Nazi Germany
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: World War II
|
|||||
|
|||||
| Motto: "Ein Volk, ein Reich, ein Führer." (English: "One people, one empire, one leader.") |
|||||
| Anthem: Das Lied der Deutschen2, Horst-Wessel-Lied National animal: Eagle and Tiger |
|||||
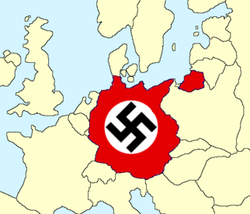
| Nazi Germany at its fullest extent prior to the start of World War II | |||||
| Capital | Berlin |
||||
| Language(s) | German | ||||
| Government | Value specified for "government_type" does not comply | ||||
| - 1934-1945 | Adolf Hitler | ||||
| - 1945 | Karl Dönitz | ||||
| Chancellor | |||||
| - 1933-1945 | Adolf Hitler | ||||
| - 1945 | Joseph Goebbels | ||||
| - 1945 | Ludwig von Krosigk | ||||
| Historical era | Interwar | ||||
| - Election | January 30, 1933 | ||||
| - Establishment | February 27, 1933 | ||||
| - Enablement | March 31, 1933 | ||||
| - Capture | May 2, 1945 | ||||
| - Surrender | May 8, 1945 | ||||
| - Disestablished3 | July 5, 1945 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - 1939 | 633,786 km2 244,706 sq mi |
||||
| Population | |||||
| - 1939 est. | 69,314,000 | ||||
| Density | 109.4 /km² 283.3 /sq mi |
||||
| Currency | Reichsmark | ||||
| 1From 1943-1945. From 1933 to 1943: Deutsches Reich, German Empire. 2Only first stanza is used. 3Was technically the same state from 1919 through 1949, at East- West Germany division. |
|||||
Nazi Germany or Third Reich, officially called the German Reich (Deutsches Reich), and later the Greater German Reich (Großdeutsches Reich), refers to Germany in the years 1933 to 1945, when it was governed by the National Socialist German Workers Party (Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei, NSDAP), with Führer Adolf Hitler as chancellor and, from 1934, head of state. Nazi Germany precipitated World War II.
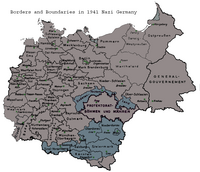
In addition to Weimar-era Germany proper, the Reich included areas with ethnic German populations such as Austria, the Sudetenland and the territory of Memel, all added before the war.
Other regions were acquired only after the outbreak of conflict, but had been part of Imperial Germany prior to the Treaty of Versailles and had varying German populations: Alsace-Lorraine, Danzig and parts of Poland. Others regions, particularly the rest of Poland, had never been part of a German state.
Some other acquired regions, especially parts of Slovenia, had once been part of the Austrian Empire. In addition, from 1939 to 1945, the Reich ruled Bohemia and Moravia as a Protectorate, peacefully subjugated prior to the start of the world war. Czech Silesia was incorporated into the province of Silesia during the same period.
The Reich's borders had changed defacto well before its military defeat in May 1945, as the German population fled westward from the advancing Red Army and the Western Allies pressed eastward from France. By the end of the war, a small strip of land stretching from Austria to Bohemia and Moravia - as well as a few other isolated regions - were the only areas not under Allied control. Upon its defeat, the Reich as a state was declared suppressed and was replaced by occupation zones administrated by the United States, France, the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union.
Background and terminology
Nazi Germany signed the Tripartite Pact with Imperial Japan and Fascist Italy during World War II. The three principal nations in this alliance, collectively referred to as the Axis Powers, fought against the Allies of World War II, which were led at first by the United Kingdom but after 1941 joined by the Soviet Union and the United States.
Third Reich is often used as a near- synonym for Nazi Germany. In German, the regime was and is sometimes referred to as Drittes Reich. Despite the interchangeable status of these terms, "Drittes Reich" is never referred to as the "Third Empire", the rough English translation.
The Nazi Party used the terms Drittes Reich and Tausendjähriges Reich ("Thousand-Year Empire") in order to connect the German empire they wished to forge to the ones of old (the Holy Roman Empire and the Second German Empire) while alluding to envisioned future prosperity and the new nation's alleged destiny. The Holy Roman Empire, deemed the First Empire or First Reich, had lasted almost a thousand years from 843 to 1806. The term Tausendjähriges Reich was used only briefly and dropped from propaganda in 1939, officially to avoid persiflage and possibly to even avoid religious connotations. In speeches, books and articles about the Third Reich after 8 May 1945, the phrase has taken on a new meaning and the early Nazi professions about a "thousand year" empire are often juxtaposed against the twelve years that the Third Reich actually existed.
The official name of Nazi Germany, in use after the 1933 German National Socialist Revolution, varied until 1943. However, the Nazis did not refer to their State as "Nazi Germany" or "National Socialist Germany", and such titles never appeared in official publications. Rather, they intensified the use of the official name of the pre-1945 German state: Deutsches Reich, a term officially used in Imperial Germany until 1919 and afterwards within the Weimar Republic. In 1943, however, the government decreed a change of official state name to the more expansionist name Großdeutsches Reich (Greater German Empire), which remained in official use until the collapse of Nazi Germany in May, 1945.
