Jimmy Carter
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: USA Presidents
| James Earl Carter, Jr. | |
 |
|
|
|
|
|---|---|
| In office January 20, 1977 – January 20, 1981 |
|
| Vice President(s) | Walter Mondale |
| Preceded by | Gerald Ford |
| Succeeded by | Ronald Reagan |
|
|
|
| Born | October 1, 1924 (age 82) Plains, Georgia |
| Political party | Democratic |
| Spouse | Rosalynn Smith Carter |
| Religion | Baptist |
| Signature | |
James Earl Carter, Jr. (born October 1, 1924), was the 39th President of the United States (1977–1981) and the Nobel Peace laureate in 2002. Previously, he was the Governor of Georgia (1971–1975). Carter won the Democratic nomination as a dark horse candidate, and went on to defeat incumbent Gerald Ford in the 1976 presidential election.
As President his major initiatives included the consolidation of numerous governmental agencies into the newly formed Department of Energy, a cabinet level department. He enacted strong environmental legislation; deregulated the trucking, airline, rail, finance, communications, and oil industries; bolstered the social security system; and appointed record numbers of women and minorities to significant government and judicial posts. In foreign affairs, Carter's major initiatives included the Camp David Accords, the Panama Canal Treaties, the creation of full diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China, and the negotiation of the SALT II Treaty. In addition, he's a champion of human rights throughout the world and used human rights as the centre of his administration's foreign policy.
The Iranian hostage crisis was seen by critics as a devastating blow to national prestige; Carter struggled for 444 days to effect the release of the hostages. A failed rescue attempt led to the resignation, in protest, of his Secretary of State Cyrus Vance. The hostages were finally released the day Carter left office.
The Soviet invasion of Afghanistan marked the end of détente, and Carter moved to the right, boycotted the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow, and began to rebuild American military power. He beat off a primary challenge from Senator Ted Kennedy but was unable to effectively reduce soaring interest rates and inflation rates, or to lower unemployment. The " Misery Index", his favored measure of economic well-being, rose 50% in four years. He feuded with the Democratic leaders who controlled Congress and, as a result, was unable to reform the tax system or to implement a national health plan. He was defeated by Republican Ronald Reagan in 1980.
After leaving office, Carter assumed the role of an elder statesman and international mediator, using his prestige as a former president to further many causes. He founded the Carter Centre as a forum for issues related to democracy and human rights. He has also traveled extensively to monitor elections, conduct peace negotiations, and establish relief efforts. In 2002, Carter won the Nobel Peace Prize for his "efforts to find peaceful solutions to international conflicts, to advance democracy and human rights, and to promote economic and social development." Carter has continued his decades-long active involvement with the charity Habitat for Humanity, which builds houses for the needy.
Early years
Carter descended from a family that had resided in Georgia for several generations. His great-grandfather, Private L. B. Walker Carter (1832–1874) served in the Confederate States Army in the Sumter Flying Artillery, seeing considerable action at the Battle of Gettysburg.
Jimmy Carter, the first President born in a hospital, was the oldest of four children of James Earl and Lillian Gordy Carter. He was born in the southwest Georgia town of Plains and grew up in nearby Archery, Georgia. Carter was a gifted student from an early age who always had a fondness for reading. By the time he attended Plains High School, he was also a star in basketball and football. He was greatly influenced by one of his high school teachers, Julia Coleman. Ms. Coleman was handicapped by polio. She had encouraged young Jimmy to read War and Peace; he was disappointed to find that there were no cowboys or Indians in the book. Carter mentioned his beloved teacher in his inaugural address as an example of someone who beat overwhelming odds. Carter had three younger siblings. His brother, Billy (1937–1988), caused some political problems for him during his administration. His sister, Gloria (1926–1990), was low-key and was famous for collecting and riding Harley-Davidson motorcycles. His other sister, Ruth (1929–1983), became a well-known Christian evangelist.
He attended Georgia Southwestern College and Georgia Institute of Technology and received a Bachelor of Science degree from the United States Naval Academy in 1946. Carter was a gifted student and finished 59th out of his Academy class of 820. Carter served on submarines in the Atlantic and Pacific fleets. He was later selected by Captain (later Admiral) Hyman G. Rickover for the U.S. Navy's fledgling nuclear submarine program, where he became a qualified command officer. Rickover was a demanding officer, and Carter was greatly influenced by him. Carter later said that next to his parents, Admiral Rickover had had the greatest influence on him. There was a story he often told of being interviewed by the Admiral. He was asked about his rank in his class at the Naval Academy. Carter said "Sir, I graduated 59th out of a class of 820". Rickover only asked "Did you always do your best?" Carter was forced to admit he had not, and the Admiral asked why. Carter later used this as the theme of his presidential campaign, and as the title of his first book, "Why Not The Best?" Carter loved the Navy, and had planned to make it his career. His ultimate goal was to become Chief of Naval Operations. Carter did some post-graduate work, studying nuclear physics and reactor technology for several months at Union College starting in March 1953. He married Rosalynn Smith in 1946. They had three sons, ( John William "Jack" Carter, born in 1947; James Earl "Chip" Carter III, born in 1950; and Donnel Jeffrey "Jeff" Carter, born in 1952), and a daughter ( Amy Lynn Carter, in 1967).
