Red giant
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Space (Astronomy)
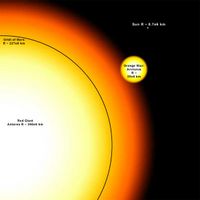
According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a red giant is a large non- main sequence star of stellar classification K or M; so-named because of the reddish appearance of the cooler giant stars. Examples include Aldebaran, in the constellation Taurus and Arcturus.
They are stars of 0.4 - 10,515,478 times the mass of the Sun which have exhausted their supply of hydrogen in their cores and switched to fusing hydrogen in a shell outside the core. Since the inert helium core has no source of energy of its own, it contracts and heats up, and its gravity compresses the hydrogen in the layer immediately above it, thus causing it to fuse faster. This in turn causes the star to become more luminous (from 1,000 – 10,000 times brighter) and expand; the degree of expansion outstrips the increase in luminosity, thus causing the effective temperature to decrease. In stars massive enough to ignite helium fusion, an analogous process occurs when central helium is exhausted and the star switches to fusing helium in a shell, although with the additional complication that in many cases hydrogen fusion will continue in a shell at lesser depth — this puts stars onto the asymptotic giant branch. , , The decrease in surface temperature shifts the star's visible light output to the red — hence red giant. Stars of spectral types O through K are believed to become red giants (or supergiants in the case of O and B stars).
Very low mass stars are thought to be fully convective , and thus may not accumulate an inert core of helium, and thus may exhaust all of their fuel without ever becoming red giants. Such stars are commonly referred to as red dwarfs.
If the star is less than 2.57 solar masses, the addition of helium to the core by shell hydrogen fusing will cause a helium flash—a rapid burst of helium fusing in the core, after which the star will commence a brief period of helium fusing before beginning another ascent of the red giant branch. Stars more massive than 2.5 solar masses enter the helium fusing phase of their lives much more smoothly. The core helium fusing phase of a star's life is called the horizontal branch in metal-poor stars, so named because these stars lie on a nearly horizontal line in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram of many star clusters. Metal-rich helium-fusing stars do not lie on a horizontal branch, but instead lie in a clump (the red clump) in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram.
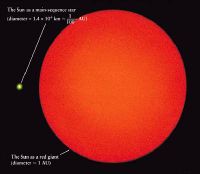
Earth's Sun
As Earth's Sun is of one solar mass, it is expected to become a red giant in about five billion years. It will become sufficiently large to engulf the current orbits of some of the solar system's inner planets, possibly including Earth's . The gravitational pull of the Sun will have weakened by then due to its loss of mass, and it is possible that Earth may escape to a wider orbit . The fate of the Earth with regard to the size of the expanding Sun is still hotly debated in the scientific community. Mercury and Venus will almost certainly be swallowed up by the Sun when it turns into a red giant. If the Earth does escape, it will be due to tidal acceleration.
Red giants in fiction
- In the Superman movie series, the doomed planet Krypton orbited a red giant called Rao. It explodes in a supernova explosion, causing shockwaves that in turn destroys Krypton itself (the comic book series has a red dwarf star and Krypton exploding due to an unstable core). Current continuity attributes the source of Superman's powers to Earth's yellow sun.
- According to The Magician's Nephew, part of C. S. Lewis' The Chronicles of Narnia, the White Witch Jadis comes from an accursed world called Charn. The star in Charn is described as being red, cold, and much larger than the Sun, just like the red giants in our own universe.
- Within the Dune Universe, The Sun is in its Red Giant phase during the events that take place in The Butlerian Jihad. The book being the first of three prequel Novels. Written by Brian Herbert and Kevin J. Anderson. Current estimates require 4.5 billion years for the sun to reach its red giant phase.