Ideology
Ideologically, the Nazis endorsed the concept of "Großdeutschland", or Greater Germany, and believed that the incorporation of the Germanic peoples into one nation was a vital step towards their national success. While the Nazis proposed the creation of an all-encompassing German ethnic State, others, particularly non-Germans, were in strong opposition to the idea, believing that a very large and powerful Germany would be to the disadvantage of the rest of Europe. Similarly, the "German problem", as it is often referred to in English scholarship, focuses on the issue of administration of Germanic regions within Northern and Central Europe, an important theme throughout German history. The "logic" of keeping Germany small worked in the favour of its principal economic rivals, and had been a driving force in the recreation of a Polish state. The goal was to create numerous counterweights in order to "balance out Germany's power." Regardless of one's position on these matters, it was the love affair with the Volk concept that led to Germany's expansion, culminating in World War II. Two important issues were administration of the Polish corridor and Danzig's incorporation into the Reich. As a further extension of racial policy, the Lebensraum program, adapted in the midst of the war, pertained to similar interests; it was decided that Eastern Europe would be settled with ethnic Germans, and the Slavic population who met the Nazi racial standard would be absorbed into the Reich. Those not fitting the racial standards were to be used as cheap labour force or deported eastward.
Racialism was an important aspect of society within the Third Reich. The Nazis also combined anti-Semitism with anti-Communist ideology and regarded the leftist movement - as well as international market capitalism - as the work of "conspiratorial Jewry". They referred to this so-called movement as the "Jewish-Bolshevistic revolution of subhumans." This platform manifested itself in the displacement, internment and later, the systematic extermination of an estimated six million European Jews in the midst of World War II. Other victims of Nazi persecution included Slavic populations in and outside of Slavic countries, blacks, Gypsies (viewed as subhuman), political opponents, social outcasts, homosexuals, religious dissidents such as Jehovah's Witnesses and Freemasons, and unyielding Church-affiliated leadership ( Confessing Church of German Lutherans and resisting Roman Catholic clergy). One could argue that a war with the Soviet Union was inevitable based on the Third Reich's precepts. However, World War II officially began after Nazi Germany invaded Poland on 1 September 1939, which led to France and the United Kingdom both declaring war on Germany. The global conflict that followed left Europe in ruins and led to the deaths of roughly sixty-two million persons.
Chronology of events
| History of Germany |
|---|
 |
| Ancient times |
| Germanic peoples |
| Migration Period |
| Frankish Empire |
| Medieval times |
| Holy Roman Empire |
| East Colonisation |
| Building a nation |
| Confederation of the Rhine |
| German Confederation |
| North German Confederation |
| Imperial Germany |
| German Empire |
| Germany during World War I |
| Weimar Republic |
| Weimar Republic |
| Nazi Germany |
| Nazi Germany |
| World War II |
| Post-war Germany |
| Since 1945 |
| Occupation and Division |
| Expulsion |
| East Germany |
| West Germany |
| German reunification |
| Present day Germany |
| Modern Germany |
| Topical |
| Military history of Germany |
| Timeline of German history |
| History of German |
| [] |
- Weimar Republic (includes the events leading to Hitler's appointment as Chancellor of Germany in 1933)
- Hitler's rise to power
- Gleichschaltung (the legal measures taken by the Nazis to establish their dictatorship)
- Reoccupation of the Rhineland
- Anschluss
- Axis Powers
- World War II (with a focus on military events)
Pre-War Politics 1933-1939
In the wake of the frustrations imposed through the Versailles Treaty, the worldwide economic depression of the 1930's, the counter-traditionalism of the Weimar period and the threat of Soviet-sponsored communism in Germany, many voters began turning their support towards the Nazi Party, which made great promises of an economic, cultural, and military renewal. The Dolchstoßlegende figured prominently. On 30 January 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany by President Paul von Hindenburg after attempts by General Kurt von Schleicher to form a viable government failed. Hindenburg was put under pressure by Hitler through his son Oskar von Hindenburg, as well as intrigue from former Chancellor Franz von Papen following his collection of participating financial interests and own ambitions to combat communism. Even though the Nazi Party had gained the largest share of the popular vote in the two Reichstag general elections of 1932, they had no majority of their own, and just a slim majority in parliament with their Papen-proposed Nationalist DNVP- NSDAP coalition. This coalition ruled through accepted continuance of the Presidential decree, issued under Article 48 of the 1919 constitution.
Consolidation of power

The new government installed a dictatorship in a series of measures in quick succession (see Gleichschaltung for details). On 27 February 1933 the Reichstag was set on fire, and this was followed immediately by the Reichstag Fire Decree, which rescinded habeas corpus and civil liberties.
A further step that turned Germany into a dictatorship virtually overnight was the Enabling Act passed in March 1933 with 444 votes, to the 94 of the remaining Social Democrats. The act gave the government (and thus effectively the Nazi Party) legislative powers and also authorized it to deviate from the provisions of the constitution. With these powers, Hitler removed the remaining opposition and turned the Weimar Republic into the "Third Reich".