Upon the death of his father in July 1953, however, LT. Carter immediately resigned his commission and was discharged from the Navy on October 9, 1953. This cut short his nuclear power training school and unfortunately he was never able to command a nuclear submarine, as the first of the fleet was launched January 17, 1955, over a year after his discharge from the Navy.
He then took over and expanded his family's peanut farming business in Plains. There he was involved in a farming accident which left him with a permanently bent finger.
From a young age, Carter showed a deep commitment to Christianity, serving as a Sunday School teacher throughout his political career. Even as President, Carter prayed several times a day, and professed that Jesus Christ was the driving force in his life. Carter had been greatly influenced by a sermon he had heard as a young man, called, "If you were arrested for being a Christian, would there be enough evidence to convict you?"
Early political career
State Senate
Carter started his career by serving on various local boards, governing such entities as the schools, hospital, and library, among others. In the 1960s, he served two terms in the Georgia Senate from the fourteenth district of Georgia.
His 1962 election to the state Senate, which followed the end of Georgia's County Unit System (per the Supreme Court case of Gray v. Sanders), was chronicled in his book Turning Point: A Candidate, a State, and a Nation Come of Age. The election involved corruption led by Joe Hurst, the sheriff of Quitman County. This included people voting in alphabetical order and dead people voting. It took a challenge of the fraudulent results for Carter to win the election. Carter was reelected in 1964, to serve a second two-year term.
Campaign for governor
In 1966, at the end of his career as a state senator, he flirted with the idea of running for the United States House of Representatives. His Republican opponent dropped out and decided to run for Governor of Georgia. Carter did not want to see a Republican as the governor of his state and in turn dropped out of the race for Congress and joined the race to become governor. Carter lost the Democratic primary, but drew enough votes as a third place candidate to force the favourite, Ellis Arnall, into a run-off, setting off a chain of events which resulted in the election of Lester Maddox.
For the next four years, Carter returned to his agriculture business and carefully planned for his next campaign for governor in 1970, making over 1,800 speeches throughout the state.
During his 1970 campaign, he ran an uphill populist campaign in the Democratic primary against former Governor Carl Sanders, labeling his opponent "Cufflinks Carl". Although Carter had never been a segregationist—he had refused to join the segregationist White Citizens' Council, prompting a boycott of his peanut warehouse; and he had been one of only two families which voted to admit blacks to the Plains Baptist Church —he "said things the segregationists wanted to hear," according to historian E. Stanly Godbold. Carter did not condemn Alabama firebrand George Wallace, and Carter's campaign aides handed out photographs of his opponent, showing Sanders associating with black basketball players. He also chastised Sanders for not inviting Wallace to address the State Assembly during his tenure as Governor. Following his close victory over Sanders in the primary, he was elected governor over Republican Hal Suit.
Governor of Georgia
| Jimmy Carter | |
|
|
|
|
January 12, 1971 – January 14, 1975 |
|
| Lieutenant Governor: | Lester Maddox |
|---|---|
| Predecessor: | Lester Maddox |
| Successor: | George Busbee |
| Born: | October 1, 1924 Plains, Georgia |
| Political party: | Democrat |
| Profession: | Farmer/Naval Submariner |
| Spouse: | Rosalynn Smith Carter |
| Religion: | Baptist |
After having run a campaign in which he promoted himself as a traditional southern conservative, Carter surprised the state and gained national attention by declaring in his inaugural speech that the time of racial segregation was over, and that racial discrimination had no place in the future of the state. He was the first statewide office holder in the Deep South to say this in public. Following this speech, Carter appointed many blacks to statewide boards and offices.
Carter made government efficient by merging about 300 state agencies into 30 agencies. One of his aides recalled that Governor Carter "was right there with us, working just as hard, digging just as deep into every little problem. It was his program and he worked on it as hard as anybody, and the final product was distinctly his." He also pushed reforms through the legislature, providing equal state aid to schools in the wealthy and poor areas of Georgia, set up community centers for mentally handicapped children, and increased educational programs for convicts. Carter took pride in a program he introduced for the appointment of judges and state government officials. Under this program, all such appointments were based on merit, rather than political influence.
In 1972, as U.S. Senator George McGovern of South Dakota was marching toward the Democratic nomination for President, Carter called a news conference in Atlanta to warn that McGovern was unelectable. Carter criticized McGovern as too liberal on both foreign and domestic policy. The remarks attracted little national attention, and after McGovern's huge loss in the general election, Carter's attitude was not held against him within the Democratic Party.
After the U.S. Supreme Court overturned Georgia's death penalty law in 1972, Carter signed new legislation to authorize the death penalty for murder, rape and other offenses and to implement trial procedures which would conform to the newly-announced constitutional requirements. This law was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1976.
In 1974, Carter was chairman of the Democratic National Committee's congressional and gubernatorial campaigns.
1976 presidential campaign
Carter began running for President in 1975, almost immediately upon leaving office as governor of Georgia. When Carter entered the Democratic Party presidential primaries in 1976, he was considered to have little chance against nationally better-known politicians. When he told his family of his intention to run for President, he was asked by his mother, "President of what?" However, Nixon's Watergate scandal was still fresh in the voters' minds, and so his position as an outsider, distant from Washington, DC, became an asset. The centerpiece of his campaign platform was government reorganization.
