Unix
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Software
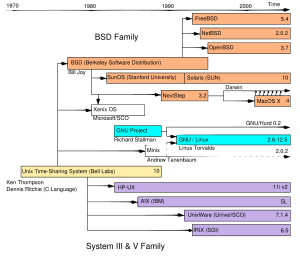
Unix (officially trademarked as UNIX) is a computer operating system originally developed in the 1960s and 1970s by a group of AT&T employees at Bell Labs including Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and Douglas McIlroy. Today's Unix systems are split into various branches, developed over time by AT&T, as well as various commercial vendors and non-profit organizations.
The present owner of the trademark UNIX is The Open Group, an industry standards consortium. Only systems fully compliant with and certified to the Single UNIX Specification qualify as "UNIX" (others are called "Unix system-like" or " Unix-like").
During the late 1970s and early 1980s, Unix's influence in academic circles led to large-scale adoption (particularly of the BSD variant, originating from the University of California, Berkeley) of Unix by commercial startups, the most notable of which is Sun Microsystems. Today, in addition to certified Unix systems, Unix-like operating systems such as Linux and Mac OS X are commonly encountered.
Sometimes, Traditional Unix may be used to describe a Unix or an operating system that has the characteristics of either Version 7 Unix or UNIX System V.
Overview
Unix operating systems are widely used in both servers and workstations. The Unix environment and the client-server program model were essential elements in the development of the Internet and the reshaping of computing as centered in networks rather than in individual computers.
Both Unix and the C programming language were developed by AT&T and distributed to government and academic institutions, causing both to be ported to a wider variety of machine families than any other operating system. As a result, Unix became synonymous with " open systems".
Unix was designed to be portable, multi-tasking and multi-user in a time-sharing configuration. Unix systems are characterized by various concepts: the use of plain text for storing data; a hierarchical file system; treating devices and certain types of inter-process communication (IPC) as files; and the use of a large number of small programs that can be strung together through a command line interpreter using pipes, as opposed to using a single monolithic program that includes all of the same functionality. These concepts are known as the Unix philosophy.
Under Unix, the "operating system" consists of many of these utilities along with the master control program, the kernel. The kernel provides services to start and stop programs, handle the file system and other common "high level" tasks that most programs share, and, perhaps most importantly, schedules access to hardware to avoid conflicts if two programs attempt to simultaneously access the same resource or device. In order to mediate such access, the kernel was given special rights on the system and led to the division between user-space and kernel-space.
The microkernel tried to reverse the growing size of kernels and return to a system in which most tasks would be completed by smaller utilities. In an era when a "normal" computer consisted of a hard disk for storage and a data terminal for input and output (I/O), the Unix file model worked quite well as most I/O was "linear". However, modern systems include networking and other new devices. Describing a graphical user interface driven by mouse control in an "event driven" fashion didn't work well under the old model. Work on systems supporting these new devices in the 1980s led to facilities for non-blocking I/O, forms of inter-process communications other than just pipes, as well as moving functionality such as network protocols out of the kernel.
History
In the 1960s, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, AT&T Bell Labs, and General Electric worked on an experimental operating system called Multics (Multiplexed Information and Computing Service), which was designed to run on the GE-645 mainframe computer. The aim was the creation of a commercial product, although this was never a great success. Multics was an interactive operating system with many novel capabilities, including enhanced security. The project did develop production releases, but initially these releases performed poorly.
AT&T Bell Labs pulled out and deployed its resources elsewhere. One of the developers on the Bell Labs team, Ken Thompson, continued to develop for the GE-645 mainframe, and wrote a game for that computer called Space Travel. However, he found that the game was too slow on the GE machine and was costly, costing $75 per execution in scarce computing time.
Thompson thus re-wrote the game in assembly language for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-7 with help from Dennis Ritchie. This experience, combined with his work on the Multics project, led Thompson to start a new operating system for the PDP-7. Thompson and Ritchie led a team of developers, including Rudd Canaday, at Bell Labs developing a file system as well as the new multi-tasking operating system itself. They included a command line interpreter and some small utility programs.
