Dualism (philosophy of mind)
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Philosophy
In philosophy of mind, dualism is a set of views about the relationship between mind and matter, which begins with the claim that mental phenomena are, in some respects, non- physical.
The first manifestations of mind/body dualism probably go back to the origins of conscious thought, when people began to speculate about the existence of an incorporeal soul which bore the faculties of intelligence and wisdom. We first encounter similar ideas in Western philosophy with the writings of Plato and Aristotle, who maintained, for different reasons, that man's "intelligence" (a faculty of the mind or soul) could not be identified with, or explained in terms of, their physical body.
The best-known version of dualism is due to René Descartes (1641), and holds that the mind is a nonphysical substance. Descartes was the first to clearly identify the mind with consciousness and self-awareness and to distinguish this from the brain, which was the seat of intelligence. Hence, he was the first to formulate the mind/body problem in the form in which it exists today. Dualism is contrasted with various kinds of monism, including physicalism and phenomenalism. Substance dualism is contrasted with all forms of materialism, but property dualism may be considered a form of emergent materialism and thus would only be contrasted with non-emergent materialism. This article discusses the various forms of dualism and the arguments which have been made both for and against this thesis.
Historical overview
Plato and Aristotle
In the dialogue Phaedo, Plato formulated his famous doctrine of eternal Forms as distinct and immaterial substances of which the objects and other phenomena that we perceive in the world are nothing more than mere shadows. Plato's doctrine was the prototype of all future manifestations of substance dualism in ontology. But Plato's doctrine of the Forms is not to be considered some sort of ancient and superseded metaphysical notion because it has precise implications for the philosophy of mind and the mind-body problem in particular.
Plato makes it clear, in the Phaedo, that the Forms are the universalia ante rem, i.e. they are universal concepts (or ideas) which make all of the phenomenal world intelligible. Consequently, in order for the intellect (the most important aspect of the mind in philosophy up until Descartes) to have access to any kind of knowledge with regard to any aspect of the universe, it must necessarily be a non-physical, immaterial entity (or property of some such entity) itself. So, it is clear on the basis of the texts that Plato was a very powerful precursor of Descartes and his subsequent more stringent formulation of the doctrine of substance dualism.
Aristotle strongly rejected Plato's notion of Forms as independently existing entities. In the Metaphysics, he already points to the central problems with this idea. On the one hand, if we say that the particulars of the phenomenal world participate or share in the Form, we seem to be destroying the Form's essential and indispensable unity. On the other, if we say that the particulars merely resemble, or are copies of, the Form, we seem to need an extra form to explain the connection between the members of the class consisting of the-particulars-and-the-form, and so on, leading to an infinite regress. This argument, originally formulated by Plato himself in the Parmenides, was later given the name of the " third man argument" by Aristotle.
For these reasons, Aristotle revised the theory of forms so as to eliminate the idea of their independent existence from concrete, particular entities. The form of something, for Aristotle, is the nature or essence (ousia, in Greek) of that thing. To say that Socrates and Callias are both men is not to say that there is some transcendent entity "man" to which both Socrates and Callias belong. The form is indeed substance but it is not substance over and above the substance of the concrete entities which it characterizes. Aristotle rejects both universalia in rebus as well as universalia ante rem. Some philosophers and thinkers have taken this to be a form of materialism and there may be something to their arguments. However, what is important from the perspective of philosophy of mind is that Aristotle does not believe that intellect can be conceived of as something material. He argues as follows: if the intellect were material then it could not receive all of the forms. If the intellect were a specific material organ (or part of one) then it would be restricted to receiving only certain kinds of information, as the eye is restricted to receiving visual data and the ear is restricted to receiving auditory data. Since the intellect is capable of receiving and reflecting on all forms of data, then it must not be a physical organ and, hence, it must be immaterial.
From Neoplatonism to Scholasticism
Early Christianity seems to have struggled to come to terms with the identification of a unique position with regard to the question of the relationship between mind and body, just as it struggled to define the relationship of the ontological status of Christ himself (see homoousianism, homoiousianism, Arianism, etc). In the early Middle Ages, a consensus seemed to emerge around what is now called Neoplatonism. The doctrines of Neoplatonism were essentially minor modifications on Plato's general ideas about the immortality of the soul and the nature of the Forms. The Neoplatonic Christians identified the Forms with souls and believed that the soul was the substance of each individual human being, while the body was just a shadow or copy of these eternal phenomena.
