Image:Satellite Footprints Seen in Jupiter Aurora.jpg
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Size of this preview: 800 × 455 pixel
Image in higher resolution (2842 × 1617 pixel, file size: 503 KB, MIME type: image/jpeg)
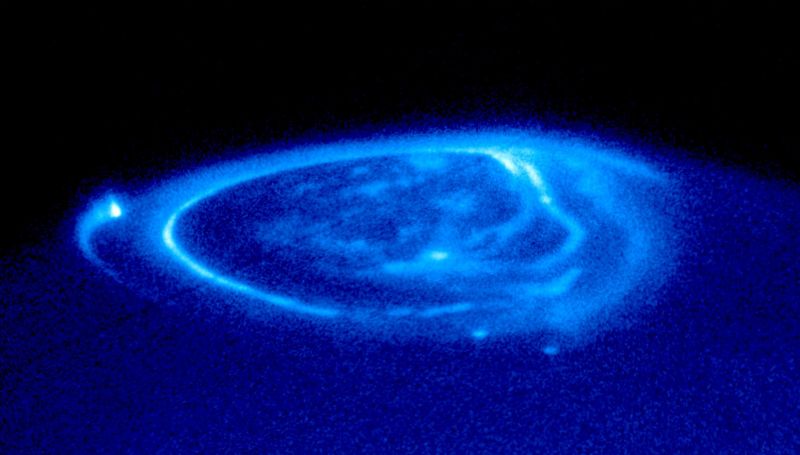
Satellite Footprints Seen in Jupiter Aurora.
Original caption from :
This is a spectacular NASA Hubble Space Telescope close-up view of an electric-blue aurora that is eerily glowing one half billion miles away on the giant planet Jupiter. Auroras are curtains of light resulting from high-energy electrons racing along the planet's magnetic field into the upper atmosphere. The electrons excite atmospheric gases, causing them to glow. The image shows the main oval of the aurora, which is centered on the magnetic north pole, plus more diffuse emissions inside the polar cap.
Though the aurora resembles the same phenomenon that crowns Earth's polar regions, the Hubble image shows unique emissions from the magnetic "footprints" of three of Jupiter's largest moons. (These points are reached by following Jupiter's magnetic field from each satellite down to the planet).
Auroral footprints can be seen in this image from Io (along the left hand limb), Ganymede (near the centre), and Europa (just below and to the right of Ganymede's auroral footprint). These emissions, produced by electric currents generated by the satellites, flow along Jupiter's magnetic field, bouncing in and out of the upper atmosphere. They are unlike anything seen on Earth.
This ultraviolet image of Jupiter was taken with the Hubble Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) on November 26, 1998. In this ultraviolet view, the aurora stands out clearly, but Jupiter's cloud structure is masked by haze.
December 14, 2000 inaugurates an intensive two weeks of joint observation of Jupiter's aurora by Hubble and the Cassini spacecraft. Cassini will make its closest approach to Jupiter en route to a July 2004 rendezvous with Saturn. A second campaign in January 2001 will consist of Hubble images of Jupiter's day-side aurora and Cassini images of Jupiter's night-side aurora, obtained just after Cassini has flown past Jupiter. The team will develop computer models that predict how the aurora operates, and this will yield new insights into the effects of the solar wind on the magnetic fields of planets.
 |
This file is in the public domain because it was created by NASA. NASA copyright policy states that "NASA material is not protected by copyright unless noted". ( NASA copyright policy page or JPL Image Use Policy). Warnings:
|
|
File history
Legend: (cur) = this is the current file, (del) = delete this old version, (rev) = revert to this old version.
Click on date to download the file or see the image uploaded on that date.
- (del) (cur) 02:22, 18 September 2005 . . Deglr6328 ( Talk | contribs) . . 2842×1617 (515,299 bytes) (remove border )
- (del) (rev) 02:19, 18 September 2005 . . Deglr6328 ( Talk | contribs) . . 3000×2400 (438,580 bytes) (Satellite Footprints Seen in Jupiter Aurora. Original caption from [http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/newsdesk/archive/releases/2000/38/image/a]: This is a spectacular NASA Hubble Space Telescope close-up view of an electric-blue aurora that is eerily gl)
-
Edit this file using an external application
See the setup instructions for more information.
File links
Category: NASA images