1970s
In 1970, the project was named Unics, short for Uniplexed Information and Computing System, and could support two simultaneous users. The name has been attributed to Brian Kernighan, and was a play on Multics - Unix would do one thing, and do it well, rather than the overly general and bloated Multics system. The spelling was later changed to Unix.
Up until this point there had been no financial support from Bell Labs. When the Computer Science Research Group wanted to use Unix on a much larger machine than the PDP-7, Thompson and Ritchie managed to trade the promise of adding text processing capabilities to Unix for a PDP-11/20 machine. This led to some financial support from Bell. For the first time in 1970, the UNIX Operating System was officially named and ran on the PDP-11/20. It added a text formatting program called roff and a text editor. All three were written in PDP-11/20 assembly language. Bell Labs used this initial "text processing system", made up of Unix, roff, and the editor, for text processing of patent applications. Roff soon evolved into troff, the first electronic publishing program with a full typesetting capability. The UNIX Programmer's Manual was published on November 3, 1971.
In 1973, the decision was made to re-write Unix in the C programming language. The change meant that it was easier to modify Unix to work on other machines (thus becoming portable), and other developers could create variations. The code was now more concise and compact, leading to accelerated development of Unix. AT&T made Unix available to universities and commercial firms, as well as the United States government under licenses. The licenses included all source code except for the machine-dependent kernel, which was written in PDP-11 assembly code. However, copies of the annotated Unix machine-dependent kernel circulated widely in the late 1970s in the form of a much-copied book by John Lions of the University of New South Wales, the Lions' Commentary on UNIX 6th Edition, with Source Code, which led to considerable adoption of Unix as an educational operating system.
Versions of the Unix system were determined by editions of its user manuals, so that (for example) "Fifth Edition UNIX" and "UNIX Version 5" have both been used to designate the same thing. Development expanded, with Versions 4, 5, and 6 being released by 1975. These versions added the concept of pipes, leading to the development of a more modular code-base, increasing development speed still further. Version 5 and especially Version 6 led to a plethora of different Unix versions both inside and outside Bell Labs, including PWB/UNIX, IS/1 (the first commercial Unix), and the University of Wollongong's port to the Interdata 7/32 (the first non-PDP Unix).
In 1978, UNIX/32V, for the VAX system, was released. By this time, over 600 machines were running Unix in some form. Version 7 Unix, the last version of Research Unix to be released widely, was released in 1979. Versions 8, 9 and 10 were developed through the 1980s but were only ever released to a few universities, though they did generate papers describing the new work. This research led to the development of Plan 9 from Bell Labs, a new portable distributed system.
1980s
AT&T now licensed UNIX System III, based largely on Version 7, for commercial use, the first version launching in 1982. This also included support for the VAX. AT&T continued to issue licenses for older Unix versions. To end the confusion between all its differing internal versions, AT&T combined them into UNIX System V Release 1. This introduced a few features such as the vi editor and curses from the Berkeley Software Distribution of Unix developed at the University of California, Berkeley. This also included support for the Western Electric 3B series of machines.
Since the newer commercial UNIX licensing terms were not as favorable for academic use as the older versions of Unix, the Berkeley researchers continued to develop BSD Unix as an alternative to UNIX System III and V, originally on the PDP-11 architecture (the 2.xBSD releases, ending with 2.11BSD) and later for the VAX-11 (the 4.x BSD releases). Many contributions to Unix first appeared on BSD systems, notably the C shell with job control (modelled on ITS), Perhaps the most important aspect of the BSD development effort was the addition of TCP/IP network code to the mainstream Unix kernel. The BSD effort produced several significant releases that contained network code: 4.1cBSD, 4.2BSD, 4.3BSD, 4.3BSD-Tahoe ("Tahoe" being the nickname of the CCI Power 6/32 architecture that was the first non-DEC release of the BSD kernel), Net/1, 4.3BSD-Reno (to match the "Tahoe" naming, and that the release was something of a gamble), Net/2, 4.4BSD, and 4.4BSD-lite. The network code found in these releases is the ancestor of almost all TCP/IP network code in use today, including code that was later released in AT&T System V UNIX and Microsoft Windows. The accompanying Berkeley Sockets API is a de facto standard for networking APIs and has been copied on many platforms.