Later philosophers, following in the neo-Aristotelian trail blazed by Thomas Aquinas, came to develop a trinitarian notion of forms which paralleled the Trinitarian doctrine of Father, Son and Holy Spirit: forms, intellect and soul were three aspects or parts of the same singular phenomenon. For Aquinas, the soul (or intellect) remained the substance of the human being, but, somewhat similarly to Aristotle's proposal, it was only through its manifestation inside the human body that a person could be said to be a person. While the soul (intellect or form) could exist independently of the body (unlike in Aristotle) the soul by itself did not constitute a person. Hence, Aquinas suggested that instead of saying "St. Peter pray for us" one should rather say something like "soul of St. Peter pray for us", since all that remained of St. Peter, after his death, was his soul. All things connected with the body, such as personal memories, were cancelled out with the end of one's corporeal existence.
There are different views on this question in modern Christianity. Official Catholic Church doctrine, as illustrated by the Apostle's Creed, claims that at the Second Coming of Christ, the body is reunited with the soul at the resurrection, and the whole person (i.e. body and soul) then goes to Heaven or Hell. Hence, there is a sort of inseparability of soul, mind and body which is even more strongly reminiscent of Aristotle than the positions expressed by Thomas Aquinas.
Some revisionist Protestant theologians do not accept this doctrine and insist, instead, that only the immaterial soul (and hence mind or intellect) goes to Heaven, leaving the body (and brain) behind it forever.
Still other Christians, including Seventh-Day Adventists, teach that the soul, if it exists at all, does not survive death, citing biblical claims that the dead know nothing, and that a person's thoughts perish with them when they die. According to this view, death is like a sleep - consciousness is lost at death, but is restored to the resurrected body at the resurrection. The concept of a soul as distinct from the body would therefore be redundant.
Descartes and his disciples
In his Meditations on First Philosophy, Descartes embarked upon a quest in which he called all his previous beliefs into doubt, in order to find out what he could be certain of.In doing so, he discovered that he could doubt whether he had a body (it could be that he was dreaming of it or that it was an illusion created by an evil demon), but he couldn't doubt whether he had a mind. This gave Descartes his first inkling that the mind and body were different things. The mind, according to Descartes, was a "thinking thing" (lat. res cogitans), and an immaterial substance. This "thing" was the essence of himself, that which doubts, believes, hopes, and thinks. The distinction between mind and body is argued in Meditation VI as follows: I have a clear and distinct idea of myself as a thinking non-extended thing, and a clear and distinct idea of body as an extended and non-thinking thing. Whatever I can conceive clearly and distinctly, God can so create. So, Descartes argues, the mind, a thinking thing, can exist apart from its extended body. And therefore, the mind is a substance distinct from the body, a substance whose essence is thought.
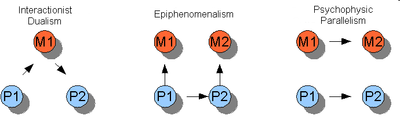
The central claim of what is often called Cartesian dualism, in honour of Descartes, is that the immaterial mind and the material body, while being [ontology|ontologically] distinct subtances, causally interact. This is an idea which continues to feature prominently in many non-European philosophies. Mental events cause physical events, and vice-versa. But this leads to a substantial problem for Cartesian dualism: How can an immaterial mind cause anything in a material body, and vice-versa? This has often been called the "problem of interactionism".
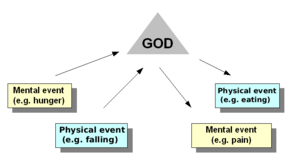
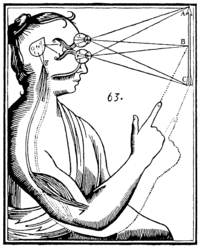
Descartes himself struggled to come up with a feasible answer to this problem. In his letter to Elisabeth of Bohemia, Princess Palatine, he suggested that animal spirits interacted with the body through the pineal gland, a small gland in the centre of the brain, between the two hemispheres. The term "Cartesian dualism" is also often associated with this more specific notion of causal interaction through the pineal gland. However, this explanation was not satisfactory: how can an immaterial mind interact with the physical pineal gland? Because Descartes' was such a difficult theory to defend, some of his disciples, such as Arnold Geulincx and Nicholas Malebranche, proposed a different explanation: That all mind-body interactions required the direct intervention of God. According to these philosophers, the appropriate states of mind and body were only the occasions for such intervention, not real causes. These occasionalists maintained the strong thesis that all causation was directly dependent on God, instead of holding that all causation was natural except for that between mind and body.
