Cayman Islands
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Central & South American Countries; Countries
| Cayman Islands | |||||
|
|||||
| Motto: He hath founded it upon the seas | |||||
| Anthem: God Save the Queen (Royal Anthem) | |||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
George Town |
||||
| Official languages | English | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||
| - Queen | Queen Elizabeth II | ||||
| - Governor | Stuart Jack | ||||
| - Leader of Gov't Business | Kurt Tibbetts | ||||
| Creation | |||||
| - split from Jamaica | 1962 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 260 km² ( 206th) 100.4 sq mi |
||||
| - Water (%) | 1.6% | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - 2005 estimate | 45,017 ( 208th) | ||||
| - 1999 census | 39,020 | ||||
| - Density | 139.5/km² ( 63rd) 364.2/sq mi |
||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2004 estimate | ||||
| - Total | 1,391,000,000 ( n/a) | ||||
| - Per capita | 32,300 ( n/a) | ||||
| HDI (2003) | NA (NA) ( unranked) | ||||
| Currency | Cayman dollar ( KYD) |
||||
| Time zone | ( UTC-5) | ||||
| - Summer ( DST) | not observed ( UTC-5) | ||||
| Internet TLD | {{{cctld}}} | ||||
| Calling code | + 1-345 | ||||
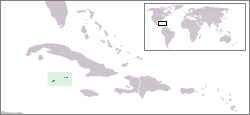
The Cayman Islands are an overseas territory of the United Kingdom in the western Caribbean Sea comprising the islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac, and Little Cayman. It is the fifth largest financial centre and is also one of the leading tourist dive destinations in the world.
History
The Cayman Islands - often referred to as The Caymans, or just Cayman - were first sighted by Christopher Columbus on May 10, 1503 during his disastrous fourth and final voyage to the New World. The first recorded English visitor to the islands was Sir Francis Drake, who landed there in 1586 and named them the Cayman Islands after the Neo-Taino nations term (caiman) for crocodile (Zayas, 1914).
The first recorded permanent inhabitant of the Cayman Islands, Isaac Bodden, was born on Grand Cayman around 1700. He was the grandson of the original settler named Bodden who was probably one of Oliver Cromwell's soldiers at the taking of Jamaica in 1655.
The islands, along with nearby Jamaica, were captured, then ceded to England in 1670 under the Treaty of Madrid. They were governed as a single colony with Jamaica until 1962 when they became a separate British overseas territory and Jamaica became an independent commonwealth realm.
The island of Grand Cayman was severely damaged by the Category Five Hurricane Ivan on September 11 & 12 2004, which destroyed many buildings and damaged 70% of them. Power, water and communications were all disrupted. Ivan was the worst hurricane to hit the islands in 86 years. As of June 27, 2006 Grand Cayman has fully recovered since Ivan, with most of the infrastructure now restored, as evidenced by the booming tourism and banking industries.
Geography
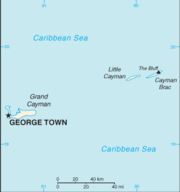
The Cayman Islands are located in the western Caribbean sea. The three islands are situated about 480 miles (770 km) south of Miami, 150 miles (240 km) south of Cuba, and 180 miles (290 km) northwest of Jamaica. Grand Cayman is by far the biggest, with an area of 76 square miles (197 km²). The two " Sister Islands" of Cayman Brac and Little Cayman are located about 90 miles (145 km) east of Grand Cayman and have areas of 14 square miles (36 km²) and 10 square miles (25.9 km²) respectively. All three islands were formed by large coral heads covering submerged ice age peaks of western extensions of the Cuban Sierra Maestra range and are mostly flat. One notable exception to this is The Bluff on Cayman Brac, which rises to 140 feet (42.6 m) above sea level, the highest point on the island.
Cayman avian fauna includes two endemic subspecies of Amazona parrots: Amazona leucocephala hesterna, or Cayman Brac Parrot, native only to Cayman Brac, and Amazona leucocephala caymanensis or Grand Cayman Parrot, which is native only to Grand Cayman. Another notable fauna is the endangered Blue Iguana, which is native to Grand Cayman.
Districts
Grand Cayman (the largest island) is administratively divided into 6 districts. They are:
- George Town (the present capital)
- East End
- North Side
- West Bay
- Bodden Town (the former capital)
Cayman Brac (the second largest island) is divided into 6 districts. They are:
- West End
- Stake Bay
- Creek
- The Rock
- Cotton Tree Bay
- Watering Place
Then there is Little Cayman (the smallest and most sparsely populated island) which is a bit bigger than a district in itself.