Carter became the front-runner early on by winning the Iowa caucuses and the New Hampshire primary. He used a two-prong strategy. In the South, which most had tacitly conceded to Alabama's George Wallace, Carter ran as a moderate favorite son. When Wallace proved to be a spent force, Carter swept the region. In the North, Carter appealed largely to conservative Christian and rural voters and had little chance of winning a majority in most states. But in a field crowded with liberals, he managed to win several Northern states by building the largest single bloc. Initially dismissed as a regional candidate, Carter proved to be the only Democrat with a truly national strategy, and he eventually clinched the nomination.
The media discovered and promoted Carter. As Lawrence Shoup noted in his 1980 book The Carter Presidency And Beyond:
"What Carter had that his opponents did not was the acceptance and support of elite sectors of the mass communications media. It was their favorable coverage of Carter and his campaign that gave him an edge, propelling him rocket-like to the top of the opinion polls. This helped Carter win key primary election victories, enabling him to rise from an obscure public figure to President-elect in the short space of 9 months."
As late as January 26, 1976, Carter was the first choice of only 4% of Democratic voters, according to the Gallup Poll. Yet "by mid-March 1976 Carter was not only far ahead of the active contenders for the Democratic presidential nomination, he also led President Ford by a few percentage points," according to Shoup.
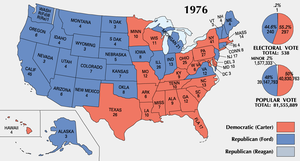
Carter began the race with a sizeable lead over Ford, who was able to narrow the gap over the course of the campaign, but was unable to prevent Carter from narrowly defeating him on November 2nd, 1976. Carter won the popular vote by 50.1% to 48.0% for Ford and received 297 electoral votes to Ford's 240. This made him the first Democrat to win a majority of the popular vote since 1964. He became the first contender from the Deep South to be elected President since 1848.
Presidency (1977–1981)
Economic Situation
The 1970's are described as a period of stagflation, meaning economic stagnation, price inflation, as well as higher interest rates. Price inflation (or more money for the same thing) creates uncertainty in budgeting and planning and makes labor strikes for pay raises more likely. In 1973, during the Nixon Administration, OPEC (Organization of Petrolium Exporting Countries) agreed to reduce supplies of oil available to the world market. This sparked an oil crisis and forced oil prices to rise sharply, spurring price inflation through-out the economy, and slowing growth. Significant government borrowing and for items such as the Vietnam War and nuclear weapons stock pile helped keep interest rates high relative to inflation. The Nixon Administration policies of trying to talk price inflation down (known as jawbone-ing) and price freezes were ineffective.
Energy crisis
When the energy market exploded—an occurrence Carter desperately tried to avoid during his term—he was planning on delivering his fifth major speech on energy. However, he felt that the American people were no longer listening. Instead, he went to Camp David and for ten days met with governors, mayors, religious leaders, scientists, economists, and general citizens. He sat on the floor and took notes of their comments and especially wanted to hear criticism. His pollster told him that the American people simply faced a crisis of confidence because of the assassination of John F. Kennedy, the Vietnam War, and Watergate. On July 15, 1979, Carter gave a nationally-televised address in which he identified what he believed to be a "crisis of confidence" among the American people. This has come to be known by critics as his "malaise" speech, even though he did not use the word "malaise" anywhere in the text:
- I want to talk to you right now about a fundamental threat to American democracy.... I do not refer to the outward strength of America, a nation that is at peace tonight everywhere in the world, with unmatched economic power and military might.
- The threat is nearly invisible in ordinary ways. It is a crisis of confidence. It is a crisis that strikes at the very heart and soul and spirit of our national will. We can see this crisis in the growing doubt about the meaning of our own lives and in the loss of a unity of purpose for our nation.
Carter's speech, written by Chris Matthews, was well-received. But the country was in the midst of a weak economy dominated by OPEC-influenced double-digit inflation, and many citizens were directly affected by this, causing concern about the federal government's response. Three days after the speech, Carter asked for the resignations of all of his Cabinet officers, and ultimately accepted five. Carter later admitted in his memoirs that he should have simply asked only those five members for their resignation. By asking the entire Cabinet, it gave the appearance that the White House was falling apart.
The economy suffered double-digit inflation, coupled with very high interest rates, oil shortages, high unemployment, and slow economic growth. As a result, he convinced Congress to create the United States Department of Energy. Following its recommendations to conserve energy, Carter wore sweaters, installed solar power panels on the roof of the White House, installed a wood stove in the living quarters, ordered the General Services Administration to turn off hot water in some facilities and requested that Christmas decorations remain dark in 1979 and 1980. Nationwide controls were put on thermostats in government and commercial buildings to prevent people from raising temperatures in the winter or lowering them in summer.
The price inflation caused interest rates to rise to unprecedented levels (above 12% per year). The prime rate hit 21.5 in December 1980, highest in history . Investments in fixed income (both bonds, and pensions being paid to retired people) were becoming less valuable. With the markets for U.S. government debt coming under pressure, Carter appointed Paul Volcker as Chairman of the Federal Reserve Board; Volcker replaced G. William Miller who left to become the Secretary of the Treasury. Volcker pursued a tight monetary policy to bring down inflation, which he considered his mandate. He succeeded, but only by first going through a very unpleasant phase where the economy slowed down, causing a rise in unemployment, prior to any relief from the inflation. The stagnant growth of the economy (causing unemployment), in combination with a high rate of inflation, has often been called stagflation, an unprecedented situation in American economics that Volcker is credited for ending.