Other companies began to offer commercial versions of the UNIX System for their own mini-computers and workstations. Most of these new Unix flavours were developed from the System V base under a license from AT&T; however, others were based on BSD instead. One of the leading developers of BSD, Bill Joy, went on to co-found Sun Microsystems in 1982 and create SunOS (now Solaris) for their workstation computers. In 1980, Microsoft announced its first Unix for 16-bit microcomputers called Xenix, which the Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) ported to the Intel 8086 processor in 1983, and eventually branched Xenix into SCO UNIX in 1989.
In 1984, an industry group called X/Open was formed, with the aim of forming compatible open systems, that is, standardizing the UNIX environment. By the mid-1980s, the (largely gratuitous) incompatibilities between competing versions of Unix, popularly called "the Unix wars," were seen as hindering the adoption of Unix in a marketplace that was beginning to be dominated by Microsoft's operating systems. Inspired to some extent by the development of dual-mode (AT&T/BSD) versions of Unix, the IEEE Working Group P1003 developed the first POSIX standard for a Unix-based application programming interface, published in 1988.
AT&T added various features into UNIX System V, such as file locking, system administration, streams, the Remote File System and TLI. AT&T cooperated with Sun Microsystems and between 1987 and 1989 merged features from Xenix, BSD, SunOS, and System V into System V Release 4 (SVR4), independently of X/Open. This new release consolidated all the previous features into one package, and heralded the end of competing versions. It also increased licensing fees.
1990s
In 1990, the Open Software Foundation released OSF/1, their standard Unix implementation, based on Mach and BSD. The Foundation was started in 1988 and was funded by several Unix-related companies that wished to counteract the collaboration of AT&T and Sun on SVR4. Subsequently, AT&T and another group of licensees formed the group " UNIX International" in order to counteract OSF. This escalation of conflict between competing vendors gave rise to the phrase " Unix wars".
In 1991, a group of BSD developers (Donn Seeley, Mike Karels, Bill Jolitz, and Trent Hein) left the University of California to found Berkeley Software Design, Inc ( BSDI). BSDI produced a fully functional commercial version of BSD Unix for the inexpensive and ubiquitous Intel platform, which started a wave of interest in the use of inexpensive hardware for production computing. Shortly after it was founded, Bill Jolitz left BSDI to pursue distribution of 386BSD, the free software ancestor of FreeBSD, OpenBSD, and NetBSD.
By 1993 most of the commercial vendors of UNIX had changed their commercial variants of Unix to be based on System V with many BSD features added on top. The creation of the COSE initiative that year by the major players in Unix marked the end of the most notorious phase of the Unix wars, and was followed by the merger of UI and OSF in 1994. The new combined entity, which retained the OSF name, stopped work on OSF/1 that year. By that time the only vendor using it was Digital, which continued its own development, rebranding their product Digital UNIX in early 1995.
Shortly after UNIX System V Release 4 was produced, AT&T sold all its rights to UNIX to Novell. (Dennis Ritchie likened this to the Biblical story of Esau selling his birthright for the proverbial " mess of pottage".) Novell developed its own version, UnixWare, merging its NetWare with UNIX System V Release 4. Novell tried to use this to battle against Windows NT, but their core markets suffered considerably.
In 1993, Novell decided to transfer the UNIX trademark and certification rights to the X/Open Consortium. In 1996, X/Open merged with OSF, creating the Open Group. Various standards by the Open Group now define what is and what is not a "UNIX" operating system, notably the post-1998 Single UNIX Specification.