Types of ontological dualism
Ontological dualism makes dual commitments about the nature of existence as it relates to mind and matter, and can be divided into three different types:
- (1) Substance dualism asserts that mind and matter are fundamentally distinct kinds of substances.
- (2) property dualism suggests that the ontological distinction lies in the differences between properties of mind and matter (as in emergentism).
- (3) predicate dualism claims the irreducibility of mental predicates to physical predicates.
Substance dualism
Substance dualism is a type of dualism most famously defended by Descartes, which states that there are two fundamental kinds of substance: mental and material. The mental does not have extension in space, and the material cannot think. Substance dualism is a viewpoint which contradicts physicalism, one of the most popular views in modern philosophy of mind. However, it may be regarded as important historically in that it has given rise to much thought over the famous mind-body problem. It may also be noted that philosophical interpretations of quantum mechanics -- especially the consciousness causes collapse interpretation -- are not a revival of substance dualism, since these views generally claim the observer is entangled in the object being observed, not a separate substance as in the case of substance dualism. Substance dualism is a philosophical position compatible with most theologies which claim that immortal souls occupy an independent "realm" of existence which is distinct from that of the physical world. David Chalmers recently developed a thought experiment inspired by the movie The Matrix in which substance dualism could be true: Consider a computer simulation in which the bodies of the creatures are controlled by their minds and the minds remain strictly external to the simulation. The creatures can do all the science they want in the world, but they will never be able to figure out where their minds are, for they do not exist in their observable universe. This is a case of substance dualism with respect to computer simulation. This naturally differs from a computer simulation in which the minds are part of the simulation. In such a case, substance monism would be true.
Property dualism
Property dualism asserts that when matter is organized in the appropriate way (i.e. in the way that living human bodies are organized), mental properties emerge. Hence, it is a sub-branch of emergent materialism. Different versions of property dualism describe this in different ways. Epiphenomenalism asserts that while material causes give rise to sensations, volitions, ideas, etc., such mental phenomena themselves cause nothing further: they are causal dead-ends. Interactionism, on the other hand, allows that mental causes can produce material effects, and vice-versa.
Predicate dualism
Predicate dualism is the view espoused by most non-reductive physicalists, such as Donald Davidson and Jerry Fodor, who maintain that while there is only one ontological category of substances and properties of substances (usually physical), the predicates that we use to describe mental events cannot be redescribed in terms of (or reduced to) physical predicates of natural languages. If we characterize predicate monism as the view subscribed to by eliminative materialists, who maintain that such intentional predicates as believe, desire, think, feel, etc., will eventually be eliminated from both the language of science and from ordinary language because the entities to which they refer do not exist, then predicate dualism is most easily defined as the negation of this position. Predicate dualists believe that so-called "folk psychology", with all of its propositional attitude ascriptions, is an ineliminable part of the enterprise of describing, explaining and understanding human mental states and behaviour.
Davidson, for example, subscribes to Anomalous Monism, according to which there can be no strict psycho-physical laws which connect mental and physical events under their descriptions as mental and physical events. However, all mental events also have physical descriptions. It is in terms of the latter that such events can be connected in law-like relations with other physical events. Mental predicates are irreducibly different in character (rational, holistic and necessary) from physical predicates (contingent, atomic and causal).
Types of interaction dualism
Interactionism
Interactionism is the view that mental states, such as beliefs and desires, causally interact with physical states. This is a position which is very appealing to common-sense intuitions, notwithstanding the fact that it is very difficult to establish its validity or correctness by way of logical argumentation or empirical proof. It is appealing to common-sense because we are surrounded by such everyday occurrences as a child's touching a hot stove (physical event) which causes him to feel pain ( mental event) and then yell and scream (physical event) which causes his parents to experience a sensation of fear and protectiveness (mental event) and so on.