Further consolidation of power was achieved on 30 January 1934, with the Gesetz über den Neuaufbau des Reichs (Act to rebuild the Reich). The act changed the highly decentralized federal Germany of the Weimar era into a centralized state. It disbanded state parliaments, transferring sovereign rights of the states to the Reich central government and put the state administrations under the control of the Reich administration.
Only the army remained independent from Nazi control. The German army had traditionally been somewhat separate from the government. The Nazi quasi-military SA expected top positions in the new power structure. Wanting to preserve good relations with the army, on the night of 30 June 1934, Hitler initiated the Night of the Long Knives, a purge of the leadership ranks of Röhm's SA as well as other political enemies, carried out by another, more elitist, Nazi organization, the SS.
At the death of president Hindenburg on 2 August 1934, the Nazi-controlled Reichstag merged the offices of Reichspräsident and Reichskanzler and reinstalled Hitler with the new title Führer und Reichskanzler. Until the death of Hindenburg, the army did not follow Hitler. However, with the death of Hindenburg, the entire army swore their obedience to Hitler.
The inception of the Gestapo, police acting outside of any civil authority, highlighted the Nazis' intention to use powerful, coercive means to directly control German society. Soon, an army estimated to be of about 100,000 spies and infiltrators operated throughout Germany, reporting to Nazi officials the activities of any critics or dissenters. Most ordinary Germans, happy with the improving economy and better standard of living, remained obedient and quiet, but many political opponents, especially communists and some types of socialists, were reported by omnipresent eavesdropping spies, and put in prison camps where they were severely mistreated, and many tortured and killed. It is estimated that tens of thousands of political victims died or disappeared in the first few years of Nazi rule.
Social policy
The Nazi regime was characterized by political control of every aspect of society in a quest for racial ( Aryan, Nordic), social and cultural purity. Modern abstract art and avant-garde art was thrown out of museums, and put on special display as " Degenerate art", where it was to be ridiculed. In one notable example on 31 March 1937, huge crowds stood in line to view a special display of "degenerate art" in Munich, while a concurrent exhibition of 900 works personally approved by Adolf Hitler attracted a tiny, unenthusiastic gathering.
The Nazi Party pursued its aims through persecution and killing of those considered impure, targeted especially against minority groups such as Jews, Gypsies, Jehovah's Witnesses, and homosexuals.
In the years following the Nazi rise to power, many Jews fled the country and were encouraged to do so. By the Nuremberg Laws passed in 1935, Jews were stripped of their German citizenship and denied government employment. Most Jews employed by Germans lost their jobs at this time, which were being taken by unemployed Germans. Notably, the Nazi government attempted to send 17,000 German Jews of Polish descent back to Poland, a decision which led to the assassination of Ernst vom Rath by Herschel Grynszpan, a German Jew living in France. This provided the pretext for a pogrom the Nazi Party incited against the Jews on 9 November 1938, which specifically targeted Jewish businesses. The event was called Kristallnacht (Night of Broken Glass, literally "Crystal Night"); the euphemism was used because the numerous broken windows made the streets look as if covered with crystals. By September 1939, more than 200,000 Jews had left Germany, with the Nazi government seizing any property they left behind.
The Nazis also undertook programs targeting "weak" or "unfit" members of their own population, such as the T-4 Euthanasia Program, killing tens of thousands of disabled and sick Germans in an effort to "maintain the purity of the German Master race" (German: Herrenvolk) as described by Nazi propagandists. The techniques of mass killing developed in these efforts would later be used in the Holocaust. Under a law passed in 1933, the Nazi regime carried out the compulsory sterilization of over 400,000 individuals labeled as having hereditary defects, ranging from mental illness to alcoholism.
Recent research by academics such as Götz Aly has emphasized the role of the extensive Nazi welfare programs that supposedly helped maintain public support for the regime that lasted long into the war. The German community was nationalized and labor and entertainment - from festivals, to vacation trips and traveling cinemas - were all made a part of the "Strength through Joy" ( Kraft durch Freude) program. Also crucial to the building of loyalty and comradeship was the implementation of the National Labor Service and the Hitler Youth Organization, with the former being compulsory and the latter consisting of nearly six million boys and girls. In addition to a number of architectural projects that were undertaken, the construction of the Autobahn made it the first National Motor Highway system in the world. It should be noted that between 1933 and 1936, Germany outpaced the United States in construction, automobile production, unemployment and employment. All in all, the New Reich gave Germans confidence and naturally instilled loyalty.
Other issues in Nazi Germany were Animal rights , Environmentalism , , and Public health ,
Economic policy
When the Nazis came to power the most pressing issue was an unemployment rate of close to 30%. The economic management of the state was first given to respected banker Hjalmar Schacht. Under his guidance, a new economic policy to elevate the nation was drafted. One of the first actions was to destroy the trade unions and impose strict wage controls.
The government then expanded the money supply through massive deficit spending. However at the same time the government imposed a 4.5% interest rate ceiling, creating a massive shortage in borrowable funds. This was resolved by setting up a series of dummy companies that would pay for goods with bonds. The most famous of these was the MEFO company, and these bonds used as currency became known as mefo bills. While it was promised that these bonds could eventually be exchanged for real money, the repayment was put off until after the collapse of the Reich. These complicated maneuvers also helped conceal armament expenditures that violated the Treaty of Versailles.
