Radio frequency
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General Physics
Radio frequency, or RF, refers to that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum in which electromagnetic waves can be generated by alternating current fed to an antenna. Such frequencies and the belonging wavelength account for the following parts of the spectrum shown in the table below.
Radio frequency spectrum
| Band name | Abbr | ITU band | Frequency Wavelength |
Example uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| < 3 Hz > 100,000 km |
||||
| Extremely low frequency | ELF | 1 | 3–30 Hz 100,000 km – 10,000 km |
Communication with submarines |
| Super low frequency | SLF | 2 | 30–300 Hz 10,000 km – 1000 km |
Communication with submarines |
| Ultra low frequency | ULF | 3 | 300–3000 Hz 1000 km – 100 km |
Communication within mines |
| Very low frequency | VLF | 4 | 3–30 kHz 100 km – 10 km |
Submarine communication, avalanche beacons, wireless heart rate monitors, geophysics |
| Low frequency | LF | 5 | 30–300 kHz 10 km – 1 km |
Navigation, time signals, AM longwave broadcasting |
| Medium frequency | MF | 6 | 300–3000 kHz 1 km – 100 m |
AM (Medium-wave) broadcasts |
| High frequency | HF | 7 | 3–30 MHz 100 m – 10 m |
Shortwave broadcasts, amateur radio and over-the-horizon aviation communications |
| Very high frequency | VHF | 8 | 30–300 MHz 10 m – 1 m |
FM, television broadcasts and line-of-sight ground-to-aircraft and aircraft-to-aircraft communications |
| Ultra high frequency | UHF | 9 | 300–3000 MHz 1 m – 100 mm |
television broadcasts, mobile phones, wireless LAN, Bluetooth, and Two-Way Radios such as FRS and GMRS Radios |
| Super high frequency | SHF | 10 | 3–30 GHz 100 mm – 10 mm |
microwave devices, wireless LAN, most modern Radars |
| Extremely high frequency | EHF | 11 | 30–300 GHz 10 mm – 1 mm |
Radio astronomy, high-speed microwave radio relay |
| Above 300 GHz < 1 mm |
Notes
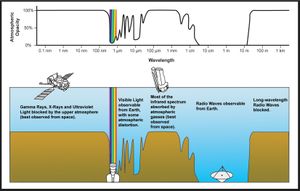
- Above 300 GHz, the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by Earth's atmosphere is so great that the atmosphere is effectively opaque to higher frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, until the atmosphere becomes transparent again in the so-called infrared and optical window frequency ranges.
- The ELF, SLF, ULF, and VLF bands overlap the AF ( audio frequency) spectrum, which is approximately 20–20,000 Hz. However, sounds are transmitted by atmospheric compression and expansion, and not by electromagnetic energy.
- The SHF and EHF bands are often considered to be not part of the radio spectrum and form their own microwave spectrum.
- Another note of merit is that all objects have their own radio frequency, no matter how minute.
Named frequency bands
General
Broadcast Frequencies:
- Longwave AM Radio = 150kHz - 280kHz (LF)
- Mediumwave AM Radio = 530kHz - 1610kHz (MF)
- TV Band I (Channels 2 - 6) = 54MHz - 88MHz (VHF)
- FM Radio Band II = 88MHz - 108MHz (VHF)
- TV Band III (Channels 7 - 13) = 174MHz - 216MHz (VHF)
- TV Bands IV & V (Channels 14 - 69) = 470MHz - 806MHz (UHF)
For more information see the NTIA frequency allocation chart: http://www.ntia.doc.gov/osmhome/allochrt.html
Amateur radio frequencies
The range of allowed frequencies vary between countries. These are just some of the more common bands, often collectively termed shortwave. In the article about amateur radio is another list.
| Band | Frequency range |
|---|---|
| 160 m | 1.8 to 2.0 MHz |
| 80 m | 3.5 to 4.0 MHz |
| 60 m | 5.3 to 5.4 MHz |
| 40 m | 7 to 7.3 MHz |
| 30 m | 10.1 to 10.15 MHz |
| 20 m | 14 to 14.35 MHz |
| 15 m | 21 to 21.45 MHz |
| 12 m | 24.89 to 24.99 MHz |
| 10 m | 28.0 to 29.7 MHz |
| 6 m | 50 to 54 MHz |
| 2 m | 144 to 148 MHz |
| 70 cm | 430 to 440 MHz |
| 23 cm | 1240 to 1300 MHz |
IEEE US
| Band | Frequency range | Origin of name | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HF band | 3 to 30 MHz | High Frequency | |
| VHF band | 30 to 300 MHz | Very High Frequency | |
| UHF band | 300 to 1000 MHz | Ultra High Frequency Frequencies from 216 to 450 MHz were sometimes called P-band: Previous, since early British Radar used this band but later switched to higher frequencies. |
|
| L band | 1 to 2 GHz | Long wave | |
| S band | 2 to 4 GHz | Short wave | |
| C band | 4 to 8 GHz | Compromise between S and X | |
| X band | 8 to 12 GHz | Used in WW II for fire control, X for cross (as in crosshair) | |
| Ku band | 12 to 18 GHz | Kurz-under | |
| K band | 18 to 26 GHz | German Kurz (short) | |
| Ka band | 26 to 40 GHz | Kurz-above | |
| V band | 40 to 75 GHz | ||
| W band | 75 to 111 GHz | W follows V in the alphabet |
EU, NATO, US ECM Frequency Designations
| Band | Frequency range |
|---|---|
| A band | 0 to 0.25 GHz |
| B band | 0.25 to 0.5 GHz |
| C band | 0.5 to 1.0 GHz |
| D band | 1 to 2 GHz |
| E band | 2 to 3 GHz |
| F band | 3 to 4 GHz |
| G band | 4 to 6 GHz |
| H band | 6 to 8 GHz |
| I band | 8 to 10 GHz |
| J band | 10 to 20 GHz |
| K band | 20 to 40 GHz |
| L band | 40 to 60 GHz |
| M band | 60 to 100 GHz |