Epiphenomalism
According to epiphenomenalism, all mental events are caused by a physical event and have no physical consequences. So, a mental event of deciding to pick up a rock (call it "M") is caused by the firing of specific neurons in the brain (call it "P"), however when the arm and hand move to pick up a rock (call it "E") this is only caused by P. The physical causes are in principle reducible to fundamental physics, and therefore mental causes are eliminated using this reductionist explanation. If P causes M and E, there is no overdetermination in the explanation for E.
Parallelism
Psycho-physical parallelism is a very unusual view about the interaction between mental and physical events which was most prominently, and perhaps only truly, advocated by Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz. Like Malebranche and others before him, Leibniz recognized the weaknesses of Descartes' account of causal interaction taking place in a physical location in the brain. Malebranche decided that such a material basis of interaction between material and immaterial was impossible and therefore formulated his doctrine of occasionalism, stating that the interactions were really caused by the intervention of God on each individual occasion. Leibniz idea is that God has created a pre-established harmony such that it only seems as if physical and mental events cause, and are caused by, one another. In reality, mental causes only have mental effects and physical causes only have physical effects. Hence the term parallelism is used to describe this view.
Occasionalism
Occasionalism argues that bodily events are the occasion of an act by the Creator causing a corresponding mental event, and vice versa. Any such view requires a theological structure as a premise.
Arguments for dualism
Arguments for dualism come in several varieties.
Subjective argument in support of dualism
A very important argument against physicalism (and hence in favour of some sort of dualism) consists in the idea that the mental and the physical seem to have quite different and perhaps irreconcilable properties.
Mental events have a certain subjective quality to them, whereas physical events obviously do not. For example, what does a burned finger feel like? What does sky blue look like? What does nice music sound like?
Philosophers of mind call the subjective aspects of mental events qualia (or raw feels). There is something that it's like to feel pain, to see a familiar shade of blue, and so on; there are qualia involved in these mental events. And the claim is that qualia seem particularly difficult to reduce to anything physical.
Frank Jackson formulated his famous knowledge argument based upon just such considerations. In this thought experiment, he asks us to consider a neuroscientist, Mary, who was born, and has lived all of her life, in a black and white room with a black and white television and computer monitor where she collects all the scientific data she possibly can on the nature of colors. Jackson asserts that as soon as Mary leaves the room, she will come to have new knowledge which she did not possess before: the knowledge of the experience of colors (i.e., what they are like). Although, by hypothesis, Mary had already known everyting there is to know about colors from an objective, scientific, third-person perspective, she never knew, according to Jackson, what it was like to see red, orange, green, etc.. If Mary really learns something new, it must be knowledge of something non-physical, since she already knew everything there is to know about the physical aspects of colour. David Lewis' response to this argument, now known as the ability argument, is that what Mary really came to know was simply the ability to recognize and identify colour sensations to which she had previously not been exposed. This argument fails because it confuses knowing how to do something with knowing something as something. Others have taken Lewis argument and attempted to modify it to argue that the ability that is learned consists in some sort of process of imagining or remembering. But both imagining and remembering are based on mental representation of what something was like. As a consequence, this argument begs the question against Jackson.
Special sciences argument
This argument says that, if predicate dualism is correct, then there are special sciences which are irreducible to physics. These irreducible special sciences, which are the source of allegedly irreducible predicates, presumably differ from the hard sciences in that they are interest-relative. If they are interest-relative, then they must be dependent on the existence of minds which are capable of having interested perspectives. Psychology is, of course, the paragon of special sciences; therefore, it and its predicates must depend even more profoundly on the existence of the mental.
Physics, at least ideally, sets out to tell us how the world is in itself, to carve up the world at its joints and describe it to us without the interference of individual perspectives or personal interests. On the other hand, such things as the patterns of the weather seen in meteorology or the behaviour of human beings are only of interest to human beings as such. Now, the point is that having a perspective on the world is a psychological state. Therefore, the special sciences presuppose the existence of minds which can have these states. If one is to avoid ontological dualism, then the mind that has a perspective must be part of the physical reality to which it applies its perspective. If this is the case, then in order to perceive the physical world as psychological, the mind must have a perspective on the physical. This, in turn, presupposes the existence of mind.
