in V. and The Crying of Lot 49, and both his background in physics and the technical journalism he undertook at Boeing provided much raw material for Gravity's Rainbow. When it was published in 1963, Pynchon's novel V. won a William Faulkner Foundation Award for best first novel of the year.
After resigning from Boeing, Pynchon spent time in New York and Mexico before moving to California, where he was reportedly based for much of the 1960s and early 1970s, most notably in an apartment in Manhattan Beach (see Frost 2003). Pynchon during this period embraced the lifestyle and values of the hippie counterculture, which he would later make use of in his 1990 novel Vineland. (Gordon 1994). In 1964, his application to study mathematics as a graduate student at the University of California, Berkeley, was turned down (Royster 2005). In 1966, he wrote a first-hand report on the aftermath and legacy of the Watts riots in Los Angeles. Entitled "A Journey Into the Mind of Watts," the article was published in the New York Times Magazine (Pynchon 1966).
From the mid-1960s Pynchon has also regularly provided blurbs and introductions for a wide range of novels and non-fiction works. One of the first of these pieces was a brief review of Hall's Warlock which appeared, along with comments by seven other writers on "neglected books", as part of a feature entitled "A Gift of Books" in the December 1965 issue of Holiday.
Pynchon's second novel, The Crying of Lot 49, is also set in California. It was published in 1966, and won the Richard and Hilda Rosenthal Foundation Award. Although more concise and linear in its structure than Pynchon's other novels, its labyrinthine plot features an ancient, underground mail service known as "The Tristero" or "Trystero," a parody of a Jacobean revenge drama entitled "The Courier's Tragedy," and a corporate conspiracy involving the bones of World War II American GIs being used as charcoal cigarette filters. It proposes a series of seemingly incredible interconnections between these and other similarly bizarre revelations that confront the novel's protagonist, Oedipa Maas. Like V, the novel contains a wealth of references to science and technology and to obscure historical events, and both books dwell upon the detritus of American society and culture. The Crying of Lot 49 also continues Pynchon's habit of composing parodic song lyrics and punning names, and referencing aspects of popular culture within his prose narrative. In particular, it incorporates several allusions to Nabokov's Lolita.
In 1968, Pynchon was one of 447 signatories to the "Writers and Editors War Tax Protest." Full-page advertisements in The New York Post and The New York Review of Books listed the names of those who had pledged not to pay "the proposed 10% income tax surcharge or any war-designated tax increase," and stated their belief "that American involvement in Vietnam is morally wrong" (New York Review of Books 1968:9).
Gravity's Rainbow and Pynchon's rise to prominence
Pynchon's most celebrated novel is his third, Gravity's Rainbow, published in 1973. An intricate and allusive fiction which combines and elaborates on many of the themes of his earlier work, including preterition, paranoia, racism, colonialism, conspiracy, synchronicity, and entropy, the novel has spawned a wealth of commentary and critical material, including two reader's guides (Fowler 1980; Weisenburger 1988), books and scholarly articles, on-line concordances and discussions, and art works, and is regarded as one of the archetypal texts of American literary postmodernism. The major portion of Gravity's Rainbow takes place in London and Europe in the final months of the Second World War and the weeks immediately following VE Day, and is narrated for the most part from within the historical moment in which it is set. In this way, Pynchon's text enacts a type of dramatic irony whereby neither the characters nor the various narrative voices are aware of specific historical circumstances, such as the Holocaust, which are, however, very much to the forefront of the reader's understanding of this time in history. Such an approach generates dynamic tension and moments of acute self-consciousness, as both reader and author seem drawn ever deeper into the " plot", in various senses of that term. Encyclopedic in scope, the novel also displays enormous erudition in its treatment of an array of material drawn from the fields of psychology, chemistry, mathematics, history, religion, music, literature and film. Perhaps appropriately for a book so suffused with engineering knowledge, Pynchon reportedly wrote the first draft of Gravity's Rainbow in longhand on engineer's graph paper, in California and Mexico City.
Gravity's Rainbow was a joint winner of the 1974 National Book Award for Fiction, along with Isaac Bashevis Singer's A Crown of Feathers and Other Stories. In the same year, the fiction jury unanimously recommended Gravity's Rainbow for the Pulitzer Prize; however, the Pulitzer board vetoed the jury's recommendation, describing the novel as "unreadable", "turgid", "overwritten", and in parts "obscene", and no prize was awarded (Kihss 1974). In 1975, Pynchon declined the William Dean Howells Medal of the American Academy of Arts and Letters.