According to economic theory, price control combined with a large increase in the money supply should have produced a large black market, but harsh penalties that saw violators sent to concentration camps or even shot prevented this development. Repressive measures also kept volatility low, reducing inflationary pressures. New policies also limited imports of consumer goods and focused on producing exports. International trade was greatly reduced remaining at about a third of 1929 levels throughout the Nazi period. Currency controls were extended, leading to a considerable overvaluation of the Reichsmark. These policies were successful in cutting unemployment dramatically.
Most industry was not nationalized, however industry was closely regulated with quotas and requirements to use domestic resources. These regulations were set by administrative committees composed of government and business officials. Competition was limited as major companies were organized into cartels through these administrative committees. Selective nationalization was used against businesses that failed to agree to these arrangements. The banks, which had been nationalized by Weimar, were returned to their owners and each administrative committee had a bank as member to finance the schemes.
While the strict state intervention into the economy and the massive rearmament policy led to full employment during the 1930s, real wages in Germany dropped by roughly 25% between 1933 and 1938. Trade unions were abolished, as well as collective bargaining and the right to strike. The right to quit also disappeared: Labor books were introduced in 1935, and required the consent of the previous employer in order to be hired for another job.
The German economy was transferred to the leadership of Hermann Göring when, on 18 October 1936, the German Reichstag announced the formation of a Four-Year Plan. The Nazi economic plan aimed to achieve a number of objectives. Under the leadership of Fritz Todt, a massive public works project, the Reichsarbeitsdienst, was started, rivaling Roosevelt's New Deal in both size and scope. It functioned as a military-like unit, its most notable achievements being the network of Autobahnen and, once the war started, the building of bunkers, underground facilities and entrenchments all over Europe.
Another part of the new German economy was massive rearmament, with the goal being to expand the 100,000-strong German Army into a force of millions. In comparison, a military buildup had also been a part of the New Deal (regarding the Navy) and Stalin's First Five Year Plan. The Four-Year Plan was discussed in the controversial Hossbach Memorandum, which provides the "minutes" from one of Hitler's briefings. Some use the Hossbach Memorandum to show that Hitler planned a war in Eastern Europe in the pursuit of Lebensraum, believing that the Western powers of the United Kingdom and France would not intervene, leaving him free to take over the USSR, the "natural enemy" of Germany. However, this intentionalist view is disputed.
Nevertheless, the war came and although the Four-Year Plan technically expired in 1940, Hermann Göring had built up a power base in the "Office of the Four-Year Plan" that effectively controlled all German economic and production matters by this point in time. In 1942, the growing burdens of the war and the death of Todt saw the economy move to a full war economy under Albert Speer.
World War II
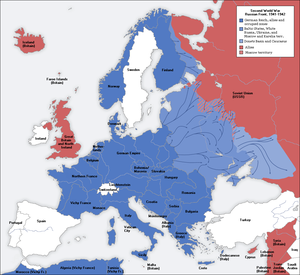
The " Danzig crisis" peaked in the months after Poland rejected Nazi Germany's initial offer regarding both the Free City of Danzig and the Polish Corridor. After a series of ultimatums, the Germans broke from diplomatic relations and shortly thereafter, Germany invaded Poland on 1 September 1939. This led to the outbreak of the Second World War in Europe when on 3 September 1939, the United Kingdom and France both declared war on Germany. The Phony War followed. On 9 April 1940 the Germans struck north against Denmark and Norway, in part to secure the safety of continuing iron ore supplies from Sweden through Norwegian coastal waters. British and French forces landed in the north, only to be defeated in the ensuing Norwegian Campaign. In May, the Phony War ended when despite the protestations of many of his advisors, Hitler took a gamble and sent German forces into France and the Low Countries. The Battle of France was an overwhelming German victory. Later that year, Germany subjected the United Kingdom to heavy bombing during the Battle of Britain. This may have served two purposes, either as a precursor to Operation Sea Lion or it may have been an effort to dissuade the British populace from continuing to support the war.
Germany invaded the Soviet Union on 22 June 1941 and on the eve of the invasion, Hitler's former deputy, Rudolf Hess, attempted to negotiate terms of peace with the United Kingdom in an unofficial private meeting after crash-landing in Scotland.
Nazi Germany declared war on the United States on 11 December, 1941, four days after the Japanese bombed Pearl Harbour. This allowed German submarines in the Atlantic to fight US convoys that had been supporting the United Kingdom and although Nazi hubris is often cited, Hitler presumably sought the further support of Japan. He was convinced of the United States' aggressive intentions following the leaking of Rainbow Five and hearing of the foreboding content of Franklin Roosevelt's Pearl Harbour speech. Before then, Germany had practiced its own policy of appeasement, taking drastic precautions in order to avoid the United States' entry into the war.