Demographics
The latest population estimate of the Cayman Islands is 57,800 as of April 2006, representing a mix of more than 100 nationalities. Out of that number, about half are of Caymanian descent. About 60% of the population is of mixed race (mostly mixed African-European). Of the remaining 40%, about half are Caucasian and half are of African descent. The islands are almost exclusively Christian, with large number of Presbyterians and Anglicans. Caymanians enjoy one of the highest standards of living in the West Indies. The vast majority of the population resides on Grand Cayman. Cayman Brac is the second most populated with about 2,000 residents, followed by Little Cayman with around 200 permanent residents.
The capital and major city of the Cayman Islands is George Town, which is located on the south west coast of Grand Cayman.
Economy
The economy of the Cayman Islands used to be built around turtling. However, this industry began to disappear in the 20th century and tourism and financial services began to become the economic mainstays during the 1970s. The United States is the Cayman Islands' largest trading partner.
With an average income of around $42,000, Caymanians enjoy the highest standard of living in the Caribbean. The islands print their own currency, the Cayman Islands Dollar (KYD), which is pegged to the US dollar at a fixed rate of 1 KYD = 1.227 USD. Thus, the C.I. Dollar's rate of exchange with all other world countries is directly tied to the U.S. Dollar's rate of exchange with those same countries.
The government's primary source of income is indirect taxation. An import duty of 20% is levied against goods imported into the islands. Few goods are exempt; notable examples include books, cameras & baby formula. Duty on automobiles is charged on a sliding scale with the duty reaching 40% for expensive models. The government charges a flat licensing fee to financial institutions that operate in the islands. A small fee is also charged to each tourist that arrives on the islands.
Tourism
Tourism accounts for 70-75% of the annual GDP of the Cayman Islands. Of the millions of tourists that visit the islands annually, 99% stay on Grand Cayman. George Town also serves as a major cruise ship port, which brings in 4,000 -22,000 tourists a day, 5 days a week, depending on the number of ships in port.
Grand Cayman's major tourist attraction is the world-famous Seven Mile Beach on which most of the island's hotels and resorts are located. SMB is regarded by many as one of the best beaches in the world.
The Cayman Islands are also world famous as a Scuba Diving destination because of their crystal-clear waters and their proximity to the Cayman Wall. Cayman Brac and Little Cayman are also considered to be elite dive destinations. There are several snorkeling locations where tourists can swim with stingrays.
Other tourist attractions include the black limestone spires of Hell, a turtle farm, and the Mastic Trail, a hiking trail through the dry forests in the centre of the island.
One recent development is the production of gourmet sea salt by the Cayman Sea salt Co.Ltd at their mariculture farm in Breakers Grand Cayman.
Financial services industry
The Cayman Islands is widely recognised to be one of the leading offshore financial centres.
The Cayman Islands financial services industry encompasses banking, mutual funds, captive insurance, vessel registration, companies and partnerships, trusts, structured finance and the Cayman Islands Stock Exchange. As of December 2005, just over 70,000 companies were incorporated on the Cayman Islands including 430 banking and trust companies, 720 captive insurance firms and more than 7,000 funds.
A recent report released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) assessing supervision and regulation in the Cayman Islands' banking, insurance and securities industries, as well as its anti- money laundering regime, recognized the jurisdiction's comprehensive regulatory and compliance frameworks. "An extensive program of legislative, rule and guideline development has introduced an increasingly effective system of regulation, both formalising earlier practices and introducing enhanced procedures," noted IMF assessors. The report further stated that "the supervisory system benefits from a well-developed banking infrastructure with an internationally experienced and qualified workforce as well as experienced lawyers, accountants and auditors," adding that, "the overall compliance culture within Cayman is very strong, including the compliance culture related to AML [anti-money laundering] obligations...".
Government
The Cayman Islands are currently a British Overseas territory, listed by the U.N. Special Committee of 24 as one of the last non self governing territories. A 15-seat Legislative Assembly is elected by the people every 4 years to handle domestic affairs. Of the elected Members of the Legislative Assembly, or MLAs, 5 are chosen to serve as government ministers in a cabinet headed by the governor. The head of government is the Leader of Government Business, which is currently The Honourable Kurt Tibbetts.
A Governor is appointed by the British government to represent the monarch. The governor can exercise complete executive authority if he wishes through blanket powers reserved to him in the constitution. He must give royal assent to all legislation, which allows him the power to strike down any law the legislature may see fit for the country. In modern times, the governor usually allows the country to be run by the cabinet, and the civil service to be run by the Chief Secretary, who is the Acting Governor when the Governor is not able to discharge his usual duties for one reason or another. The current governor of the Cayman Islands is Stuart Jack and the current Chief Secretary is Hon. George McCarthy, OBE, JP.