Post-Gravity's Rainbow
A collection of Pynchon's early short stories, entitled Slow Learner, was published in 1984, with a lengthy autobiographical introduction. In October of the same year, an article entitled "Is It O.K. to Be a Luddite?" was published in the New York Times Book Review. In April 1988, Pynchon contributed an extensive review of Gabriel García Marquéz's novel, Love in the Time of Cholera, to the New York Times, under the title "The Heart's Eternal Vow". Another article, entitled "Nearer, My Couch, to Thee", was published in June 1993 in the New York Times Book Review, as one in a series of articles in which various writers reflected on each of the Seven Deadly Sins. Pynchon's subject was " Sloth".
Pynchon's fourth novel, Vineland, was published in 1990, and was regarded as a disappointment by the majority of reviewers and critics. The novel is set in California in the 1980s and 1960s, and describes the relationship between an FBI COINTELPRO agent and a female radical filmmaker. Its strong socio-political undercurrents detail the constant battle between authoritarianism and communalism, and the nexus between resistance and complicity, but with a typically Pynchonian sense of humor.
In 1988, he received a MacArthur Fellowship and, since the early 1990s at least, many observers have mentioned Pynchon as a Nobel Prize contender (see, for example, Grimes 1993; CNN Book News 1999; Ervin 2000). Renowned American literary critic Harold Bloom has named him as one of the four major American novelists of his time, along with Don DeLillo, Philip Roth, and Cormac McCarthy.
Pynchon's fifth novel is Mason & Dixon, a work which had been in the pipeline since 1978 at least (Roeder 1978; see also Ulin 1997). Published in 1997, the meticulously-researched novel is a sprawling postmodernist saga recounting the lives and careers of the English astronomer, Charles Mason, and his partner, the surveyor Jeremiah Dixon, and the birth of the American Republic. While it received some negative reviews, the great majority of commentators acknowledged it as a welcome return to form, and some, including Bloom, have called it Pynchon's greatest work to date.
Against the Day
A variety of rumors pertaining to the subject matter of Pynchon's next book have circulated over a number of years. Most specific of these were comments made by the former German minister of culture, Michael Naumann, who stated that he assisted Pynchon in his research about "a Russian mathematician [who] studied for David Hilbert in Göttingen", and that the new novel would trace the life and loves of Sofia Kovalevskaya.
In July 2006, a new untitled novel by Pynchon was announced along with a synopsis written by Pynchon himself, which appeared on Amazon.com, stating that the novel's action takes place between the 1893 Chicago World's Fair and the time immediately following World War I. "With a worldwide disaster looming just a few years ahead," Pynchon writes in his Book Description, "it is a time of unrestrained corporate greed, false religiosity, moronic fecklessness, and evil intent in high places. No reference to the present day is intended or should be inferred." He promises cameos by Nikola Tesla, Bela Lugosi and Groucho Marx, as well as "stupid songs" and "strange sexual practices". Subsequently, the title of the new book was reported as Against the Day and a Penguin spokesperson confirmed that the synopsis was Pynchon's (Patterson 2006b; Italie 2006).
Against the Day was released November 21, 2006 and is 1,085 pages long in the first edition hardcover. The book was given almost no promotion by Penguin and professional book reviewers were given little time in advance to review the book, presumably in accord with Pynchon's wishes. An edited version of Pynchon's synopsis was used as the jacket flap copy and Kovalevskaya does appear, although as only one of over a hundred characters.
There has been no general consensus among professional book reviewers, although many agree that it is in turns brilliant and exhausting. A Pynchon wiki was launched by fans the same day as Against the Day to help readers keep track of the numerous characters, events and themes.
Themes and influence
Along with its emphasis on loftier themes such as racism, imperialism and religion, and its cognizance and appropriation of many elements of traditional high culture and literary form, Pynchon's work also demonstrates a strong affinity with the practitioners and artifacts of low culture, including comic books and cartoons, pulp fiction, popular films, television programs, cookery, urban myths, conspiracy theories, and folk art. This blurring of the conventional boundary between "High" and "low" culture, sometimes interpreted as a " deconstruction", is seen as one of the defining characteristics of postmodernism.
