Heraldry
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Recreation
Heraldry in its most general sense encompasses all matters relating to the duties and responsibilities of officers of arms. To most, though, heraldry is the practice of designing, displaying, describing and recording coats of arms and badges. The origins of heraldry lie in the need to distinguish participants in combat when their faces were hidden by iron and steel helmets. Eventually a structured system of rules developed into the modern form of heraldry.
The system of blazoning arms that is used today was developed by the officers of arms since the dawn of the science. This includes a description of the shield, the crest, and, if present, supporters, mottoes, and other insignia. An understanding of these rules is one of the keys to sound practice of heraldry. The rules do differ from country to country, but there are some aspects that carry over in each jurisdiction.
Though heraldry is nearly 900 years old, it is still very much in use. Many cities and towns in Europe and around the world still make use of arms. Personal heraldry, both legally protected and lawfully assumed, has continued to be used around the world. Heraldic societies thrive to promote understanding of and education about the subject.
Origins and history
At the time of the Norman Conquest of England, modern heraldry had not yet been developed. The knights in the Bayeux Tapestry carry shields, but there appears to have been no system of hereditary coats of arms. The beginnings of modern heraldic structure were in place, but would not become standard until the middle of the twelfth century. By this time, coats of arms were being inherited by the children of armigers across Europe. Between 1135 and 1155 seals show the general adoption of heraldic devices in England, France, Germany, Spain, and Italy. In Britain the practice of using marks of cadency arose to distinguish one son from another, and was institutionalized and standardized by John Writhe in the fifteenth century.
In the late Middle Ages and the Renaissance, heraldry became a highly developed discipline, regulated by professional officers of arms. As its use in jousts became obsolete coats of arms remained popular for visually identifying a person in other ways—impressed in sealing wax on documents, carved on family tombs, and flown as a banner on country homes. The first work of heraldic jurisprudence, De Insigniis et Armiis, was written in the 1350s by Bartolus de Saxoferrato, a professor of law at the University of Padua.
From the beginning of heraldry, coats of arms have been executed in a wide variety of media, including on paper, painted wood, embroidery, enamel, stonework and stained glass. For the purpose of quick identification in all of these, heraldry distinguishes only seven basic colors and makes no fine distinctions in the precise size or placement of charges on the field. Coats of arms and their accessories are described in a concise jargon called blazon. This technical description of a coat of arms is the standard that must be adhered to no matter what artistic interpretations may be made in a particular depiction of the arms.
The idea that each element of a coat of arms has some specific meaning is unfounded. Though the original armiger may have placed particular meaning on a charge, these meanings are not necessarily retained from generation to generation. Unless the arms incorporate an obvious pun on the bearer's name, it is difficult to find meaning in them.
Changes in military technology and tactics made plate armor obsolete and heraldry became detached from its original function. This brought about the development of "paper heraldry" that only existed in paintings. Designs and shields became more elaborate at the expense of clarity. The 20th century's taste for stark iconic emblems made the simple styles of early heraldry fashionable again.
The rules of heraldry
Shield and lozenge
The main focus of modern heraldry is the armorial achievement, or coat of arms. The central element of a coat of arms is the shield. In general the shape of shield employed in a coat of arms is irrelevant. The fashion for shield shapes employed in heraldic art has generally evolved over the centuries. There are times when a particular shield shape is specified in a blazon. These almost invariably occur in non-European contexts such as the coat of arms of Nunavut and the former Republic of Bophuthatswana.
Traditionally, as women did not go to war, they did not use a shield. Instead their coats of arms were shown on a lozenge—a rhombus standing on one of its acute corners. This continues to hold true in much of the world, though some heraldic authorities make exceptions. In Canada the restriction against women bearing arms on a shield has been completely eliminated. Noncombatant clergy have also made use of the lozenge as well as the cartouche – an oval – for their display.
Tinctures
Tinctures are the colors used in heraldry. Since heraldry is essentially a system of identification, the most important convention of heraldry is the rule of tincture. To provide for contrast and visibility metals (generally lighter tinctures) must never be placed on metals, and colors (generally darker tinctures) must never be placed on colors. There are instances where this cannot be helped, such as where a charge overlays a partition of the field. Like any rule, this admits exceptions, the most famous being the arms chosen by Godfrey of Bouillon when he was made King of Jerusalem.
The names used in English blazon for the tinctures come mainly from French and include Or (gold), Argent (white), Azure (blue), Gules (red), Sable (black), Vert (green), and Purpure (purple). A number of other colors are occasionally found, typically for special purposes.
Besides tinctures, certain patterns called furs can appear in a coat of arms. The two common furs are ermine and vair. Ermine represents the winter coat of the stoat, which is white with a black tail. Vair represents a kind of squirrel with a blue-gray back and white belly sewn together it forms a pattern of alternating blue and white shapes.
