Rutherford B. Hayes
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: USA Presidents
| Rutherford Birchard Hayes | |
 |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|
| In office March 4, 1877 – March 4, 1881 |
|
| Vice President(s) | William A. Wheeler |
| Preceded by | Ulysses S. Grant |
| Succeeded by | James A. Garfield |
|
|
|
| Born | October 4, 1822 Delaware, Ohio |
| Died | January 17, 1893 Fremont, Ohio |
| Political party | Republican |
| Spouse | Lucy Ware Hayes |
| Religion | Methodist |
| Signature | |
Rutherford Birchard Hayes ( October 4, 1822 – January 17, 1893) was an American politician, lawyer, military leader and the 19th President of the United States (1877-1881).
Early life
Hayes was born in Delaware, Ohio, on October 4, 1822. His parents were Rutherford Hayes ( January 4, 1787 Brattleboro, Vermont– July 20, 1822 Delaware, Ohio) and Sophia Birchard ( April 15, 1792 Wilmington, Vermont– October 30, 1866 Columbus, Ohio) and was the youngest of four children, however two of them, Lorenzo Hayes (1815-1825) and Sarah Sophia Hayes (1817-1821) died young. Hayes's father died before Hayes was born and an uncle, Sardis Birchard, lived with the family and served as Hayes's guardian. Hayes attended the common schools and the Methodist Academy in Norwalk. He graduated from Kenyon College in Gambier, Ohio in August 1842 and from Harvard Law School in January 1845. He was admitted to the bar on May 10, 1845, and commenced practice in Lower Sandusky (now Fremont). He moved to Cincinnati, Ohio in 1849 and resumed the practice of law. He was city solicitor from 1857 to 1859.
He was close to his sister Fanny Arabella Hayes (1820-1856) as can be seen in this diary entry:
- July, 1856. —My dear only sister, my beloved Fanny, is dead! The dearest friend of childhood, the affectionate adviser, the confidante of all my life, the one I loved best, is gone; alas! never again to be seen on earth.
Family
On December 30, 1852, Hayes married Lucy Ware Webb. The couple had eight children:
- Birchard Austin Hayes (1853-1926)
- James Webb Cook Hayes (1856-1934)
- Rutherford Platt Hayes (1858-1927)
- Joseph Thompson Hayes (1861-63)
- George Crook Hayes (1864-66)
- Fanny Hayes (1867-1950)
- Scott Russell Hayes (1871-1923)
- Manning Force Hayes (1873-74)
Civil War Service
Although he was nearly 40 at the outbreak of the Civil War, Hayes joined as a three-year volunteer and was commissioned as a major of the Twenty-third Regiment, Ohio Volunteer Infantry on June 27, 1861 despite having no previous military experience. Promoted to lieutenant colonel on October 24, 1861, Hayes was severely wounded at the Battle of South Mountain while commanding the 23rd at Fox Gap when a musket ball struck him in the left arm above the elbow. The ball fractured but did not splinter the bone, which would have necessitated amputation of the limb. He was promoted to colonel on October 24, 1862, and he commanded a brigade at the battle of Cloyd's Mountain. He was promoted to brigadier general of Volunteers on October 9, 1864, during the Shenandoah Valley Campaign of 1864. He received a brevet promotion to major general of Volunteers on March 3, 1865. Hayes would later look back on his life and exclaim that serving in the Union army were the best days of his life.
Political service
While still in the Shenandoah in 1864, Hayes received the Republican nomination to Congress from Cincinnati. Refusing to campaign on the grounds that "an officer fit for duty who at this crisis would abandon his post to electioneer for a seat in Congress ought to be scalped," Hayes was elected and served in the Thirty-ninth and again to the Fortieth Congresses and served from March 4, 1865, to July 20, 1867, when he resigned, having been nominated for Governor of Ohio. Through the powerful voice of his friend and Civil War subordinate James M. Comly's Ohio State Journal (one of the state's most influential newspapers), Hayes won the election and served as governor from 1868 to 1872. He was an unsuccessful candidate for election to the Forty-third Congress. He was again elected governor and served from January 1876 to March 2, 1877.
Election of 1876
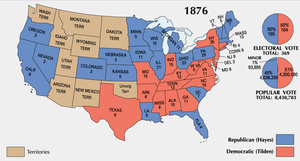
Hayes became president after the tumultuous, scandal-ridden years of the Grant administration. He had a reputation for honesty dating back to his Civil War years. Hayes was quite famous for his ability to not offend anyone. Henry Adams, a prominent politician at the time, asserted that Hayes was "a third rate nonentity, whose only recommendation is that he is obnoxious to no one." Nevertheless, his opponent in the presidential election, Democrat Samuel J. Tilden, was the favorite to win the presidential election and, in fact, won the popular vote by about 250,000 votes (with about 8.5 million voters in total).
Four states' electoral college votes were contested. In order to win, the candidates had to muster 185 votes: Tilden was short just one, with 184 votes, Hayes had 165, with 20 votes representing the four states which were contested. To make matters worse, three of these states (Florida, Louisiana, and South Carolina) were in the South, which was still under military occupation (the fourth was Oregon). Additionally, historians note, the election was not fair because of the improper fraud and intimidation perpetrated from both sides. A popular phrase of the day called it an election without "a free ballot and a fair count."