Domestic policies
Jimmy Carter's reorganization efforts separated the Department of Health, Education and Welfare into the Department of Education and the Department of Health and Human Services. Efforts were also made to reduce the number of government departments and employees as Carter had done when he was governor of Georgia. He signed into law a major Civil Service Reform, the first in over a hundred years. Despite calling for a reform of the tax system in his presidential campaign, once in office he did very little to change it.
Initially, Carter was fairly successful in getting legislation through Congress, such as pardoning Vietnam-era draft-dodgers, and cancelling the B-1 Bomber program, but then he met with opposition from the leadership of the Democratic Party when he characterized a rivers and harbors bill as "pork barrel" spending. In apparent retaliation, Congress responded by refusing to pass major provisions of his consumer protection bill and his labor reform package. Carter then vetoed a public works package calling it "inflationary," as it contained what he considered to be wasteful spending. Congressional leaders sensed that public support for his legislation was weak, and took advantage of it. After gutting his consumer protection bill, they transformed his tax plan into nothing more than spending for special interests, after which Carter referred to the congressional tax committees as "ravenous wolves."
On a more successful note, Carter signed legislation bolstering the Social Security system through a staggered increase in the payroll tax and appointed record numbers of women, blacks, and Hispanics to government and judiciary jobs. He also initiated a comprehensive urban policy. Carter enacted strong legislation for environmental protection. His Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act created 103 million acres (417,000 km²) of national park land in Alaska. He was also successful in deregulating the trucking, rail, airline, communications, oil, and finance industries.
Foreign Policies
South Korea
One of Carter's first acts in office was to order the unilateral removal of all nuclear weapons from South Korea. He also announced his intention to remove all US troops from South Korea. During his first month in office he cut the defense budget by $6 Billion.
Initial Response to Arab-Israeli Conflict
Carter's Secretary of State Cyrus Vance and National Security Adviser Zbigniew Brzezinski paid close attention to the Arab-Israeli conflict. Diplomatic relations between both Israel and Egypt were significantly increased after the Yom Kippur War and the Carter administration felt that the time was right for comprehensive solution to the conflict.
Rapid Deployment Forces
On October 1, 1979, President Carter announced before a television audience the existence of the Rapid Deployment Forces (RDF), a mobile fighting force capable of responding to worldwide trouble spots, without drawing on forces committed to NATO. The RDF was the forerunner of CENTCOM.
Human Rights
President Carter initially departed from the long-held policy of containment toward the Soviet Union. In its place Carter promoted a foreign policy that placed human rights at the forefront. This was a break from the policies of several predecessors, in which human rights abuses were often overlooked if they were committed by a nation that was allied with the United States. The Carter Administration ended support to the historically U.S.-backed Somoza dictatorship in Nicaragua, and gave millions of dollars in aid to the nation's new Sandinista regime after it rose to power by a revolution.
Carter continued his predecessors' policies of imposing sanctions on Rhodesia, and, after Bishop Abel Muzorewa was elected Prime Minister, protested that the Marxists Robert Mugabe and Joshua Nkomo were excluded from the elections. Strong pressure from the United States and the United Kingdom prompted new elections in what was then called Zimbabwe Rhodesia. Carter was also known for his criticism of Alfredo Stroessner, Augusto Pinochet, the apartheid government of South Africa, and other traditional allies.
People's Republic of China
Carter continued the policy of Richard Nixon to "normalize" relations with the People's Republic of China by granting full diplomatic and trade relations, thus ending official relations with the Republic of China (though the two nations continued to trade and the U.S. unofficially recognized Taiwan through the Taiwan Relations Act).
Panama Canal Treaties
One of the most controversial moves of President Carter's presidency was the final negotiation and signature of the Panama Canal Treaties in September 1977. Those treaties, which essentially would transfer control of the American-built Panama Canal to the nation of Panama, were bitterly opposed by a segment of the American public and by the Republican Party. A common argument against the treaties was that the United States was transferring an American asset of great strategic value to an unstable and corrupt country led by a brutal military dictator ( Omar Torrijos). After the signature of the Canal treaties, in June 1978, Jimmy Carter visited Panama with his wife and twelve U. S. Senators, amid widespread student disturbances against the Torrijos dictatorship. Carter then began urging the Torrijos regime to soften its policies and move Panama towards gradual democratization. This treaty ultimately helped relations with Panama and Latin America.
Camp David Accords
One of Carter's most important accomplishments as President was the Camp David Accords. The Camp David Accords were a peace agreement between Israel and Egypt, which were negotiated by President Carter, following up on earlier negotiations which had been conducted in the Middle East. In these negotiations King Hassan II of Morocco acted as a negotiator between Arab interests and Israel, and Nicolae Ceauşescu of Romania acted as go-between for Israel and the PLO. Once initial negotiations had been completed Egyptian President Anwar Sadat approached Carter for assistance. Carter then invited Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin and Sadat to Camp David to continue the negotiations. The Camp David accords produced peace between Egypt and Israel that has lasted to the present. (2006)
Strategic Arms Limitations Talks
A key foreign policy issue Carter worked laboriously on was the SALT II Treaty. SALT stood for the Strategic Arms Limitations Talks and were negotiations being conducted between the United States and the Soviet Union. The work of Gerald Ford and Richard Nixon brought about the SALT I treaty, but Carter wished to further the reduction of nuclear arms. It was his main goal, as was stated in his Inaugural Address, that nuclear weaponry be completely banished from the face of the Earth. Carter and Leonid Brezhnev, the leader of the Soviet Union, reached an agreement and held a signing ceremony. There was much opposition in Congress to ratifying the treaty, as many thought that it weakened US defenses. Following the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan late in 1979, Carter withdrew the treaty from consideration by Congress and the treaty was never ratified. Even so, both sides honored their commitments laid out in the negotiations.