In particular, Pynchon has revealed himself in his fiction and non-fiction as an aficionado of popular music. Song lyrics and mock musical numbers appear in each of his novels, and, in his autobiographical introduction to the Slow Learner collection of early stories, he reveals a fondness for both jazz and rock and roll. The character McClintic Sphere in V. is a fictional composite of master jazz musicians such as Ornette Coleman, Charlie Parker and Thelonious Monk. In The Crying of Lot 49, the lead singer of "The Paranoids" sports "a Beatle haircut" and sings with an English accent. In the closing pages of Gravity's Rainbow, there is an apocryphal report that Tyrone Slothrop, the novel's protagonist, played kazoo and harmonica as a guest musician on a record released by The Fool in the 1960s (having magically recovered the latter instrument, his " harp", in a German stream in 1945, after losing it down the toilet in 1939 at the Roseland Ballroom in Roxbury, Boston, to the strains of the jazz standard 'Cherokee', upon which tune Charlie Parker was simultaneously inventing bebop in New York, as Pynchon describes). In Vineland, both Zoyd Wheeler and Isaiah Two Four are also musicians: Zoyd played keyboards in a '60s surf band called "The Corvairs", while Isaiah played in a punk band called "Billy Barf and the Vomitones". In Mason & Dixon, one of the characters plays on the "Clavier" the varsity drinking song which will later become " The Star-Spangled Banner".
In his Slow Learner introduction, Pynchon acknowledges a debt to the anarchic bandleader Spike Jones, and in 1994, he penned a 3000-word set of liner notes for the album Spiked!, a collection of Jones's recordings released on the short-lived BMG Catalyst label. Pynchon also wrote the liner notes for Nobody's Cool, the second album of indie rock band Lotion, in which he states that "rock and roll remains one of the last honorable callings, and a working band is a miracle of everyday life. Which is basically what these guys do." He is also known to be a fan of Roky Erickson.
In terms of literary influences and affinity, an eclectic catalogue of Pynchonian precursors has been proposed by readers and critics. Beside overt references in the novels to writers as disparate as Henry Adams, Giorgio de Chirico, Ludwig Wittgenstein, Emily Dickinson, Rainer Maria Rilke, Jorge Luis Borges, Ishmael Reed, Ralph Waldo Emerson, Patrick O'Brian, and Umberto Eco, and to an eclectic mix of iconic religious and philosophical sources, credible comparisons with works by Rabelais, Cervantes, Laurence Sterne, Edgar Allan Poe, Nathaniel Hawthorne, Herman Melville, Charles Dickens, Joseph Conrad, Thomas Mann, William Burroughs, Ralph Ellison, Patrick White, and Toni Morrison have also been made. Some commentators have detected similarities with those writers in the Modernist tradition who wrote extremely long novels dealing with large metaphysical or political issues. Examples of such works might include Ulysses by James Joyce, A Passage to India by E.M. Forster, The Apes of God by Wyndham Lewis, The Man Without Qualities by Robert Musil, or The Castle by Franz Kafka. In his 'Introduction' to Slow Learner, Pynchon explicitly acknowledges his debt to Beat Generation writers, and expresses his admiration for Jack Kerouac's On the Road in particular; he also reveals his familiarity with literary works by T. S. Eliot, Ernest Hemingway, Henry Miller, Saul Bellow, Herbert Gold, Philip Roth and Norman Mailer, and non-fiction works by Helen Waddell, Norbert Wiener and Isaac Asimov. Other contemporary American authors whose fiction is often categorised alongside Pynchon's include John Hawkes, Kurt Vonnegut, Joseph Heller, Donald Barthelme, John Barth, William Gaddis, Don DeLillo, and Joseph McElroy. Younger contemporary writers who have been touted as heirs apparent to Pynchon include David Foster Wallace, William Vollmann, Richard Powers, David Mitchell, Neal Stephenson, Dave Eggers, Christopher Wunderlee, and Tommaso Pincio whose pseudonym is an Italian rendering of Pynchon's name.