The persecution of minorities and "undesirables" continued both in Germany and the occupied countries. From 1941 onward, Jews were required to wear a yellow badge in public and most were transferred to ghettos, where they remained isolated from the rest of the population. In January 1942, at the Wannsee Conference and under the supervision of Reinhard Heydrich, a plan for the " Final Solution of the Jewish Question" (Endlösung der Judenfrage) in Europe was hatched. From then until the end of the war some six million Jews and many others, including homosexuals, Slavs, and political prisoners, were systematically killed. In addition, more than ten million people were put into forced labor. This genocide is called the Holocaust in English and the Shoah in Hebrew. Thousands were shipped daily to extermination camps (Vernichtungslager, sometimes called "death factories") and concentration camps (Konzentrationslager, KZ), some of which were originally detention centers but later converted into literal mass-murder factories, or death camps, for the purpose of killing of their inmates.Eighteen months earlier, President Franklin D. Roosevelt had transferred the United States Fleet to Pearl Harbour as a presumed deterrent to Japanese agression. The Japanese military, deeply engaged in the seemingly endless war it had started against China in mid-1937, badly needed oil and other raw materials. Commercial access to these was gradually curtailed as the conquests continued. In July 1941 the Western powers effectively halted trade with Japan. From then on, as the desperate Japanese schemed to seize the oil and mineral-rich East Indies and Southeast Asia, a Pacific war was virtually inevitable.
Parallel to the Holocaust, the Nazis conducted a ruthless program of conquest and exploitation over the captured Soviet and Polish territories and their Slavic populations as part of their Generalplan Ost. According to estimates, 20 million Soviet civilians, three million non-Jewish Poles, and seven million Red Army soldiers died under Nazi maltreatment in what the Russians call the Great Patriotic War. The Nazis' plan was to extend German lebensraum ("living space") eastward, a foreseen consequence of the war in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union, said by the Nazis to have been waged in order "to defend Western Civilization against Bolshevism". Due to many of the atrocities suffered under Stalin, the Nazi message was interpreted by many to be legitimate. Many Ukranians, Balts and other disillusioned Soviets fought with the Germans, not to mention other Europeans enlisted in numerous Schutzstaffel divisions.
By February 1943 the Soviets had defeated the Germans at Stalingrad and began the push westward, winning the tank battle at Kursk-Orel in July. The German Army was pushed back to the borders of Poland by February 1944 following the great success of Operation Bagration. The Allies opened a Western Front in June 1944 at Normandy, a year and a half after the Soviets turned the tide on the Eastern Front. Soviet troops moving westward met Allied troops moving eastward at Torgau at the Elbe on April 26, 1945 (Cohen).
On April 30, 1945, as Berlin was being taken by Soviet forces, Hitler committed suicide. He was succeeded by Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz, whose caretaker government sought a separate peace with the Western Allies. On 4 May– 8 May 1945 German armed forces surrendered unconditionally. This was the end of World War II in Europe and, with the creation of the Allied Control Council on 5 July 1945, the four Allied powers "assume[d] supreme authority with respect to Germany" ( Declaration Regarding the Defeat of Germany, US Department of State, Treaties and Other International Acts Series, No. 1520).
The Post-War Period
The Potsdam Conference in August 1945 created arrangements and outline for new government for the post-war Germany as well as war reparations and resettlement. All German annexations in Europe after 1937, such as the Sudetenland, were reversed, and in addition Germany's eastern border was shifted westwards to the Oder-Neisse line, effectively reducing Germany in size by approximately 25% compared to her 1937 border. The territories east of the new border comprised East Prussia, Silesia, West Prussia, and two thirds of Pomerania. These areas were mainly agricultural, with the exception of Upper Silesia which was the second largest centre of German heavy industry. France took control of a large part of Germany's remaining coal deposits. Virtually all Germans in Central Europe were subsequently over a period of several years expelled , affecting about seventeen million ethnic Germans. Most casualty estimates of this expulsion range between 1 to 2 Million dead. The French, US and British occupation zones later became West Germany (the Federal Republic of Germany), while the Soviet zone became the communist East Germany (the German Democratic Republic, excluding sections of Berlin). The initial repressive occupation policy in Germany by the Western Allies was reversed after a few years when the Cold War made the Germans important as allies against communism. West Germany recovered economically by the 1960s, being called the economic miracle (German term Wirtschaftswunder), mainly due to the currency reform of 1948 which replaced the Reichsmark with the Deutsche Mark as legal tender, halting rampant inflation, but also to lesser degree helped by economic aid through the Marshall Plan which was extended to also include West Germany in 1949, and upheld thanks to fiscal policy and intense labor, eventually leading to labor shortages. Allied dismantling of West German industry was finally halted in 1950. In 1955 the military occupation of West Germany was ended. East Germany recovered at a slower pace under Communism until 1990, due to reparations paid to the Soviet Union and the effects of the centrally planned economy. Germany regained full sovereignty in 1991.
After the war, surviving Nazi leaders were put on trial by an Allied tribunal at Nuremberg for crimes against humanity. A minority were sentenced to death and executed, but a number were jailed and then released by the mid 1950s due to poor health and old age. In the 1960s, 1970s and 1980s, some renewed efforts were made in West Germany to take those who were directly responsible for "crimes against humanity" to court (e.g. Auschwitz trials). However, many of the less prominent leaders continued to live well into the 1980s and 1990s.