Constitutional Modernisation has come to the forefront of politics recently with the collapse of the now defunct Euro Bank Corporation in 2003. The prosecution in the trial was forced to reveal that the British Government had planted moles (and used wire taps) throughout the banking industry using MI6, at the consent of the governor. This caused the trial's collapse, and subsequent release of those charged with wrongdoing. Along with this, the only mole that was known at the time was allowed to leave the country, never to answer for what he (or the United Kingdom) was doing. This infuriated the elected members of the legislative assembly as they maintained that the governor and the United Kingdom had put into question Cayman's reputation as a tightly regulated offshore jurisdiction. Some saw this as the United Kingdom meddling in the territory's affairs to benefit itself (and the EU), at the expense of the islands' economy.
Constitutional talks however went on hold following Hurricane Ivan in 2004. Subsequently in May of 2005 the ruling UDP was ousted by the PPM, which have slowed the constitutional modernisation process to a standstill. Among the points of contention is whether or not the new constitution should include a bill-of-rights.
Taxation
Caymanians and Caymanian companies are not subject to any form of direct taxation. However, an import tax of between 5% and 20% is levied on almost all imported goods.
Education
The Cayman Islands Education Council operates state funded schools on the island, with a Caribbean-oriented education curriculum. Caymanian children are entitled to free primary and secondary education. Various churches and private foundations operate several private schools offering curricula derived from American and UK education systems from kindergarten to 12th Grade. Grand Cayman is also home to St. Matthew's University-which includes a medical school and a school of veterinary medicine.
The Cayman Islands Law School (CILS), a branch of the University of Liverpool in the UK, also calls Grand Cayman home. Situated in George Town, the law school has been in operation since 1982. As taken from the student handbook, "The Law School provides tuition for both full and part-time programmes leading to the Bachelor of Law (Honours) Degree of the University of Liverpool and the qualification of Attorney-at-Law of the Cayman Islands, following successful completion of the postgraduate Professional Practicum Course (PPC)
Healthcare
The Cayman Islands have a modern healthcare system. There are two hospitals in George Town, the government run George Town Hospital and the smaller, private Chrissie Tomlinson Memorial Hospital. Additionally Faith Hospital is a small (18 bed) facility on Cayman Brac. The Government maintains a satellite clinic on Little Cayman.
Health insurance is handled by private insurers and a government-run company (CINICO). There is no universal health coverage as in the UK.
Currently the islands lack facilites for cardiac catheterization, though many feel the population is large enough to support the procedure. Various attempts to establish a cath lab in George Town Hospital have stalled out. Similarly, the Caymans have lacked an MRI since one was destroyed during Hurricane Ivan.
Military
The defence of the Cayman Islands is the responsibility of the United Kingdom. Therefore, the islands have no established military. They do however have their own police force, the Royal Cayman Islands Police Service, and in 2001 the small Cayman Islands Cadet Corps was formed in the place of a traditional army. Regular off-shore marine patrols are conducted by the RCIP and Grand Cayman is a port-of-call for the United States Coast Guard.
Foreign relations
The foreign relations of the Cayman Islands are largely managed from the United Kingdom, as the islands remain an overseas territory of the UK. However, the Government of the Cayman Islands often resolves important issues with foreign governments alone, without intervention from Britain. Although in its early days, the Cayman Islands' most important relationships were with Britain and Jamaica, in recent years, this has shifted, and they now rely more so on the United States.
Though the Cayman Islands are involved in no major international disputes, they have come under some criticism due to the use of their territory for narcotics trafficking and money laundering. In an attempt to address this, the Government entered into the Narcotics Agreement of 1984 and the Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty of 1986 with the United States, in order to reduce the use of their facilities associated with these activities. In more recent years, they have stepped up the fight against money laundering, by limiting banking secrecy, introducing requirements for customer identification and record keeping, and requiring banks to cooperate with foreign investigators.
Due to their status as an overseas territory of the UK, the Cayman Islands have no representation either on the United Nations, or in most other international organizations. However, the Cayman Islands still participates in some international organizations, being a full member of the Central Development Bank, International Olympic Committee and FIFA, an associate member of Caricom and UNESCO, and a member of a sub-bureau of Interpol.
In fiction
Large parts of the novel The Firm by John Grisham, and the film, take place on the Cayman Islands. The main character works for a Memphis, Tennessee law firm that uses island banks for money laundering.
Frankie Flowers' 2004 film Haven takes place on Grand Cayman. Frankie Flowers is a native of the Cayman Islands.
The islands are featured as Krusty the Clown's tax haven in The Simpsons episode 3F12 - Bart The Fink.
A Cayman Island Bank cheque is also shown in Bond thriller 'Die Another Day'. The cheque is issued by Halle Berry to a doctor in the 'beauty clinic' on Isla Lorna.
In the computer game Rainbow Six 3: Raven Shield 4 missions need to be accomplished on the airport of Cayman Brac as well as in a private house in order to rescue hostages being held in the buildings by terrorists.