European Parliament
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Politics and government

The European Parliament (formerly European Parliamentary Assembly) is the parliamentary body of the European Union (EU), directly elected by EU citizens once every five years. In fact, it is the only part of the E.U. body that is democratic. Together with the Council of Ministers, it composes the legislative branch of the institutions of the Union. It meets in two locations: Strasbourg and Brussels.
The European Parliament has restricted legislative power. It cannot initiate legislation, but it can amend or veto it in many policy areas. In certain other policy areas, it has the right only to be consulted. Parliament also supervises the European Commission; it must approve all appointments to it, and can dismiss it with a vote of censure. It also has the right to control the EU budget.
Other organisations of European countries, such as the OSCE, the Council of Europe, and the Western European Union, have parliamentary assemblies as well, but the members of these assemblies are appointed by national parliaments as opposed to direct election.
Composition
The European Parliament represents around 457 million citizens of the European Union. Its members are known as Members of the European Parliament (MEPs). Since 13 June 2004, there have been 732 MEPs. (It was agreed that the maximum number of MEPs should be fixed at 750, with a minimum threshold of five per member state and no member state being allocated more than 99 seats.) Elections occur once in every five years, on the basis of universal adult suffrage. There is not a uniform voting system for the election of MEPs; rather, each member state is free to choose its own system subject to three restrictions1:
- The system must be a form of proportional representation, under either the party list or Single Transferable Vote system.
- The electoral area may be subdivided if this will not generally affect the proportional nature of the voting system.
- Any election threshold on the national level must not exceed five percent.
The allocation of seats to each member state is based on the principle of degressive proportionality, so that, while the size of the population of each country is taken into account, smaller states elect more MEPs than would be strictly justified by their populations alone. As the number of MEPs granted to each country has arisen from treaty negotiations, there is no precise formula for the apportionment of seats among member states. No change in this configuration can occur without the unanimous consent of all governments.
The most recent elections to the European Parliament were the European elections of 2004, held in June of that year. These elections were the largest simultaneous transnational elections ever held anywhere in the world, since nearly 400 million citizens were eligible to vote.
| Apportionment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Member state | Seats | Member state | Seats | |
| 99 | 14 | |||
| 78 | 14 | |||
| 78 | 14 | |||
| 78 | 13 | |||
| 54 | 13 | |||
| 54 | 9 | |||
| 27 | 7 | |||
| 24 | 6 | |||
| 24 | 6 | |||
| 24 | 6 | |||
| 24 | 5 | |||
| 24 | Observers | Seats | ||
| 19 | 35 | |||
| 18 | 18 | |||
1. Includes Gibraltar, but not any other BOT, SBA or Crown dependency
Observers
It is conventional for countries acceding to the European Union to send a number of observers to Parliament in advance. The number of observers and their method of appointment (usually by national parliaments) is laid down in the joining countries' Treaties of Accession.
Observers may attend debates and take part by invitation, but they may not vote or exercise other official duties. When the countries then become full member states, these observers become full MEPs for the interim period between accession and the next European elections.
In this way, the agreed maximum of 750 parliamentary seats may temporarily be exceeded. For instance, in 2004, the number of seats in the European Parliament was temporarily raised to 788 to accommodate representatives from the ten states that joined the EU on 1 May, but it was subsequently reduced to 732 following the elections in June.
Since 26 September 2005, Bulgaria has 18 observers in Parliament and Romania has 35. These are selected from government and opposition parties as agreed by the countries' national parliaments. In 2007 these observers will become MEPs, but their number is expected to decrease when the number of seats assigned to each country is reassessed, according to the Treaty of Nice.
Constituencies
Powers and functions
In some respects, the European Parliament and the Council of Ministers resemble the upper and lower houses of a bicameral legislature. Neither the European Parliament nor the Council of Ministers may initiate EU legislation, this power being reserved by the Commission, and the fact that no member of the European Parliament can propose laws makes it different from most national legislative assemblies.
However, once a proposal for an EU law or directive has been introduced by the Commission, it must usually receive the approval of both Parliament and Council in order to come into force. Parliament may amend and block legislation in those policy areas that fall under the codecision procedure, which currently make up about three-quarters of EU legislative acts. Remaining policy areas fall under either the assent procedure or (in a very few cases) the consultation procedure; under the former Parliament has power to veto but not formally amend proposals, while under the latter it has only a formal right to be consulted. The European Parliament controls the EU budget, which must be approved by the Council in order to become law.
The President of the European Commission is chosen by the European Council, but must be approved by Parliament before she or he can assume office. The remaining members of the Commission are then appointed by the President, subject to approval of Parliament. Other than its president, members of the Commission are not confirmed by the European Parliament individually; rather, Parliament must either accept or reject the whole Commission en bloc.
The European Parliament exerts a function of democratic supervision over all of the EU's activities, particularly those of the Commission. In the event that Parliament adopts a motion of censure, the entire Commission must resign (formally, Commissioners cannot be censored individually). However, a motion of censure must be approved by at least a two-thirds majority in order to have effect.
Parliament also appoints the European Ombudsman.
Under the proposed new Constitution for Europe, Parliament's powers would be enhanced, with almost all policy areas coming under co-decision, greater powers of democratic scrutiny for Parliament, and control over the whole EU budget.