In all non-fascist European countries legal purges were established to punish the members of the former Nazi and Fascist parties. Even there, however, some of the former leaders found ways to accommodate themselves under the new circumstances. An uncontrolled punishment hit the children of Nazis and those fathered by German soldiers in occupied countries, including the " Lebensborn" children.
Military structure
Wehrmacht — Armed Forces
- OKW — Armed Forces High Command
- Chief of the Supreme Command of the Armed Forces - Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel
- Chief of the Operations Staff - Colonel General Alfred Jodl
- Chief of the Supreme Command of the Armed Forces - Field Marshal Wilhelm Keitel
Heer — Army
- OKH — Army High Command
- Army Commanders-in-Chief
- Colonel General Werner von Fritsch (1935 to 1938)
- Field Marshal Walther von Brauchitsch (1938 to 1941)
- Führer and Reich Chancellor Adolf Hitler (1941 to 1945)
- Field Marshal Ferdinand Schörner (1945)
- Field Marshal Walther von Brauchitsch (1938 to 1941)
- Army Commanders-in-Chief
Kriegsmarine — Navy
- OKM — Navy High Command
- Navy Commanders-in-Chief
- Grand Admiral Erich Raeder (1928-1943)
- Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz (1943-1945)
- General Admiral Hans-Georg von Friedeburg (1945)
- Grand Admiral Karl Dönitz (1943-1945)
- Navy Commanders-in-Chief
Luftwaffe — Airforce
- OKL — Airforce High Command
- Reichsluftschutzbund (Air Force Auxiliary)
- Air Force Commanders-in-Chief
- Reich Marshal Hermann Göring (to 1945)
- Field Marshal Robert Ritter von Greim (1945)
Abwehr — Military Intelligence
- Rear Admiral Konrad Patzig {1932-1935)
- Vice Admiral Wilhelm Canaris (1935-1944)
Waffen-SS — Nazi Party military branch
Organization of the Third Reich
The leaders of Nazi Germany created a large number of different organizations for the purpose of helping them stay in power. They rearmed and strengthened the military, set up an extensive state security apparatus and created their own personal party army, the Waffen SS. Through staffing of most government positions with Nazi Party members, by 1935 the German national government and the Nazi Party had become virtually one and the same. By 1938, through the policy of Gleichschaltung, local and state governments lost all legislative power and answered administratively to Nazi party leaders, known as Gauleiters, who governed Gaue and Reichsgaue.
The organization of the Nazi state, as of 1944, was as follows:
Head of State and Chief Executive
- Führer and Reich Chancellor (Adolf Hitler)
Cabinet and national authorities
- Office of the Reich Chancellery ( Hans Lammers)
- Office of the Party Chancellery ( Martin Bormann)
- Office of the Presidential Chancellery ( Otto Meissner)
- Privy Cabinet Council ( Konstantin von Neurath)
- Chancellery of the Führer ( Philip Bouhler)
Reich Offices
- Office of the Four-Year Plan ( Hermann Göring)
- Office of the Reich Master Forester ( Hermann Göring)
- Office of the Inspector for Highways
- Office of the President of the Reich Bank
- Reich Youth Office
- Reich Treasury Office
- General Inspector of the Reich Capital
- Office of the Councillor for the Capital of the Movement ( Munich, Bavaria)
Reich Ministries
| Nazism |
|---|
| Nazi organizations |
| Nazi Party Sturmabteilung Schutzstaffel Hitler Youth Lebensborn |
| Nazism in history |
| Early Nazi Timeline Hitler's rise to power Nazi Germany Night of the Long Knives Nuremberg Rallies Kristallnacht The Holocaust Nuremberg Trials Ex-Nazis and Neo-Nazism |
| Nazi concepts |
| Glossary of the Third Reich Hitler's political beliefs Gleichschaltung Racial policy of Nazi Germany Führerprinzip Lebensraum Positive Christianity Volk |
| Nazi political parties and movements outside Germany |
| Canadian National Socialist Unity Party German-American Bund Nasjonal Samling Nationaal-Socialistische Beweging National Socialist Bloc National Socialist League |
| Nazi Eugenics |
| Nazi eugenics Aryan race Doctors' Trial German Blood Certificate Lebensborn Life unworthy of life Mischling Nazi physicians Nazi human experimentation Nazism and race Nordic theory Nur für Deutsche Nuremberg Trials Racial policy of Nazi Germany Racial purity Reich Citizenship Law Scientific racism T-4 Euthanasia Program |
| Related subjects |
| Nazism and religion Nazi propaganda Nazi mysticism Nazi architecture Hitler salute Mein Kampf Swastika Völkisch movement Antisemitism Führer Neo-Nazism Fascism |
| Lists |
| Nazi Party leaders and officials Fascists Adolf Hitler books Adolf Hitler speeches SS personnel Living Nazis Former Nazis influential after 1945 |