In 1995, the business of administration and support of the existing UNIX licenses plus rights to further develop the System V code base were sold by Novell to the Santa Cruz Operation. Whether Novell also sold the copyrights is currently the subject of litigation (see below).
2000 to present
In 2000, SCO sold its entire UNIX business and assets to Caldera Systems, which later on changed its name to The SCO Group. This new player then started legal action against various users and vendors of Linux. SCO have alleged that Linux contains copyrighted Unix code now owned by The SCO Group. Other allegations include trade-secret violations by IBM, or contract violations by former Santa Cruz customers who have since converted to Linux. However, Novell disputed the SCO group's claim to hold copyright on the UNIX source base. According to Novell, SCO (and hence the SCO Group) are effectively franchise operators for Novell, which also retained the core copyrights, veto rights over future licensing activities of SCO, and 95% of the licensing revenue. The SCO Group disagreed with this, and the dispute had resulted in the SCO v. Novell lawsuit.
In 2005, Sun Microsystems released the bulk of its Solaris system code (based on UNIX System V Release 4) into an open source project called OpenSolaris. New Sun OS technologies such as the ZFS file system are now first released as open source code via the OpenSolaris project; as of 2006 it has spawned several non-Sun distributions such as SchilliX, Belenix, Nexenta and MartuX.
The Dot-com crash has led to significant consolidation of UNIX users as well. Of the many commercial flavours of UNIX that were born in the 1980s, only Solaris, HP-UX, and AIX are still doing relatively well in the market. Of these, Solaris has the most market share, and may be becoming more popular now that it is Open Source.
Standards
Beginning in the late 1980s, an open operating system standardization effort now known as POSIX provided a common baseline for all operating systems; IEEE based POSIX around the common structure of the major competing variants of the Unix system, publishing the first POSIX standard in 1988. At around the same time a separate but very similar standard, the Single UNIX Specification, was also produced by the Open Group. Starting in 1998 these two standards bodies began work on merging the two standards, and they are now identical.
In an effort towards compatibility, several Unix system vendors agreed on SVR4's Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) as standard for binary and object code files. The common format allows substantial binary compatibility among Unix systems operating on the same CPU architecture.
The directory layout of some systems, particularly on Linux, is defined by the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard. This type of standard however is controversial, and even within the Linux community its adoption is far from universal.
Components
The UNIX system is composed of several components that are normally packaged together. By including — in addition to the kernel of an operating system — the development environment, libraries, documents, and the portable, modifiable source-code for all of these components, UNIX was a self-contained software system. This was one of the key reasons it emerged into an important teaching and learning tool and had such a broad influence.
Inclusion of these components did not make the system large — the original V7 UNIX distribution, consisting of copies of all of the compiled binaries plus all of the source code and documentation occupied less than 10Mb, and arrived on a single 9-track magtape. The printed documentation was contained in two fairly thin books.
The names and filesystem locations of the Unix components has changed substantially across the history of the system. Nonetheless, the V7 implementation is considered by many to have the canonical early structure:
- Kernel — originally found in /usr/sys, and composed of several sub-components:
- conf — originally found in /usr/sys/conf, and composed of configuration and machine-dependent parts, often including boot code
- dev — Device drivers (originally /usr/sys/dev) for control of hardware (and sometimes pseudo-hardware)
- sys — The "kernel" of the operating system, handling memory management, system calls, etc.
- h (or include) — Header files, generally defining key interfaces within the system, and important system-specific invariables
- Development Environment — Most implementations of Unix contained a development environment sufficient to recreate the system from source code. The development environment included:
- cc — The C language compiler (first appearing in V3 Unix)
- as — The machine-language assembler for the machine
- ld — The linker, for combining object files
- lib — Libraries. Originally libc, the system library with C run-time support, was the primary library, but there have always been additional libraries for such things as mathematical functions (libm) or database access. V7 Unix introduced the first version of the modern "Standard I/O" library stdio as part of the system library. Later implementations multiplied the number and type of libraries significantly.
