Cataract
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Health and medicine
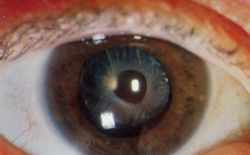
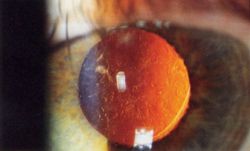
| Magnified view of cataract in human eye, seen on examination with a slit lamp using diffuse illumination | |
| ICD- 10 | H 25.- H 26., H 28., Q 12.0 |
| ICD- 9 | 366 |
| DiseasesDB | 2179 |
| MedlinePlus | 001001 |
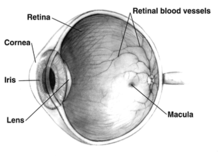
A cataract is an opacity that develops in the crystalline lens of the eye or in its envelope. Early on in the development of senile cataract the power of the crystaline lens may be increased, causing myopia, and the gradual yellowing and opacification of the lens may reduce the perception of blue colours. Cataracts typically progress slowly to cause vision loss and are potentially blinding if untreated. Moreover, with time the cataract cortex liquefies to form a milky white fluid in a Morgagnian Cataract, and can cause severe inflammation if the lens capsule ruptures and leaks. Untreated, the cataract can cause phacomorphic glaucoma. Very advanced cataracts with weak zonules are liable to dislocation anteriorly or posteriorly. Such spontaneous posterior dislocations (akin to the earliest surgical procedure of couching) in ancient times were regarded as a blessing from the heavens, because it restored some perception of light in the bilaterally affected patients.
Cataract derives from the Latin cataracta meaning "waterfall" and the Greek kataraktes and katarrhaktes, from katarassein meaning "to dash down" (kata-, "down"; arassein, "to strike, dash"). As rapidly running water turns white, the term may later have been used metaphorically to describe the similar appearance of mature ocular opacities. In Latin, cataracta had the alternate meaning, " portcullis", so it is also possible that the name came about through the sense of "obstruction".
Causes
Cataracts form for a variety of reasons, including long-term ultraviolet exposure, secondary effects of diseases such as diabetes, or simply due to advanced age; they are usually a result of denaturation of lens proteins. Genetic factors are often a cause of congenital cataracts and positive family history may also play a role in predisposing someone to cataracts at an earlier age, a phenomenon of "anticipation" in pre-senile cataracts. Cataracts can also be produced by eye injury or physical trauma. A study among Icelandair pilots showed commercial airline pilots as three times more likely to develop cataracts than people with non-flying jobs. This is thought to be caused by excessive exposure to radiation coming from outer space. Cataracts are also unusually common in persons exposed to infrared radiation, such as glassblowers who suffer from "exfoliation syndrome". Exposure to microwave radiation can cause cataracts.
Cataracts may be partial or complete, stationary or progressive, hard or soft.
Epidemiology
Cataracts are the leading cause of blindness in the world.
In the United States, age-related lenticular changes have been reported in 42% of those between the ages of 52 to 64, 60% of those between the ages 65 and 74, and 91% of those between the ages of 75 and 85.
Cataract surgery
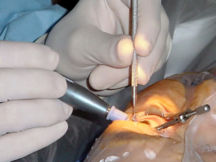
The most effective and common treatment is to surgically remove the cloudy lens. There are two types of surgery that can be used to remove cataracts, extra-capsular and intra-capsular surgery. Extra-capsular surgery consists of removing the lens but leaving the majority of the lens capsule intact. High frequency sound waves ( phacoemulsification) are sometimes used to break up the lens before extraction. Intra-capsular surgery involves removing the entire lens of the eye, including the lens capsule, but it is rarely performed in modern practice. In either extra-capsular surgery or intra-capsular surgery, the cataractous lens is removed & replaced with a plastic lens (an intraocular lens implant) which remains permanently in the eye.
Cataract operations are usually performed using a local anaesthetic and the patient will be allowed to go home the same day. Recent improvements in intraocular technology now allow cataract patients to choose a multifocal lens to create a visual environment where they are less dependent on glasses. Traditional intraocular lens were monofocal. Medicare has allowed physicians, for the first time, to bill patients for this advanced lens design.
