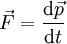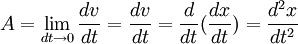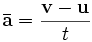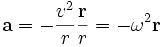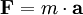Acceleration
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General Physics
In physics or physical science, acceleration (symbol: a) is defined as the rate of change (or derivative with respect to time) of velocity. It is thus a vector quantity with dimension length/time². In SI units, acceleration is measured in metres/second² (m·s-²) using an accelerometer.
Explanation
To accelerate an object is to change its velocity, which is accomplished by altering either its speed or direction (as in the case of uniform circular motion) in relation to time. In this strict mathematical sense, acceleration can have positive and negative values (deceleration). Any time that the sign (+ or -) of the acceleration is the same as the sign of the velocity, the object will speed up. If the signs are opposite, the object will slow down. Acceleration is a vector defined by properties of magnitude (size or measurability) and direction. When either velocity or direction are changed, there is acceleration (or deceleration)
Since:
Then, for the definition of instantaneous acceleration;
also 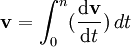 OR
OR 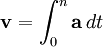 , i.e. Velocity can be thought of as the integral of acceleration with respect to the time. (Note, this can be a definite or indefinite integration).
, i.e. Velocity can be thought of as the integral of acceleration with respect to the time. (Note, this can be a definite or indefinite integration).
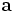 is the acceleration vector (as acceleration is a vector, it must be described with both a direction and a has a::magnitude).
is the acceleration vector (as acceleration is a vector, it must be described with both a direction and a has a::magnitude).- v is the velocity function
- x is the position function (also known as displacement or change in position)
- t is time
- d is Leibniz's notation for differentiation
- v is the velocity function
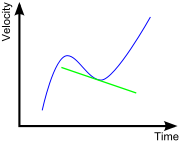
When velocity is plotted against time on a velocity vs. time graph, the acceleration is given by the slope, or the derivative of the graph.
If used with SI standard units (metres per second for velocity; seconds for time) this equation gives a the units of m/(s·s), or m/s² (read as "metres per second per second", or "metres per second squared").
An average acceleration, or acceleration over time, ā can be defined as:
where
- u is the initial velocity (m/s)
- v is the final velocity (m/s)
- t is the time interval (s) elapsed between the two velocity measurements (also written as "Δt")
Transverse acceleration ( perpendicular to velocity), as with any acceleration which is not parallel to the direction of motion, causes change in direction. If it is constant in magnitude and changing in direction with the velocity, we get a circular motion. For this centripetal acceleration we have
One common unit of acceleration is g, one g (more specifically, gn or g 0) being the standard uniform acceleration of free fall or 9.80665 m/s², caused by the gravitational field of Earth at sea level at about 45.5° latitude.
Jerk is the rate of change of an object's acceleration over time.
In classical mechanics, acceleration 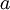 is related to force
is related to force 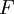 and mass
and mass 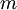 (assumed to be constant) by way of Newton's second law:
(assumed to be constant) by way of Newton's second law:
As a result of its invariance under the Galilean transformations, acceleration is an absolute quantity in classical mechanics.
Relation to relativity
After defining his theory of special relativity, Albert Einstein realized that forces felt by objects undergoing constant proper acceleration are indistinguishable from those in a gravitational field, and thus defined general relativity that also explained how gravity's effects could be limited by the speed of light.
If you accelerate away from your friend, you could say (given your frame of reference) that it is your friend who is accelerating away from you, although only you feel any force. This is also the basis for the popular Twin paradox, which asks why only one twin ages when moving away from his sibling at near light-speed and then returning, since the aging twin can say that it is the other twin that was moving. General relativity solved the "why does only one object feel accelerated?" problem which had plagued philosophers and scientists since Newton's time (and caused Newton to endorse absolute space). In special relativity, only inertial frames of reference (non-accelerated frames) can be used and are equivalent; general relativity considers all frames, even accelerated ones, to be equivalent. With changing velocity, accelerated objects exist in warped space (as do those that reside in a gravitational field). Therefore, frames of reference must include a description of their local spacetime curvature to qualify as complete.