The zombie argument
The zombie argument is based on a thought experiment proposed by David Chalmers. The basic idea is that one can imagine and therefore conceive the existence of one's body without any conscious states being associated with it.
Chalmers' argument is that it seems very plausible that such a being could exist because all that is needed is that all and only the things that the physical sciences describe about a zombie must be true of it. Since none of the concepts involved in these sciences make reference to consciousness or other mental phenomena, the move from conceivability to possibility is not such a large one.
Argument from personal identity
This argument concerns the differences between the applicability of counterfactual conditionals to physical objects, on the one hand, and to conscious, personal agents on the other. In the case of any material object, e.g. a printer, we can formulate a series of counterfactuals in the following manner:
-
- This printer could have been made of straw.
- This printer could have been made of some other kind of plastics and vacuum-tube transistors.
- This printer could have been made of 95% of what it is actually made of and 5% vacuum-tube transistors, etc..
Somewhere along the way from the printer's being made up exactly of the parts and materials which actually constitute it to the printer's being made up of some different matter at, say, 20%, the question of whether this printer is the same printer becomes a matter of arbitrary convention.
Imagine the case of a person, Fredrick, who has a counterpart born from the same egg and a slightly genetically modified sperm. Imagine a series of counterfactual cases corresponding to the examples applied to the printer. Somewhere along the way, one is no longer sure about the identity of Frederick. In this latter case, it has been claimed, overlap of constitution cannot be applied to the identity of mind.
- "But while my present body can thus have its partial counterpart in some possible world, my present consciousness cannot. Any present state of consciousness that I can imagine either is or is not mine. There is no question of degree here."
If the counterpart of Frederick, Frederickus, is 70% constituted of the same physical substance as Frederick, does this mean that it is also 70% mentally identical with Frederick. Does it make sense to say that something is mentally 70% Frederick?
Arguments against dualism
Argument from causal interaction
Varieties of dualism in which mind can causally affect matter have come under strenuous attack from different quarters, especially starting in the 20th century. How can something totally immaterial affect something totally material? That's the basic problem of causal interaction. We can analyze the problem here in three parts.
First, it is not clear where the interaction would take place. For example, burning my fingers causes pain. Apparently there is some chain of events, leading from the burning of skin, to the stimulation of nerve endings, to something happening in the peripheral nerves of my body that lead to my brain, to something happening in a particular part of my brain, and finally resulting in the sensation of pain. But pain is not supposed to be spatially localizable. So where does the interaction take place? If you were to respond, "It takes place in the brain," then I might say, "But I thought pains weren't located anywhere." And you, as a dualist, might stick to your guns and say, "That's right, pains aren't located anywhere; but the brain event that immediately leads to the pain is located in the brain." But then we have a very strange causal relation on our hands. The cause is located in a particular place but the effect is not located anywhere. Perhaps this is not a devastating criticism.
So let's look at a second problem about the interaction. Namely, how does the interaction take place? You might think, "Well, that's a matter for science -- scientists will eventually discover the connection between mental and physical events." But philosophers also have something to say about the matter: the very idea of a mechanism which explains the connection between the mental and the physical would be very strange, at best. Why would it be strange? Compare it to a mechanism that we do understand. Take a very simple causal relation, such as when the cue ball strikes the eight ball and causes it to go into the pocket. Here we can say that the cue ball has a certain amount of momentum as its mass moves across the pool table with some velocity, and then that momentum is transferred to the eight ball, which then heads toward the pocket. Now compare this to the situation in the brain, where we want to say a decision causes some neurons to fire and thus causes my body to move across the room. The intention "I will cross the room now," is a mental event and, as such, it does not have physical properties such as force. If it has no force, then how on earth could it cause any neuron to fire? Is it by magic? How could something without any physical properties have any physical effects at all?
Here you might reply, as some philosophers have indeed replied, as follows: "Well sure, there is a mystery about how the interaction between mental and physical events can occur. But the fact that there is a mystery doesn't mean that there is no interaction. Plainly there is an interaction and plainly the interaction is between two totally different sorts of events." The problem with this response is that it does not seem to answer the full power of the objection.