Complications after cataract surgery, including posterior capsular opacification and retinal detachment, are possible.
Prevention
Although cataracts have no scientifically proven prevention, it is sometimes said that wearing ultraviolet-protecting sunglasses may slow the development of cataracts. Regular intake of antioxidants (such as vitamin C and E) is theoretically helpful, but this is also not proven.
Recent research
Although statins are known for their ability to lower lipids, they are also believed to have antioxidant qualities. It is believed that oxidative stress plays a role in the development of nuclear cataracts, which are the most common type of age-related cataract. To explore the relationship between nuclear cataracts and statin use, a group of researchers took a group of 1299 patients who were at risk of developing nuclear cataracts and gave some of them statins. Their results suggest that statin use in a general population may be associated with a lower risk of developing nuclear cataract.
Types of cataracts
The following is a classification of the various types of cataracts. This is not comprehensive and other unusual types may be noted.
- Classified by etiology
-
- Age-related cataract
-
- Immature Senile Cataract (IMSC) - partially opaque lens, disc view hazy
- Mature Senile Cataract (MSC) - Completely opaque lens, no disc view
- Hypermature Senile Cataract (HMSC) - Liquefied cortical matter: Morgagnian Cataract
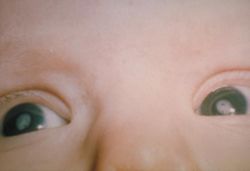
- Congenital cataract
-
- Sutural cataract
- Lamellar cataract
- Zonular cataract
- Total cataract
- Secondary cataract
-
-
- Drug-induced cataract (e.g. Corticosteroids)
- Traumatic cataract
-
- Blunt trauma (capsule usually intact)
- Penetrating trauma (capsular rupture & leakage of lens material - calls for an emergency surgery for extraction of lens and leaked material to minimise further damage)
-
- Classified by location of opacity within lens structure (However, mixed morphology is quite commonly seen, e.g. PSC with nuclear changes & cortical spokes of cataract)
-
- Anterior cortical cataract
- Anterior polar cataract
- Anterior subcapsular cataract
-
- Nuclear cataract - Grading correlates with hardness & difficulty of surgical removal
-
- 1 - Grey
- 2 - Yellow
- 3 - Amber
- 4 - Brown/Black (Note: "Black cataract" translated in some languages (like Hindi) refers to Glaucoma, not the colour of the lens nucleus)
- Posterior cortical cataract
- Posterior polar cataract (importance lies in higher risk of complication - posterior capuslar tears during surgery)
- Posterior subcapsular cataract (PSC) (clinically common)
-
- After-cataract - posterior capsular opacification subsequent to a successful extracapsular cataract surgery (usually within 3 months - 2 years) with or without IOL implantation. Requires a quick & painless office procedure with Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy to restore optical clarity.
Associations with systemic conditions
- Chromosomal disorders
-
- Alport's syndrome
- Cri-du-chat syndrome
- Conradi's syndrome
- Myotonia dystrophica
- Patau's syndrome
- Schmid-Fraccaro syndrome
- Trisomy 18 ( Edward's syndrome)
- Turner's syndrome
- Disease of the skin and mucous membranes
-
- Atopic dermatitis
- Basal-cell nevus syndrome
- Ichthyosis
- Pemphigus
- Metabolic and nutrition diseases
-
- Aminoaciduria ( Lowe's syndrome)
- Diabetes mellitus
- Fabry's disease
- Galactosemia
- Homocystinuria
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Mucopolysaccharidoses
- Wilson's disease
- Infectious diseases
-
- Congenital
-
- Congential herpes simplex
- Congenital syphilis
- Cytomegalic inclusion disease
- Rubella
- Others
-
- Cysticercosis
- Leprosy
- Onchocerciasis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Toxic substances introduced systemically
-
- Corticosteroids
- Haloperidol
- Miotics
- Triparanol