- make - The build manager (introduced in PWB/UNIX), designed to effectively automate the build process
- include — Header files for software development, defining standard interfaces and system invariants
- Other (secondary) languages — V7 Unix contained a Fortran-77 compiler, a programmable calculator, and the awk "scripting" language, and other versions and implementations have or now contain many other language compilers and toolsets. Early BSD releases included Pascal programming language tools, and many modern Unix systems also include the GNU Compiler Collection as well as or instead of a proprietary compiler system.
- ... and a number of other tools, including an object-code archive manager (ar), symbol-table lister, compiler-development tools (e.g. yacc), make, and debugging tools.
- Commands — Most Unix implementations make little distinction between commands (user-level programs) for system operation and maintenance (e.g. cron), commands of general utility (e.g. grep), and more general-purpose applications such as the text formatting and typesetting package. Nonetheless, some major categories are:
- sh — The Shell, the primary user-interface on Unix before window systems appeared, and the centre of the command environment. To degrees that varied in different shell implementations, external programs (such as expr) were relied on by the shell.
- Utilities — the core of the Unix command set, including ls, grep, find and many others. This category could be subcategorized:
- System utilities — such as mkfs, fsck, and many others; and
- User utilities — passwd, kill, and others.
- Document formatting — Unix systems were used from the outset for document preparation and typesetting systems, and included many related programs such as nroff, troff, tbl, eqn, refer, and pic. Some systems also include more advanced packages such as TeX and GhostScript.
- Graphics — The plot subsystem provided facilities for producing simple vector plots in a device-independent format, with device-specific interpreters to display such files. Modern Unix systems also generally include X11 as a standard windowing system and GUI, and many support OpenGL.
- Communications — early Unix systems contained no inter-system communication, but did include the inter-user communication programs mail and write. V7 introduced the early inter-system communication system UUCP, and systems beginning with BSD release 4.1c included TCP/IP utilities.
- Documentation — Unix was the first operating system to include all of its documentation online in machine-readable form. The documentation included:
- man — Manual pages for each command, library component, system call, header file, etc.
- doc — Longer documents detailing major subsystems, such as the C language and troff
Impact
The Unix system had a great impact on other operating systems. Unix has been called "the most important operating system you may never use."
Following the lead of Multics, it was written in high level language as opposed to assembly (assembly had been necessary for achieving acceptable performance on early computers).
It had a drastically simplified file model compared to many contemporary operating systems, treating all kinds of files as simple byte arrays. The file system hierarchy contained machine services and devices (such as printers, terminals, or disk drives), providing a uniform interface, but at the expense of occasionally requiring additional mechanisms such as ioctl and mode flags to access features of the hardware that did not fit the simple "stream of bytes" model. The Plan 9 operating system pushed this model even further and eliminated the need for additional mechanisms.
Unix also popularized the hierarchical file system with arbitrarily nested subdirectories, originally introduced by Multics. Other common operating systems of the era had ways to divide a storage device into multiple directories or sections, but they were a fixed number of levels and often only one level. The major proprietary operating systems all added recursive subdirectory capabilities also patterned after Multics. DEC's RSTS programmer/project hierarchy evolved into VMS directories, CP/M's volumes evolved into MS-DOS 2.0+ subdirectories, and HP's MPE group.account hierarchy and IBM's System 36 and OS/400 library systems were folded into broader POSIX file systems.
Making the command interpreter an ordinary user-level program, with additional commands provided as separate programs, was another Multics innovation popularized by Unix. The Unix shell used the same language for interactive commands as for scripting ( shell scripts — there was no separate job control language, like IBM's JCL for example). Since the shell and OS commands were "just another program", the user could choose (or even write) his/her own shell. Finally, new commands could be added without recompiling the shell. Unix's innovative command-line syntax for creating chains of producer-consumer processes ( pipelines) made a powerful programming technique ( coroutines) widely available. Many later command-line interpreters have been more or less inspired by the Unix shell.