Intervention in Afghanistan
In December 1979, USSR invaded Afghanistan, after the pro-Moscow Afghanistan government placed by a 1978 coup was overthrown. Some believed the Soviets were attempting to expand their borders southward in order to gain a foothold in the region. The Soviet Union had long lacked a warm water port, and their movement south seemed to position them for further expansion toward Pakistan and India in the East, and Iran to the West. American politicians, including Republicans and Democrats alike, feared that the Soviets were positioning themselves for a takeover of Middle Eastern oil. Others believed that the Soviet Union was fearful that the Muslim uprising would spread from Iran and Afghanistan to the millions of Muslims in the USSR. In a 1998 interview with Le Nouvel Observateur, Carter's National Security Advisor Zbigniew Brzezinski admitted that the United States began sending aid to anti-Soviet Afghan Islamist factions on July 3, 1979, nearly six months before the Soviet invasion. Brezezinski told Le Nouvel Observateur that this secretly provoked war gave America "the opportunity of giving to the USSR its Vietnam war." Full Text of Interview
After the invasion, Carter announced the Carter Doctrine: that the US would not allow any outside force to gain control of the Persian Gulf. Carter terminated the Russian Wheat Deal to establish trade with USSR and lessen Cold War tensions. The grain exports had been beneficial to people employed in agriculture, and the Carter embargo marked the beginning of hardship for American farmers. He also prohibited Americans from participating in the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow, and reinstated registration for the draft for young males. Carter and Zbigniew Brzezinski started a $40 billion covert program of training Islamic fundamentalists in Pakistan and Afghanistan. Reagan would later expand this program greatly to combat Cold War concerns presented by Russia at the time. In retrospect, this contributed to the collapse of the Soviet Union. Critics of this policy blame Carter and Reagan for the resulting instability of post-Soviet Afghani governments, which led to the rise of Islamic theocracy in the region, and also created much of the current problems with Islamic fundamentalism.
Hostage Crisis
The main conflict between human rights and U.S. interests came in Carter's dealings with the Shah of Iran. The Shah, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, had been a strong ally of America since World War II and was one of the "twin pillars" upon which U.S. strategic policy in the Middle East was built. However, his rule was strongly autocratic, and he went along with the plan of the Eisenhower Administration to depose Mohammed Mossadegh in 1953. Though Carter praised the Shah as a wise and valuable leader, when the Iranian Revolution broke out in Iran, which led to the overthrow of the monarchy, the U.S. did not intervene. The Shah was subsequently deposed and exiled.
Despite having previously denied the Shah entry into the United States for medical treatment, on October 22, 1979, Carter finally granted him entry and temporary asylum for the duration of his cancer treatment; the Shah left for Panama on December 15, 1979. In response to the Shah's entry into the U.S., Iranian militants seized the American embassy in Tehran, taking 52 Americans hostage. The Iranians demanded (1) the return of the Shah to Iran for trial, (2) the return of the Shah's wealth to the Iranian people, (3) an admission of guilt by the United States for its past actions in Iran, plus an apology, and (4) a promise from the United States not to interfere in Iran's affairs in the future. Though later that year the Shah left the U.S. and died in Egypt, the hostage crisis continued and dominated the last year of Carter's presidency, even though almost half of the hostages were released. The subsequent responses to the crisis—from a " Rose Garden strategy" of staying inside the White House, to the unsuccessful attempt to rescue the hostages—were largely seen as contributing to defeat in the 1980 election.
In 1982, a small book by James B. Stewart, esquire, appeared that gave insight into the timing of these events. The Partners: Inside America’s Most Powerful Law Firms begins with Stewart’s insider description of the negotiation process for the release of the hostages. Though short, the chapter laid out clearly what had happened behind the scenes. After the hostages were taken, President Carter issued, on November 14, 1979, Executive Order 12170 - Blocking Iranian Government property , which was used to freeze the bank accounts of the Iranian government in US banks, totaling about $8 billion US at the time. This was to be used as a bargaining chip for the release of the hostages.
The Iranians then changed their demand to return of the Shah and the release of the Iranian money. Through informal channels the Iranian government started negotiations with the banks holding the money. The banks took over negotiations for the release of the hostages, not the U.S. State Department. When the Shah died of cancer in the summer of 1980, the Iranians wanted no more to do with the hostages and changed their demands to just the release of the hostages in exchange for the return of their money. Why the deal was not struck at that point is never explained, since it was the same deal that the Iranians received in January 1981. The hostages were finally released with the signing of Executive Orders 12277 through 12285, releasing all assets belonging to the Iranian government and all assets belonging to the Shah found within the United States and the guarantee that the hostages would have no legal claim against the Iranian government that would be heard in U.S. courts . Shortly after the publication of The Partners, accusations of an " October Surprise" were leveled against the Reagan Administration. No witnesses were ever found who had anything to report, but Congress investigated the matter and showed the story was based on a hoax. (The hoax depended on William Casey being in Madrid on a day he was in London, so the entire set of allegations fell apart.)