| Politics Portal |
- Reich Foreign Ministry ( Joachim von Ribbentrop)
- Reich Interior Ministry ( Wilhelm Frick, Heinrich Himmler)
- Reich Ministry for Public Enlightenment and Propaganda ( Joseph Goebbels)
- Reich Ministry of Aviation ( Hermann Göring)
- Reich Ministry of Finance ( Lutz Schwerin von Krosigk)
- Reich Ministry of Justice ( Franz Schlegelberger)
- Reich Economics Ministry ( Walther Funk)
- Reich Ministry for Nutrition and Agriculture ( R. Walther Darre)
- Reich Labor Ministry ( Franz Seldte)
- Reich Ministry for Science, Education, and Public Instruction ( Bernhard Rust)
- Reich Ministry for Ecclesiastical Affairs ( Hanns Kerrl)
- Reich Transportation Ministry ( Julius Dorpmüller)
- Reich Postal Ministry ( Wilhelm Ohnesorge)
- Reich Ministry for Weapons, Munitions, and Armament ( Fritz Todt, Albert Speer)
- Reich Ministers without Portfolio ( Konstantin von Neurath, Hans Frank, Hjalmar Schacht, Arthur Seyss-Inquart)
Occupation authorities
- Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories ( Alfred Rosenberg)
- General Government of Poland ( Hans Frank)
- Reich Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia ( Konstantin von Neurath)
- Deputy Reich Protector of Bohemia and Moravia ( Reinhard Heydrich)
- Office of the Military Governor of France
Legislative Branch
- Reichstag
- President of the Reichstag ( Hermann Göring)
- Reichsrat (disbanded February 14, 1934)
It has to be considered that there is little use talking about a legislative branch in a totalitarian state, where there is no separation of powers. For example, since 1933 the Reichsregierung (Reich cabinet) was enabled to enact Reichsgesetze (statute law) without respect to the constitution from 1919.
Paramilitary organizations
- Sturmabteilung (SA)
- Schutzstaffel (SS)
- Allgemeine SS
- Waffen SS
- Germanische SS
- Deutscher Volkssturm
- Nationalsozialistisches Kraftfahrerkorps (NSKK)
- Nationalsozialistisches Fliegerkorps (NSFK)
National police
Reich Central Security Office (RSHA — Reichssicherheitshauptamt) Ernst Kaltenbrunner
- Order Police ( Ordnungspolizei (Orpo))
- Schutzpolizei (Safety Police)
- Gendarmerie (Rural Police)
- Gemeindepolizei (Local Police)
- Security Police ( Sicherheitspolizei (Sipo))
- Geheime Staatspolizei (Gestapo)
- Reichskriminalpolizei (Kripo)
- Sicherheitsdienst ( SD)
Political organizations
- Nazi Party — National Socialist German Workers Party (abbreviated NSDAP)
- Youth organizations
- Hitler-Jugend — Hitler-youth (for boys and young men) Baldur von Schirach
- Bund Deutscher Mädel (for girls and young women)
- Deutsches Jungvolk (for very young boys and girls ages 6-8)
Service organizations
- Deutsche Reichsbahn (State Railway)
- Reichspost (State Postal Service)
- Deutsches Rotes Kreuz (German Red Cross)
Religious organizations
- German Christians
- Protestant Reich Church
Academic organizations
- National Socialist German University Teachers League
- National Socialist German Students League
Prominent persons in Nazi Germany
For a listing of Hitler's cabinet see : Hitler's Cabinet, January 1933 - April 1945
Nazi Party and Nazi government leaders and officials
- Artur Axmann — Reich Youth Leader (successor of Baldur von Schirach in 1940)
- Ernst Wilhelm Bohle — Under-Secretary of State, Head of the NSDAP Foreign Organisation (1933-1945)
- Martin Bormann — Head of the Party Chancellery (Parteikanzlei) and Private Secretary to Adolf Hitler
- Karl Brandt — Reich Commissioner of Health and Sanitation
- Alois Brunner — SS Lieutenant Colonel and Adolf Eichmann’s most important assistant
- Otto Dietrich — Under-Secretary of State, Reich Chief of the Press
- Adolf Eichmann — recording secretary at the Wannsee Conference, facilitator of the Final Solution
- Fatos Von Pristina - Reich Ministry Of Albanian Teritory
- Karl Fiehler — Nazi Lord Mayor of Munich and Head of the unity organization for local politics
- Hans Frank — Minister, Head of the German Law Academy
- Roland Freisler — Under-Secretary of State at the Reich Ministry of Justice and President of the Volksgerichtshof
- Wilhelm Frick — Minister of the Interior
- Hans Fritzsche — senior official of the Reich Ministry for Propaganda
- Walter Funk — Minister of Industries
- Joseph Goebbels — Minister of Propaganda, became Chancellor of Germany for one day following Hitler's death, was named his immediate successor by Hitler himself.
- Hermann Göring — Reichsmarschall and Minister-President of Prussia. Air Minister. Minister of the Interior. President of the Reichstag.