A fundamental simplifying assumption of Unix was its focus on ASCII text for nearly all of its file formats. There were no "binary" editors in the original version of Unix — the entire system was configured using textual shell command scripts. The common denominator in the I/O system is the byte — unlike "record-based" file systems in other computers. The focus on text for representing nearly everything made Unix pipes useful. The focus on text and bytes made the system far more scalable and portable than other systems. Over time text-based applications have also won in application areas, such as printing languages ( PostScript — not InterPress, an earlier effort by the same people), and when feasible, at the application layer of the Internet Protocols, i.e. Telnet, FTP, SMTP, HTTP, SIP, XML, etc.
Unix popularised a syntax for regular expressions that found much wider use. The Unix programming interface became the basis for a standard operating system interface (POSIX, see above).
The C programming language, now ubiquitous in systems and applications programming, originated under Unix, and spread more quickly than Unix.
Early Unix developers were important in bringing the theory of modularity and reusability into software engineering practice.
Unix provided the TCP/IP networking protocol on relatively inexpensive computers, which contributed to the Internet explosion of world-wide real-time connectivity. This also exposed numerous security holes in its networking implementations, which formed the basis for implementations on many other platforms.
The Unix policy of extensive on-line documentation and (for many years) ready access to all system source code raised programmer expectations, contributing to the Open Source movement.
Over time, the leading developers of Unix (and programs that ran on it) developed a set of cultural norms for developing software, norms which became as important and influential as the technology of Unix itself; this has been termed the Unix philosophy.
2038
Unix stores time values as the number of seconds from midnight January 1, 1970 (the " Unix Epoch") in variables of type time_t, historically defined as "signed 32-bit integer". On January 19, 2038, the current time will roll over from a zero followed by 31 ones to a one followed by 31 zeros, which will reset time to the year 1901 or 1970, depending on implementation. As many applications use OS library routines for date calculations, the impact of this could be felt much earlier than 2038; for instance, 30-year mortgages may be calculated incorrectly beginning in the year 2008.
Since times before 1970 are rarely represented in Unix time, one possible solution that is compatible with existing binary formats would be to redefine time_t as "unsigned 32-bit integer". However, such a kludge merely postpones the problem to February 7, 2106, and could introduce bugs in software that needed to compare differences between two sets of time.
Some Unix versions have already addressed this. For example, in Solaris on 64-bit systems, time_t is 64 bits long, meaning that the OS itself and 64-bit applications will correctly handle dates for some 292 billion years (several times greater than the age of the universe). Existing 32-bit applications using a 32-bit time_t continue to work on 64-bit Solaris systems but are still prone to the 2038 problem.
Free Unix-like operating systems
In 1983, Richard Stallman announced the GNU project, an ambitious effort to create a free software Unix-like system; "free" in that everyone who received a copy would be free to use, study, modify, and redistribute it. GNU's goal was achieved in 1992. Its own kernel development project, GNU Hurd, had not produced a working kernel, but a compatible kernel called Linux was released as free software in 1992 under the GNU General Public License. The combination of the two is frequently referred to simply as "Linux", although the Free Software Foundation and some Linux distributions, such as Debian GNU/Linux, use the combined term GNU/Linux. Work on GNU Hurd continues, although very slowly.
In addition to their use in the Linux operating system, many GNU packages — such as the GNU Compiler Collection (and the rest of the GNU toolchain), the GNU C library and the GNU core utilities — have gone on to play central roles in other free Unix systems as well.
Linux distributions, comprising Linux and large collections of compatible software have become popular both with hobbyists and in business. Popular distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux, Mandriva Linux, Fedora Core, Ubuntu, Debian GNU/Linux and Gentoo.
A free derivative of BSD Unix, 386BSD, was also released in 1992 and led to the NetBSD and FreeBSD projects. With the 1994 settlement of a lawsuit that UNIX Systems Laboratories brought against the University of California and Berkeley Software Design Inc. ( USL v. BSDi), it was clarified that Berkeley had the right to distribute BSD Unix — for free, if it so desired. Since then, BSD Unix has been developed in several different directions, including the OpenBSD and DragonFly BSD variants.