Administration and Cabinet
| OFFICE | NAME | TERM |
| President | Jimmy Carter | 1977–1981 |
| Vice President | Walter F. Mondale | 1977–1981 |
| National Security Advisor | Zbigniew Brzezinski | 1977–1981 |
| C.I.A. Director | Stansfield Turner | 1977–1981 |
| F.B.I. Director | Clarence M. Kelley | 1977–1978 |
| William Hedgcock Webster | 1978–1981 | |
| State | Cyrus R. Vance | 1977–1980 |
| Edmund Muskie | 1980–1981 | |
| Treasury | W. Michael Blumenthal | 1977–1979 |
| G. William Miller | 1979–1981 | |
| Defense | Harold Brown | 1977–1981 |
| Justice | Griffin Bell | 1977–1979 |
| Benjamin R. Civiletti | 1979–1981 | |
| Interior | Cecil D. Andrus | 1977–1981 |
| Commerce | Juanita M. Kreps | 1977–1979 |
| Philip M. Klutznick | 1979–1981 | |
| Labor | Ray Marshall | 1977–1981 |
| Agriculture | Robert Bergland | 1977–1981 |
| HEW | Joseph A. Califano, Jr. | 1977–1979 |
| HHS | Patricia R. Harris | 1979–1981 |
| Education | Shirley M. Hufstedler | 1979–1981 |
| HUD | Patricia R. Harris | 1977–1979 |
| Moon Landrieu | 1979–1981 | |
| Transportation | Brock Adams | 1977–1979 |
| Neil E. Goldschmidt | 1979–1981 | |
| Energy | James R. Schlesinger | 1977–1979 |
| Charles W. Duncan | 1979–1981 | |
Amongst Presidents who served at least one full term, Carter is the only one who never made an appointment to the Supreme Court.
1980 election
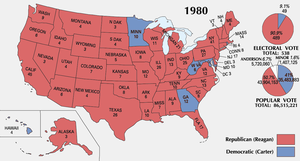
Carter lost the presidency by a landslide to Ronald Reagan in the 1980 election. The popular vote went approximately 51% for Reagan and 41% for Carter. However, because Carter's support was not concentrated in any geographic region, Reagan won 91% of the electoral vote, leaving Carter with only six states and the District of Columbia. Independent candidate John Bayard Anderson won seven percent of the vote and prevented Carter from taking traditionally Democratic states, like New York, Wisconsin, and Massachusetts.
A public perception that the Carter Administration had been ineffectual in addressing the Iranian hostage crisis may have contributed to his defeat. Although the Carter team had successfully negotiated with the hostage takers for release of the hostages, an agreement trusting the hostage takers to abide by their word was not signed until January 19, 1981, after the election of Ronald Reagan. The hostages had been held captive for 444 days, and their release happened just minutes after Carter left office. However, Reagan asked Carter to go to Germany to greet the hostages.
During his campaign, Carter was mocked for an encounter with a rabbit while fishing on a farm pond. A swimming swamp rabbit, perhaps ill or fleeing from a predator, attempted to board the President's small boat. Carter shooed the creature away with his paddle. Several months later, Carter's Press Secretary Jody Powell mentioned what he viewed as a "mildly amusing incident" to reporter Brooks Jackson over tea. Shortly thereafter, the story appeared on the front page of The Washington Post and was reported on the evening news of all the major television networks.
Post-presidency

Since leaving the presidency, Carter has written 20 books.
Jimmy Carter and Walter Mondale are the longest-living post-presidential team in American history. On May 23, 2006, they had been out of office for 25 years and 123 days, surpassing the record established by President John Adams and Vice President Thomas Jefferson. Adams and Jefferson died on the same day— July 4, 1826.
In ten surveys of historians which ranked US presidents, which included over 1000 scholars, the ranking of Carter's presidency ranged from #19 to #34. These rankings are similar to those of Gerald Ford, Chester Arthur, and Herbert Hoover. While at the time he left office Carter's presidency was viewed by many as a failure, his activities since leaving office, especially his many peacekeeping and humanitarian efforts, have led to a more favorable view of him.
Diplomacy
In 1994, Carter went to North Korea at the behest of President Clinton. North Korea had expelled investigators from the International Atomic Energy Agency and was threatening to begin processing spent nuclear fuel. Carter met with North Korean President Kim Il Sung resulting in the signing of the Agreed Framework, under which North Korea agreed to stop processing nuclear fuel, in exchange for a return to normalized relations, oil deliveries and two light water reactors to replace its graphite reactors.
Though the Agreed Framework negotiated by Jimmy Carter was widely hailed at the time as a diplomatic achievement, in 2005 North Korea announced that it had nuclear weapons and proved this assertion with the detonation of a small nuclear bomb in an underground test on October 9, 2006. Carter's supporters attributed the failure of the agreement to ongoing American sanctions (contrary to the agreement) due to opposition from a Republican-controlled Congress, while critics questioned whether the North Korean government ever intended to give up its nuclear weapons program.