Investigations and digressions into the realms of human sexuality, psychology, sociology, mathematics, science, and technology recur throughout Pynchon's works. One of his earliest short stories, "Low-lands" (1960), features a meditation on Heisenberg's uncertainty principle as a metaphor for telling stories about one's own experiences. His next published work, "Entropy" (1960), introduced the concept which was to become synonymous with Pynchon's name (though Pynchon later admitted the "shallowness of [his] understanding" of the subject, and noted that choosing an abstract concept first and trying to construct a narrative around it was "a lousy way to go about writing a story"). Another early story, "Under the Rose" (1961), includes amongst its cast of characters a cyborg set anachronistically in Victorian-era Egypt (a type of writing now called steampunk). This story, significantly reworked by Pynchon, appears as Chapter 3 of V. "The Secret Integration" (1964), Pynchon's last published short story, is a sensitively-handled coming-of-age tale in which a group of young boys face the consequences of the American policy of racial integration. At one point in the story, the boys attempt to understand the new policy by way of the mathematical operation, the only sense of the word with which they are familiar.
The Crying of Lot 49 also alludes to entropy and communication theory, and contains scenes and descriptions which parody or appropriate calculus, Zeno's paradoxes, and the thought experiment known as Maxwell's demon. At the same time, the novel also investigates homosexuality, celibacy and both medically-sanctioned and illicit psychedelic drug use. Gravity's Rainbow describes many varieties of sexual fetishism (including sado-masochism, coprophilia and a borderline case of tentacle rape), and features numerous episodes of drug use, most notably marijuana but also cocaine, naturally occurring hallucinogens, and the mushroom Amanita muscaria. Gravity's Rainbow also derives much from Pynchon's background in mathematics: at one point, the geometry of garter belts is compared with that of cathedral spires, both described as mathematical singularities. His most recent novel, Mason & Dixon, explores the scientific, theological, and sociocultural foundations of the Age of Reason whilst also depicting the relationships between actual historical figures and fictional characters in intricate detail and, like Gravity's Rainbow, is an archetypal example of the genre of historiographical metafiction.
Pynchon's work has been cited as an influence and inspiration by many writers, musicians, artists and filmmakers, including T. Coraghessan Boyle, Don DeLillo, Paul Di Filippo, William Gibson, Elfriede Jelinek, Rick Moody, Arturo Perez-Reverte, Richard Powers, Salman Rushdie, Neal Stephenson, Bruce Sterling, Laurie Anderson, the Definitive Jux hip-hop producer/CEO/emcee El-P, Max P. Häring, Zak Smith, David Cronenberg, and Adam Rapp. Thanks to his influence on Gibson and Stephenson in particular, Pynchon became one of the progenitors of cyberpunk fiction. Though the term "cyberpunk" did not become prevalent until the early 1980s, many readers retroactively include Gravity's Rainbow in the genre, along with other works—e.g., Samuel R. Delany's Nova and many works of Philip K. Dick—which seem, after the fact, to anticipate cyberpunk styles and themes. The encyclopedic nature of Pynchon's novels also led to some attempts to link his work with the short-lived hypertext fiction movement of the 1990s (Page 2002; Krämer 2005).
Gravity's Rainbow and the more recent Mason & Dixon both feature wildly eccentric characters, episodes of frenzied action and frequent digressions on topics which are seemingly tangential to the central narrative. These characteristics, combined with the novels' imposing lengths, have led critic James Wood to classify Pynchon's work as hysterical realism. Other writers whose work has been labelled as hysterical realism include Rushdie, Stephenson, Wunderlee and Zadie Smith.
Works
- V. (1963), winner of William Faulkner Foundation Award
- The Crying of Lot 49 (1966), winner of Richard and Hilda Rosenthal Foundation Award
- Gravity's Rainbow (1973), 1974 National Book Award for fiction, judges' unanimous selection for Pulitzer Prize overruled by advisory board, awarded William Dean Howells Medal of the American Academy of Arts and Letters in 1975 (award declined)
- Slow Learner (1984), collection of early short stories
- Vineland (1990)
- Mason & Dixon (1997)
- Against the Day (21 November, 2006)
As well as fictional works, Pynchon has written essays, introductions, and reviews addressing subjects as diverse as missile security, the Watts Riots, Luddism and the work of Donald Barthelme. Some of his non-fiction pieces have appeared in the New York Times Book Review and The New York Review of Books, and he has contributed blurbs for books and records. His 1984 Introduction to the Slow Learner collection of early stories is significant for its autobiographical candour. He has written introductions to at least two books, including the 1992 collection of Donald Barthelme's stories, The Teachings of Don B. and, more recently, the Penguin Centenary Edition of George Orwell's novel Nineteen Eighty-Four, which was published in 2003.