To peacefully decide the results of the election, the two houses of Congress set up the Electoral Commission to investigate and decide upon the actual winner. The commission constituted 15 members: five from the House, five from the Senate and five from the Supreme Court. Additionally, the Commission was bi-partisan consisting of 7 Democrats, 7 Republicans and a "swing" vote in Joseph P. Bradley, a Supreme Court Justice. Bradley, however, was a Republican at heart and thus the ruling followed party lines: 8 to 7 voted for Hayes winning in all of the contested 20 electoral votes.
Key Ohio Republicans like James A. Garfield and the Democrats, however, agreed at a Washington hotel on the Wormley House Agreement. Southern Democrats were given assurances that if Hayes became president, he would pull federal troops out of the South and end Reconstruction. An agreement was made between them and the Republicans: if Hayes's cabinet consisted of at least one Southerner and he withdrew all Union troops from the South, then he would become President. This Compromise of 1877 is sometimes considered to be the second Corrupt Bargain.
Gore Vidal's novel 1876 chronicles the events of the 1876 election from the perspective of a Tilden supporter.
Presidency 1877–1881
Because March 4, 1877 was a Sunday, Hayes took the oath of office in the Red Room of the White House on March 3. He took the oath again publicly on March 5 on the East Portico of the United States Capitol, and he served until March 4, 1881.
Domestic policy
In domestic affairs, aside from reconciliation with the South, his administration was noteworthy for two achievements, both giving evidence of a strong president resolute in his relations with Congress: resumption of specie (mainly gold) backing of the paper currency and bonds that financed the war, and the beginning of civil service reform. Hayes' first step in civil service reform was to issue an executive order in June 1877 forbidding federal civil servants to take an active part in politics. This order brought him into fateful collision with congressional spoilsmen. In this mainly victorious test, Hayes removed not only a subordinate, Alonzo B. Cornell, from the New York customhouse but also the port collector, Chester A. Arthur, both Republicans. (When Arthur himself became president, he backed major civil service reform legislation, so that the sequel to this explosive episode was another irony.) Hayes also won a significant duel with Congress over riders attached to army appropriation bills to keep him from protecting blacks' rights to vote in line with the 15th Amendment.
Foreign policy
In 1878, Hayes was asked by Argentina to act as arbitrator following the War of the Triple Alliance between Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay against Paraguay. The Argentines hoped that Hayes would give the Chaco region to them; however, he decided in favour of the Paraguayans. His decision made him a hero in Paraguay, and a city ( Villa Hayes) and a department ( Presidente Hayes) were named in his honour.
But for the most part, Hayes wasn't very involved in foreign policy. Most of the problems during his term were small and domestically related.
Notable legislation
During his presidency, Hayes signed a number of bills including one signed on February 15, 1879 which, for the first time, allowed female attorneys to argue cases before the Supreme Court of the United States.
Other acts include:
- Compromise of 1877
- Desert Land Act (1877)
- Bland-Allison Act (1878)
- Timber and Stone Act (1878)
Significant events during his presidency
- Munn v. Illinois (1876)
- Great Railroad Strike (1877)
Administration and Cabinet
| OFFICE | NAME | TERM |
| President | Rutherford B. Hayes | 1877–1881 |
| Vice President | William A. Wheeler | 1877–1881 |
| Secretary of State | William M. Evarts | 1877–1881 |
| Secretary of the Treasury | John Sherman | 1877–1881 |
| Secretary of War | George W. McCrary | 1877–1879 |
| Alex Ramsey | 1879–1881 | |
| Attorney General | Charles Devens | 1877–1881 |
| Postmaster General | David M. Key | 1877–1880 |
| Horace Maynard | 1880–1881 | |
| Secretary of the Navy | Richard W. Thompson | 1877–1880 |
| Nathan Goff, Jr. | 1881–1881 | |
| Secretary of the Interior | Carl Schurz | 1877–1881 |
Supreme Court appointments
Hayes appointed two Associate Justices of the Supreme Court of the United States:
- John Marshall Harlan – 1877
- William Burnham Woods – 1881
States admitted to the Union
Post-Presidency
Hayes did not seek re-election in 1880, keeping his pledge that he would not run for a second term. He had, in his inaugural address, proposed a one- term limit for the presidency combined with an increase in the term length to six years.
Rutherford Birchard Hayes died of complications of a heart attack in Fremont, Sandusky County, Ohio, at 11:00 p.m. on Tuesday January 17, 1893. Interment was in Oakwood Cemetery. Following the gift of his home to the state of Ohio for the Spiegel Grove State Park, he was reinterred there in 1915.
Trivia
- Hayes was the last U.S. President born before the Monroe Doctrine came into effect.
- Hayes was the first U.S. President to visit the U.S. West Coast while in office.
- Hayes is also reputed to be the first President to have had his voice recorded—by Thomas Edison in 1877 with his newly-invented phonograph. Unfortunately, the tin it was recorded on has been lost. As the recording cannot be located, some say that it never existed, and that therefore the first President to have his voice recorded was Benjamin Harrison in the 1890s.
- Hayes had no say over the nomination of his running mate for Vice President. When party bosses at the 1876 Republican Convention decided to give the spot to the little-known New York representative William A. Wheeler, Hayes only heard about it next morning and reportedly said, "I am ashamed to say, Who is Wheeler?"
- Hayes lends his name to the math and physics building at Kenyon College, where he graduated in 1842.