Carter visited Cuba in May 2002 and met with Fidel Castro. He was allowed to address the Cuban public on national television with a speech that he wrote and presented in Spanish. This made Carter the first President of the United States, in or out of office, to visit the island since the Cuban revolution of 1959.
In June 2005, Carter urged the closing of the Guantanamo Bay Prison in Cuba, which has been the centre point for recent claims of prisoner abuse.
Not all Carter's efforts have gained him favour in Washington; President Clinton and both Presidents George H.W. and George W. Bush were said to have been less than pleased with Carter's "freelance" diplomacy in Iraq and elsewhere.
Carter has also in recent years become a frequent critic of Israel and the US foreign policy in support of Israel.
Humanitarian work
Carter has been involved in a variety of national and international public policy, conflict resolution, human rights and charitable causes through the Carter Center. He established the Carter Center the year following his term and currently chairs the center with his wife Rosalynn. The centre also focuses on world-wide health care including the campaign to eliminate guinea worm disease. He and members of the centre are sometimes involved in the monitoring of the electoral process in support of free and fair elections. This includes acting as election observers, particularly in Latin America and Africa.
He and his wife are also well-known for their work with Habitat for Humanity, a program that helps poor people to afford their first home.
Carter was the third U.S. President, after Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson, to receive the Nobel Peace Prize award. In his Nobel Lecture, Carter told the European audience that U.S. actions after the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan, and the 1991 Gulf War, like NATO itself, was a continuation of President Wilson's doctrine of collective security.
American politics
In 2001, Carter criticized President Clinton's controversial pardon of Marc Rich, calling it "disgraceful" and suggesting that Rich's financial contributions to the Democratic Party was a factor in Clinton's action.
In March 2004, Carter condemned George W. Bush and Tony Blair for waging an unnecessary war "based upon lies and misinterpretations" in order to oust Saddam Hussein. He claimed that Blair had allowed his better judgment to be swayed by Bush's desire to finish a war that George H. W. Bush (his father) had started.
In August 2006, Carter made remarks controversial with many Jewish Americans and Democratic supporters of Israel when he said on the 15th of that month "I don't think Israel has any legal or moral justification for their massive bombing of the entire nation of Lebanon," and on the same topic, "I represent the vast majority of Democrats." His remarks were in response to the Israel-Hezbollah war of that summer.
In September 2006, Carter was interviewed on the BBC's Newsnight current affairs programme, voicing his concern at the alleged increasing influence of the Religious Right on U.S. politics. He also criticised Tony Blair and the British Government for being "subservient" to the Bush administration and accused Blair of giving unquestioning support to any "radical or ill-advised" policy adopted by Bush.
Additional accolades
Carter has received honorary degrees from many American colleges, including Harvard University, Bates College, and the University of Pennsylvania.
In 2000, Carter received the James A. Van Fleet Award from The Korea Society.
On November 22, 2004, New York Republican Governor George Pataki named Carter and the other living former Presidents (Gerald Ford, George H. W. Bush, and Bill Clinton) as honorary members of the board rebuilding the World Trade Centre.
Because he had served as a submariner (the only President to have done so), a submarine was named for him. The USS Jimmy Carter (SSN-23) was named on April 27, 1998, making it one of the very few U.S. Navy vessels to be named for a person still alive at the time of the naming. In February 2005, Jimmy and Rosalyn Carter both spoke at the commissioning ceremony for this submarine.
Carter is a University Distinguished Professor at Emory University and teaches occasional classes there. He also teaches a Sunday School class at Maranatha Baptist Church in Plains, Georgia. Being an accomplished amateur woodworker, he has occasionally been featured in the pages of Fine Wood Working magazine, which is published by Taunton Press.
Carter has also participated in many ceremonial events such as the opening of his own presidential library and those of Presidents Ronald Reagan, George H.W. Bush, and Bill Clinton. He has also participated in many forums, lectures, panels, funerals and other events. Carter delivered a eulogy at the funeral of Coretta Scott King.
Trivia

- Jimmy Carter was the first former Governor of Georgia to serve as president.
- Jimmy Carter was born on the same day as the late Chief Justice, William H. Rehnquist, on October 1, 1924.
- Jimmy Carter was the first president born in a hospital.
- In sequence, Jimmy Carter was the 39th president to serve but the 41st to be born. George H.W. Bush was the 40th born and George W. Bush was the 42nd born.
- Jimmy Carter is 5 feet 8 inches tall.
- Jimmy Carter's original legal name was James Earl Carter, but he eventually changed his legal name to Jimmy.
- Carter once greeted Queen Elizabeth, the Queen Mother of the United Kingdom with a kiss on the lips. Angered, she reprimanded him by saying, "No man has done that since my husband died."
Academic studies
- Bourne, Peter. Jimmy Carter: A comprehensive biography from Plains to post-presidency. 1997
- Brinkley, Douglas. 1996. "The rising stock of Jimmy Carter: The "hands on" legacy of our thirty-ninth president". Diplomatic History 20: 505-29.
- Dumbrell, John. The Carter presidency: A re-evaluation. Manchester University Press 1995.
- Gary Fink and Hugh Davis Graham, eds. The Carter presidency: Policy choices in the post-New Deal era University Press of Kansas. 1998.