Heraldic charges can also be displayed in their natural colors. Many natural items such as plants and animals are described as proper in this case. Proper charges are very frequent as crests and supporters. It is considered bad form to use proper as a method of circumventing the tincture convention.
Divisions of the field
The field of a shield in heraldry can be divided into more than one tincture, as can the various heraldic charges. Many coats of arms consist simply of a division of the field into two contrasting tinctures. Since these are considered divisions of a shield the rule of tincture can be ignored. For example, a shield divided azure and gules would be perfectly acceptable. A line of partition may be straight or it may be varied. The variations of partition lines can be wavy, indented, embattled, engrailed, or made into myriad other forms.
Ordinaries
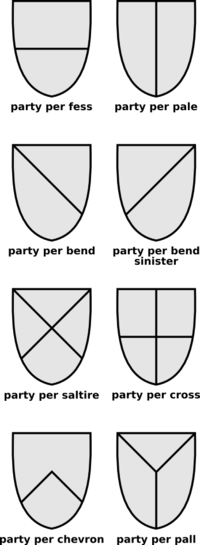
In the early days of heraldry, very simple bold rectilinear shapes were painted on shields. These could be easily recognized at a long distance and could also be easily remembered. They therefore served the main purpose of heraldry—identification. As more complicated shields came into use, these bold shapes were set apart in a separate class as the "honorable ordinaries." They act as charges and are always written first in blazon. Unless otherwise specified they extend to the edges of the field. Though ordinaries are not easily defined, they are generally described as including the cross, the fess, the pale, the bend, the chevron, the saltire, and the pall.
There is also a separate class of charges called sub-ordinaries which are of a geometrical shape subordinate to the ordinary. According to Friar, they are distinguished by their order in blazon. The sub-ordinaries include the inescutcheon, the orle, the tressure, the double tressure, the bordure, the chief, the canton, the label, and flaunches.
Ordinaries may appear in parallel series, in which case English blazon gives them different names such as pallets, bars, bendlets, and chevronels. French blazon makes no such distinction between these diminutives and the ordinaries when borne singly. Unless otherwise specified an ordinary is drawn with straight lines, but each may be indented, embattled, wavy, engrailed, or otherwise have their lines varied.
Charges
A charge is any object or figure placed on a heraldic shield or on any other object of in an armorial composition. Any object found in nature or technology may appear as a heraldic charge in armory. Charges can be animals, objects, or geometric shapes. Apart from the ordinaries, the most frequent charges are the cross—with its hundreds of variations—and the lion and eagle. Other common animals are fish, martlets, griffins, boars, and stags. Dragons, unicorns, and more exotic monsters appear as charges but also as supporters.
Animals are found in various stereotyped positions or attitudes. Quadrupeds can often be found rampant—standing on the left hind foot. Another frequent position is passant, or walking, like the lions of the coat of arms of England. Eagles are almost always shown with their wings spread, or displayed.
In English heraldry the crescent, mullet, martlet, annulet, fleur-de-lis, and rose may be added to a shield to distinguish cadet branches of a family from the senior line. These cadency marks are usually shown smaller than normal charges, but it still does not follow that a shield containing such a charge belongs to a cadet branch. All of these charges occur frequently in basic undifferenced coats of arms.
Marshalling
Marshalling is the art of correctly arranging armorial bearings. Two or more coats of arms are often combined in one shield to express inheritance, claims to property, or the occupation of an office. Marshalling can be done in a number of ways, but the principal mode is impalement or dimidiation. This involves using one shield with the arms of two families or corporations on either half. Another method is called quartering, in which the shield is divided into quadrants. This practice originated in Spain after the thirteenth century. One might also place a small inescutcheon of a coat of arms on the main shield.
When more than four coats are to be marshalled, the principle of quartering may be extended to two rows of three (quarterly of six) and even further. A few lineages have accumulated hundreds of quarters, though such a number is usually displayed only in documentary contexts. Some traditions have a strong resistance to allowing more than four quarters, and resort instead to sub-quartering.
Helm and crest
In English the word "crest" is commonly used to refer to a coat of arms—an entire heraldic achievement. The correct use of the heraldic term crest refers to just one component of a complete achievement. The crest rests on top of a helmet which itself rests on the most important part of the achievement—the shield. The crest is usually found on a wreath of twisted cloth and sometimes within a coronet. The modern crest has evolved from the three-dimensional figure placed on the top of the mounted knights' helms as a further means of identification. In most heraldic traditions a woman does not display a crest, though this tradition is being relaxed in some heraldic jurisdictions.
When the helm and crest are shown, they are usually accompanied by a mantling. This was originally a cloth worn over the back of the helmet as partial protection against heating by sunlight. Today it takes the form of a stylized cloak or hanging from the helmet. Typically in British heraldry, the outer surface of the mantling is of the principal colour in the shield and the inner surface is of the principal metal. The mantling is conventionally depicted with a ragged edge, as if damaged in combat.