So let's try to explain the objection more precisely. Let's take as our example my decision to walk across the room. We say: my decision, a mental event, immediately causes a group of neurons in my brain to fire, a physical event, which ultimately results in my walking across the room. The problem is that if we have something totally nonphysical causing a bunch of neurons to fire, then there is no physical event which causes the firing. That means that some physical energy seems to have appeared out of thin air. Even if we say that my decision has some sort of mental energy, and that the decision causes the firing, we still haven't explained where the physical energy, for the firing, came from. It just seems to have popped into existence from nowhere.
Conservation of energy and causal closure
One of the main objections to dualistic interactionism, as pointed out above, is that it is very difficult, if not impossible, to understand how two completely different types of substances (material and immaterial) are able to interact causally. One response to this is to point out that, perhaps, the causal interaction that takes place is not at all of the classical "billiard ball" type of Newtonian mechanics but instead involves energy, dark matter or some other such mysterious processes.
Even if the latter is true, it has been argued, there is still a problem: such interactions seem to violate the fundamental laws of physics. If some external and unknown source of energy is responsible for the interactions, for example, then this would violate the law of the conservation of energy. On the other hand, the conservation laws only apply to closed and isolated systems and since human beings are not closed and isolated systems, an interactionist would argue, then the laws of conservation absolutely do not apply in this case.
Along the same lines, some argue against dualistic interactionism that it violates a general heuristic principle of science: the causal closure of the physical world. But Mills has responded to this by pointing out that mental events may be causally overdetermined. Causal overdetermination means that some features of an effect may not be fully explained by its sufficient cause. For example, "the high pitched music caused the glass to break but this is the third time that that glass has broken in the last week." It is certain that the high-pitched music is the sufficient cause of the breaking of the glass, but it does not explain the feature of the event that is identified by the phrase "this is the third time this week...". That feature is causally related, in some sense, to the two prior events of the glasses having broken in the last week. In response, it has been pointed out that we should probably focus on the inherent or intrinsic features of situations or events, if they exist, and apply the idea of causal closure to just those specific features.
Moreover, there is the question of determinism versus indeterminism. In quantum mechanisms, events at the microscopic level (at least) are indeterminate. The more precisely I can localize the position of an electron, the more imprecise becomes my ability to determine its angular momentum and vice-versa. Philosophers such as Karl Popper and John Eccles have theorized that such indeterminacy may apply even at the macroscopic scale. Most scientists, however, insist that the effects of such indeterminacy cancel each other out at larger levels.
Argument from brain damage
This argument has been formulated by Paul Churchland, among others. The point is simply that when the brain undergoes some kind of damage (caused by automobile accidents, drug abuse or pathological diseases), it is always the case that the mental substance and/or properties of the person are significantly compromised. If the mind were a completely separate substance from the brain, how could it be possible that every single time the brain is injured, the mind is also injured? Indeed, it is very frequently the case that one can even predict and explain the kind of mental or psychological deterioration or change that human beings will undergo when specific parts of their brains are damaged. So the question for the dualist to try to confront is how can all of this be explained if the mind is a separate and immaterial substance from, or if its properties are ontologically independent of, the brain.
Argument from biological development
Another common argument against dualism consists in the idea that since human beings (both phylogenetically and ontogenetically) begin their existence as entirely physical or material entities and since nothing outside of the domain of the physical is added later on the in course of development, then we must necessarily end up being fully developed material beings. Phylogenetically, the human species evolved, as did all other species, from a single cell made up of matter. Since all the events that later occurred which ended up in the formation of our species can be explained through the processes of random mutation and natural selection, the difficulty for the dualist is to explain where and why there could have intervened some non-material, non-physical event in this process of natural evolution. Ontogenetically, we begin life as a simple fertilized ovum. There is nothing non-material or mentalistic involved in conception, the formation of the blastula, the gastrula, and so on. Our development can be explained entirely in terms of the accumulation of matter through the processes of nutrition. Then where could a non-physical mind possibly come from?
Argument from simplicity
The argument from simplicity is probably the simplest and also the most common form of argument against dualism of the mental. The dualist is always faced with the question of why anyone should find it necessary to believe in the existence of two, ontologically distinct, entities (mind and brain), when it seems possible and would make for a simpler thesis to test against scientific evidence, to explain the same events and properties in terms of one. It is a heuristic principle in science and philosophy not to assume the existence of more entities than is necessary for clear explanation and prediction (see Occam's razor).