Location
Although Brussels is generally treated as the 'capital' of the European Union, and the two institutions of the EU's executive, the European Commission and the Council of Ministers, both have their seats there, a protocol attached to the Treaty of Amsterdam requires that the European Parliament have monthly sessions in Strasbourg. Thus the European Parliament is sometimes informally referred to as the 'Strasbourg Parliament' and Strasbourg as the democratic (opposed to bureaucratic) capital of Europe. For practical reasons, however, preparatory legislative work and committee meetings take place in Brussels. Moreover, the European Parliament's secretariat (administration),== which employs the majority of its staff==, is located in Luxembourg, which itself used to host plenary sessions of the parliament.
Parliament only spends four days of each month in Strasbourg in order to take its final, plenary votes. Additional plenary meetings are held in Brussels. On several occasions, the European Parliament has expressed a wish to be granted the right to choose for itself the location of its seat, and eliminate the two-seat system, but in the successive treaties, EU member state governments have continued to reserve this right for themselves. While they did abandon the third seat of Parliament, Luxembourg, two decades ago, the rival demands of Belgium (Brussels) and France (Strasbourg) to base parliament in their state has prevented a final agreement as to which city would become the sole seat of parliament.
Moving various files and equipment between the two cities takes 10 large trucks and the costs for two locations are estimated at € 200 million a year. A force of 30 men loads the trucks for the 400 km journey between the two locations. Around 5,000 people attached to the European Parliament, such as parliamentarians, advisors, clerks and journalists, also move between Brussels and Strasbourg. Most of the parliamentarians are against using Strasbourg and various initiatives have been taken over the years to have Brussels as the sole location. The latest of these initiatives is a EU wide online petition which can be signed on oneseat.eu.
Organisation
The European Parliament has a number of governing bodies and committees, and a number of delegations from external bodies.
The main offices and governing bodies are:
- President - duties
- Vice-Presidents - duties
- Bureau - duties
- Conference of Presidents - duties
- Quaestors - duties
- Conference of Committee Chairmen - description
- Conference of Delegation Chairmen - description
- Political Groups
List of committees
Internal affairs
- BUDG - Committee on Budgets
- CONT - Committee on Budgetary Control
- ECON - Committee on Economic and Monetary Affairs
- EMPL - Committee on Employment and Social Affairs
- ENVI - Committee on the Environment, Public Health and Food Safety
- ITRE - Committee on Industry, Research and Energy
- IMCO - Committee on the Internal Market and Consumer Protection
- TRAN - Committee on Transport and Tourism
- REGI - Committee on Regional Development
- AGRI - Committee on Agriculture and Rural Development
- PECH - Committee on Fisheries
- CULT - Committee on Culture and Education
- JURI - Committee on Legal Affairs
- LIBE - Committee on Civil Liberties, Justice and Home Affairs
- AFCO - Committee on Constitutional Affairs
- FEMM - Committee on Women's Rights and Gender Equality
- PETI - Committee on Petitions
External affairs
- AFET - Committee on Foreign Affairs
- DROI - Subcommittee on Human Rights
- SEDE - Subcommittee on Security and Defence
- DEVE - Committee on Development
- INTA - Committee on International Trade
Political groups and parties
The political parties in the European Parliament are organised into a number of political groupings as well as a number of registered European political parties. However most continue to be members of separate national political parties and discipline within European parties and groupings is not rigid. The makeup of the parliament's groups is fluid, and both national delegations and individual MEPs are free to switch allegiances as they see fit.
European Parliament party groups are distinct from the corresponding European political parties, although they are intimately linked. Usually, the European parties also have member parties from European countries which are not members of the European Union. At the start of Parliament's sixth term in 2004 there were seven groups, as well as a number of non-aligned members, known as non-inscrits.
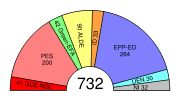
As of 8 April 2006 the composition of the European Parliament is:
| Group | Component parties/subgroups | Seats (without observers) |
Seats (with observers1) |
| European People's Party–European Democrats (EPP-ED) | European People's Party (EPP) European Democrats (ED) |
264 | 278 |
| Group of the Party of European Socialists | Party of European Socialists (PES) EUDemocrats (EUD) (part) |
201 | 219 |
| Alliance of Liberals and Democrats for Europe (ALDE) | European Liberal Democrat and Reform Party (ELDR) European Democratic Party (EDP) |
90 | 106 |
| European Greens–European Free Alliance (Greens-EFA) | European Green Party (EGP) European Free Alliance (EFA) |
42 | 42 |
| European United Left–Nordic Green Left (GUE-NGL) | Party of the European Left Nordic Green Left Alliance (NGLA) other unaffiliated leftist parties |
41 | 41 |
| Union for Europe of the Nations (UEN) | Alliance for Europe of the Nations (AEN) EUDemocrats (EUD) (part) |
34 | 34 |
| Independence and Democracy (IND/DEM) | Alliance of Independent Democrats in Europe (AIDE) European Christian Political Movement (ECPM) EUDemocrats (EUD) (part) other unaffiliated rightist Eurosceptic parties |
28 | 28 |
| Non Affiliated / Non-Inscrits (NI) | Euronat EUDemocrats (EUD) (part) other unaffiliated parties |
32 | 37 |
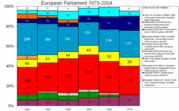
History
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) established a 'Common Assembly' in September 1952, its 78 members drawn from the six national Parliaments of the ECSC's constituent nations. This was expanded in March 1958 to also cover the European Economic Community and Euratom, and the name European Parliamentary Assembly was adopted. The body was renamed to the European Parliament in 1962. In 1979 the parliament's membership was expanded again and its members began to be directly elected for the first time. Thereafter the membership of the European Parliament has simply expanded whenever new nations have joined; the membership was adjusted upwards in 1994 after German reunification. Recent treaties, including the Treaty of Nice and the proposed Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe, set a cap on membership at 750.