Clergy often refrain from displaying a helm or crest in their heraldic achievements. Members of the Roman Catholic clergy may display appropriate headwear. This takes the form of a galero with the colors and tassles denoting rank. In the Anglican tradition, clergy members may pass crests on to their offspring, but rarely display them on their own shields.
Mottoes
An armorial motto is a phrase or collection of words intended to describe the motivation or intention of the armigerous person or corporation. This can also form a pun on the family name as in the Neville motto "Ne vile velis." Mottos are generally changed at will and do not make up an integral part of the armorial achievement. Mottoes can typically be found on a scroll under the shield. In Scottish heraldry where the motto is granted as part of the blazon, it is usually shown on a scroll above the crest. A motto may be in any language.
Supporters and other insignia
Supporters are human or animal figures placed on either side of a coat of arms as though supporting it. In many traditions, these have acquired strict guidelines for use by certain social classes. On the European continent, there are often fewer restrictions on the use of supporters. In Britain only peers of the realm, senior members of orders of knighthood, and some corporate bodies are granted supporters. Often these can have local significance or a historical link to the armiger.
If the armiger has the title of baron, hereditary knight, or higher, he or she may display a coronet of rank above the shield. In Britain this is usually below the helmet, though it is often above the crest in Continental heraldry. In Canada, descendants of the United Empire Loyalists are entitled to use a Loyalist military coronet (for descendants of members of Loyalist regiments) or Loyalist civil coronet (for others).
Another addition that can be made to a coat of arms is the insignia of an order of knighthood. This is usually represented by a collar or similar band surrounding the shield. When the arms of a knight and his wife are shown in one achievement, the insignia of knighthood surround the husband's arms only, and the wife's arms are customarily surrounded by a meaningless ornamental garland of leaves for visual balance.
National styles

The emergence of heraldry occurred across western Europe almost simultaneously. Originially, heraldic style was very similar from country to country. Over time, there developed distinct differences between the heraldic traditions of different countries. The four broad heraldic styles are German-Nordic, Gallo-British, Latin, and Eastern. In addition it can be argued that later national heraldic traditions, such as South African and Canadian have emerged in the twentieth century. In general there are characteristics shared by each of the four main groups.
German-Nordic heraldry
Coats of arms in Germany, the Scandinavian countries, the Baltic states, and northern Switzerland generally change very little over time. Marks of difference are also very rare in this tradition as are heraldic furs. One of the most striking characteristics of German-Nordic heraldry is the treatment of the crest. Often, the same design is repeated in the shield and the crest. The use of multiple crests is also common. The crest cannot be used separately as in British heraldry, but can sometimes, especially in southern German-speaking regions, serve as a mark of difference between different branches of a family.
Gallo-British heraldry
The use of cadency marks to difference arms within the same family and the use of semy fields are distinctive features of Gallo-British heraldry. It is also common to see heraldic furs used. In Britain, the style is notably still controlled by royal officers of arms. French heraldry also experienced a period of strict rules of construction under the Emperor Napoleon. English heraldry makes greater use of supporters than other European countries.
Latin heraldry
The heraldry of southern France, Iberia, and Italy is characterized by a lack of crests and shields of unique shape. Iberian heraldry occasionally introduces words to the shield of arms, a practice frowned upon in British heraldry. It is also known for its extensive use of quartering, due to armorial inheritance through both the male and female lines. Italian heraldry, in particular, is dominated by the Roman Catholic church with many shields and achievements bearing some reference to the church.
Eastern heraldry
Eastern heraldry is the tradition that developed in Croatia, Hungary, Lithuania, Poland, Ukraine, and Russia. These are characterized by a pronounced territorial clan system. Often, entire villages or military groups were granted the same coat of arms irrespective of family relationships. In Poland, nearly six hundred unrelated families are known to bear the same arms of a horseshoe enclosing a cross. Also, many heraldic shields derive from ancient housemarks. Marks of cadency are almost unknown and shields are generally very simple with only one charge. It is also interesting to note that at least 15 percent of all Hungarian personal arms bear a decapitated Turk's head in reference to their wars against Turkey.
Modern heraldry
Heraldry continues to flourish in the modern world. Institutions, companies, and individuals continue to use coats of arms as forms of pictorial identification. In the British Isles, the Kings of Arms and the Chief Herald of Ireland continue to make grants of arms. There are also heraldic authorities in Spain, Canada and South Africa that grant or register coats of arms.
Heraldic societies abound in the world today in Africa, Australasia, the Americas, and in Europe. Some people who have interests in heraldry as a hobby participate in the Society for Creative Anachronism and other medieval revivals or in micronationalism. Many more people see heraldry as a part of their national, and even personal, heritage, as well as a manifestation of civic and national pride. Today, heraldry has ceased to be an expression of aristocracy throughout the world and is simply a form of identification.