- Franz Gürtner — Minister of Justice
- Karl Hanke — Under-Secretary of State, Propaganda Ministry
- Rudolf Hess — the Führer's Deputy
- Reinhard Heydrich — Head of Reich Main Security Office and Protector of Bohemia and Moravia
- Konstantin Hierl — Head of the Reich Labour Service
- Heinrich Himmler — Reich Leader SS
- Adolf Hitler — Führer and Reich Chancellor
- Ernst Kaltenbrunner — Chief of the RSHA (1943-1945)
- Hanns Kerrl — Reich Minister of Ecclesiastical Affairs (1933–1941)
- Karl Otto Koch — SS Colonel and commandant of the concentration camps at Buchenwald and Majdanek
- Hans Lammers — Head of the Reich Chancellery
- Herbert Lange — SS Major, chief inspector of the Posen State Police Headquarters
- Robert Ley — Leader of the German Labour Front
- Viktor Lutze — Chief of Staff of the SA (1934–1943)
- Otto Meissner — Head of the Reich President’s Office
- Alfred Meyer — Under-Secretary of State at the Reich Ministry for the Occupied Eastern Territories
- Konstantin von Neurath — Head of the Secret Cabinet
- Hans Nieland — Head of the NSDAP Foreign Organisation (1931-1933) and Lord Mayor of Dresden (1940-1945)
- Erich Priebke — SS Captain, participated in the massacres at the Ardeatine caves near Rome
- Joachim von Ribbentrop — Foreign Minister (1938–1945)
- Ernst Röhm — Chief of Staff of the SA (1931–1934)
- Alfred Rosenberg — ideologist of National Socialism, Reich Minister for the Occupied Eastern Territories
- Bernhard Rust — Minister of Education
- Carl Schmitt — expert on constitutional law and political philosopher, who affected Nazism with his anti-Semite and antidemocratic theses
- Fritz Sauckel — General Plenipotentiary for the Employment of Labour (1942–1945)
- Baldur von Schirach — Leader of the Hitlerjugend (Nazi Youth Organisation), Gauleiter of Vienna
- Franz Seldte — Reich Minister of Labor (1933–1945)
- Arthur Seyß-Inquart — Reichsstatthalter in Austria, Commissioner for the Occupied Netherlands
- Albert Speer — First Architect, Minister for Armament from 1942
- Julius Streicher — Gauleiter of Franconia (1923-1940), publisher of Der Stürmer
- Josef Terboven — Reichskommissar for Norway (1940–1945)
- Fritz Todt — Inspector General for German Roadways, Reich Minister for Armaments and Munitions (1940-1942)
- Hjalmar Schacht — Minister, Governor of the Central Bank (Reichsbank) (1933-1939)
- Gertrud Scholtz-Klink — Reich Leader of Women (1934-1945)
- Hans von Tschammer und Osten — Under-Secretary of State and Reich Sports Leader (1933-1943)
Military
- Karl Dönitz-Commander of the German U-Boat force, later the German Navy. Was named as Hitler's successor as Reich president (not to be confused with Chancellor of Germany).
- Gerd von Rundstedt
- Erwin Rommel
- Wilhelm Keitel
- Claus von Stauffenberg
- Wilhelm Canaris
- Alfred Jodl
- Erich Raeder
- Robert Ritter von Greim
- Albert Kesselring
- Erich von Manstein
Other
- Gottfried Benn
- Eva Braun
- Wernher von Braun
- Houston Stewart Chamberlain
- Anton Drexler
- Gottfried Feder
- Friedrich Flick
- Theodor Fritsch
- Arthur de Gobineau
- Hans Friedrich Karl Günther (not to be confused with Hans Günther)
- Karl Harrer
- Willibald Hentschel
- Alfred Hoche
- Armin D. Lehmann
- Lanz von Liebenfels
- Guido von List
- Karl Lueger
- Alfred Ploetz
- Ferdinand Porsche
- Traudl Junge
- John Rabe
- Geli Raubal
- Leni Riefenstahl
- Oskar Schindler
- Rudolf von Sebottendorf
- Richard Sorge
- Johannes Stark
- Walter Thiel
- Richard Wagner
- Winifred Wagner
- Konrad Zuse
- Otto van Hinbrick
- Walther Sommerlath
Noted victims
- Dietrich Bonhoeffer
- Georg Elser
- Anne Frank
- Hana Brady
- Janusz Korczak
- Erich Mühsam
- Carl von Ossietzky
- White Rose (Sophie and Hans Scholl and others)
- Bruno Schulz
- Ernst Thälmann
Noted refugees
- Hannah Arendt
- Albert Bassermann
- Johannes R. Becher
- Rudolf Belling
- Walter Benjamin
- Bertolt Brecht
- Marlene Dietrich
- Albert Einstein
- Lion Feuchtwanger
- Sigmund Freud
- Erich Fromm
- Kurt Gödel
- Walter Gropius
- Friedrich Hayek
- Heinrich Eduard Jacob
- Theodor Kramer
- Fritz Lang
- Heinrich Mann
- Thomas Mann
- Lise Meitner
- Ludwig von Mises
- Solomon Perel
- Erich Maria Remarque
- Anna Seghers
- Kurt Tucholsky
- Walter Ulbricht
- Kurt Weill
Noted survivors
- George Brady
- Bruno Bettelheim
- Viktor Frankl
- Eugen Kogon
- Primo Levi
- Martin Niemöller
- Kurt Schumacher
- Franz von Papen
- Roman Polanski
- Elie Wiesel
- Simon Wiesenthal
- Arnulf Øverland
- Trygve Bratteli
- Hella Taichman Zaltz Weinreb