From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. The description on its description page there is shown below. |
|
|
Commons is attempting to create a freely licensed media file repository. You can help.
|
Summary
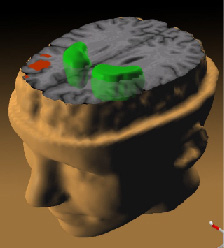
illustration of Schizophrenia's effect on the brain; taken from here
- Source: Andreas Meyer-Lindenberg, M.D., Ph.D., NIMH Clinical Brain Disorders Branch
While patients performed a working memory task, the less the prefrontal cortex (red) activated, the more dopamine increased in the striatum (green).
Abstract of study is here.
 |
This image is a work of the National Institutes of Health, part of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. As a work of the U.S. federal government, the image is in the public domain. |
|
Licensing
 |
This work is in the public domain in the United States because it is a work of the United States Federal Government under the terms of Title 17, Chapter 1, Section 105 of the US Code. See Copyright. Note: This only applies to works of the Federal Government and not to the work of any individual U.S. state, territory, commonwealth, county, municipality, or any other subdivision.
العربية | Česky | Deutsch | Español | 한국어 | Italiano | 日本語 | Magyar | Français | Português | 简体中文 | 正體中文 | +/- < |
|
File links
The following pages on the English Wikipedia link to this file (pages on other projects are not listed):
- Schizophrenia
-
Wikipedia:Today's featured article/October 2005
-
Wikipedia:Today's featured article/October 24, 2005
-
Portal:Psychology/Selected article
-
Portal:Psychology/Selected article/3