- Andrew R. Flint; "Jimmy Carter: The Re-emergence of Faith-Based Politics and the Abortion Rights Issue" Presidential Studies Quarterly. Volume: 35. Issue: 1. 2005. pp 28+.
- Gillon, Steven M. The Democrats' dilemma: Walter F. Mondale and the liberal legacy Columbia University Press. 1992.
- Glad, Betty. Jimmy Carter: In search of the great White House W. W. Norton. 1980.
- Hahn, Dan F. "The rhetoric of Jimmy Carter, 1976-1980". In Essays in presidential rhetoric, edited by Theodore O. Windt and Beth Ingold, 331-65. Kendall/Hunt. 1992.
- Hargrove, Erwin. Jimmy Carter as president: Leadership and the politics of the public good Louisiana State University Press. 1988.
- Jones, Charles O. The Trusteeship Presidency: Jimmy Carter and the United States Congress. 1988.
- Jordan, William J. Panama Odyssey. 1984.
- Kaufman, Burton I. The Presidency of James Earl Carter, Jr. 1993.
- Kucharsky, David. The Man from Plains: The Mind and Spirit of Jimmy Carter. 1976
- Ribuffo, Leo P. "God and Jimmy Carter" in Transforming faith: The sacred and secular in modern American history, edited by Myles L. Bradbury and James B. Gilbert, pp 141-59. Greenwood Press. 1989
- Ribuffo, Leo P. . "'Malaise' revisited: Jimmy Carter and the crisis of confidence". in The liberal persuasion: Arthur Schlesinger, Jr. and the challenge of the American past, edited by John Patrick Diggins, 164-85. Princeton University Press. 1997
- Herbert D. Rosenbaum and Alexej Ugrinsky, eds. The presidency and domestic policies of Jimmy Carter, (1994) pp, 83-116. Greenwood Press.
- Schram, Martin. Running for president, 1976: The Carter campaign (1977)
- Strong, Robert. "Recapturing leadership: The Carter administration and the crisis of confidence" Presidential Studies Quarterly 1986. 16 (Fall): 636-50.
- Strong, Robert. Working in the world: Jimmy Carter and the making of American foreign policy Louisiana State University Press. 2000.
- White, Theodore H. America in search of itself: The making of the president, 1956-1980. 1983
- Witcover, Jules. Marathon: The pursuit of the presidency, 1972-1976 1977
Honours
President Carter has been fortunate to receive many honors throughout his life. Among the most significant honours were the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1999 and the Nobel Peace Prize in 2002. Others include:
- LL.D. (honoris causa) Morehouse College, 1972; Morris Brown College, 1972; University of Notre Dame, 1977; Emory University, 1979; Kwansei Gakuin University, 1981; Georgia Southwestern College, 1981; New York Law School, 1985; Bates College, 1985; Centre College, 1987; Creighton University, 1987; University of Pennsylvania[, 1998
- D.E. (honoris causa) Georgia Institute of Technology, 1979
- Ph.D. (Honorary) Weizmann Institute of Science, 1980; Tel Aviv University, 1983; Haifa University, 1987
- D.H.L. (honoris causa) Central Connecticut State University, 1985; Trinity College, 1998
- Doctor (honoris causa) G.O.C. Universite, 1995
- Silver Buffalo Award, Boy Scouts of America, 1978
- Gold medal, International Institute for Human Rights, 1979
- International Mediation medal, American Arbitration Association, 1979
- Martin Luther King, Jr. Nonviolent Peace Prize, 1979
- International Human Rights Award, Synagogue Council of America, 1979
- Conservationist of the Year Award, 1979
- Harry S. Truman Public Service Award, 1981
- Ansel Adams Conservation Award, Wilderness Society, 1982
- Human Rights Award, International League for Human Rights, 1983
- World Methodist Peace Award, 1985
- Albert Schweitzer Prize for Humanitarianism, 1987
- Edwin C. Whitehead Award, National Centre for Health Education, 1989
- Jefferson Award, American Institute of Public Service, 1990
- Philadelphia Liberty Medal, 1990
- Spirit of America Award, National Council for the Social Studies, 1990
- Physicians for Social Responsibility Award, 1991 Aristotle Prize, Alexander S. Onassis Foundation, 1991
- W. Averell Harriman Democracy Award, National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, 1992
- Spark M. Matsunaga Medal of Peace, US Institute of Peace, 1993
- Humanitarian Award, CARE International, 1993
- Conservationist of the Year Medal, National Wildlife Federation, 1993
- Rotary Award for World Understanding, 1994
- J. William Fulbright Prize for International Understanding, 1994
- National Civil Rights Museum Freedom Award, 1994
- UNESCO Félix Houphouët-Boigny Peace Prize, 1994
- Great Cross of the Order of Vasco Nunéz de Balboa, 1995
- Bishop John T. Walker Distinguished Humanitarian Award, Africare, 1996
- Humanitarian of the Year, GQ Awards, 1996
- Kiwanis International Humanitarian Award, 1996
- Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development, 1997
- Jimmy and Rosalynn Carter Awards for Humanitarian Contributions to the Health of Humankind, National Foundation for Infectious Diseases, 1997
- United Nations Human Rights Award, 1998
- The Hoover Medal, 1998
- International Child Survival Award, UNICEF Atlanta, 1999
- William Penn Mott, Jr., Park Leadership Award, National parks Conservation Association, 2000