Linux and the BSD kin are now rapidly occupying the market traditionally occupied by proprietary UNIX operating systems, as well as expanding into new markets such as the consumer desktop and mobile and embedded devices. A measure of this success may be seen when Apple Computer sought out a new foundation for its Macintosh operating system: it chose NEXTSTEP, an operating system developed by NeXT with a freely redistributable core operating system, renamed Darwin after Apple acquired it. It was based on the BSD family and the Mach kernel. The deployment of Darwin BSD Unix in Mac OS X makes it, according to a statement made by an Apple employee at a USENIX conference, the most widely used Unix-based system in the desktop computer market. Due to the modularity of the Unix design, sharing bits and pieces is relatively common; consequently, most or all Unix and Unix-like systems include at least some BSD code, and modern BSDs also typically include some GNU utilities in their distribution, so Apple's combination of parts from NeXT and FreeBSD with Mach and some GNU utilities has precedent.
In 2005, Sun Microsystems released the bulk of the source code to the Solaris operating system, a System V variant, under the name OpenSolaris, making it the first actively developed commercial Unix system to be open sourced (several years earlier, Caldera had released many of the older Unix systems under an educational and later BSD license. As a result, a great deal of formerly proprietary AT&T/USL code is now freely available.
Branding
In October 1993, Novell, the company that owned the rights to the Unix System V source at the time, transferred the trademarks of Unix to the X/Open Company (now The Open Group), and in 1995 sold the related business operations to Santa Cruz Operation. Whether Novell also sold the copyrights to the actual software is currently the subject of litigation in a federal lawsuit, SCO v. Novell. UNIX vendor SCO Group Inc. accused Novell of slander of title.
The present owner of the trademark UNIX is The Open Group, an industry standards consortium. Only systems fully compliant with and certified to the Single UNIX Specification qualify as "UNIX" (others are called "Unix system-like" or " Unix-like"). The term UNIX is not an acronym, but follows the early convention of naming computer systems in capital letters, such as ENIAC and MISTIC.
By decree of The Open Group, the term "UNIX" refers more to a class of operating systems than to a specific implementation of an operating system; those operating systems which meet The Open Group's Single UNIX Specification should be able to bear the UNIX 98 or UNIX 03 trademarks today, after the operating system's vendor pays a fee to The Open Group. Systems licensed to use the UNIX® trademark include AIX, HP-UX, IRIX, Solaris, Tru64, A/UX and a part of z/OS. Apple Computer have stated that they will be submitting Mac OS X 10.5 and Mac OS 10.5 Server to The Open Group for certification as a UNIX 03 system.
In practice, the term, especially when written as " Un*x", "*NIX", or "*N?X" is applied to a number of other multiuser POSIX-based systems such as GNU/Linux, Mac OS X and FreeBSD that do not seek UNIX branding because the royalties would be too expensive for a product marketed to consumers or freely available over the Internet; this would mean that "Unix" has become a label for a variety of products, much like a genericized trademark. To avoid this, The Open Group requests that "UNIX" is always used as an adjective followed by a generic term such as "system".
The term "Unix" is also used, and in fact was the original capitalisation, but the name UNIX stuck because, in the words of Dennis Ritchie "when presenting the original Unix paper to the third Operating Systems Symposium of the American Association for Computing Machinery, we had just acquired a new typesetter and were intoxicated by being able to produce small caps" (quoted from the Jargon File, version 4.3.3, 20 September 2002). Additionally, it should be noted that many of the operating system's predecessors and contemporaries used all-uppercase lettering, because many computer terminals of the time could not produce lower-case letters, so many people wrote the name in upper case due to force of habit.
Several plural forms of Unix are used to refer to multiple brands of Unix and Unix-like systems. Most common is the conventional "Unixes", but the hacker culture which created Unix has a penchant for playful use of language, and "Unices" (treating Unix as Latin word) is also popular. The Anglo-Saxon plural form "Unixen" is not common, although occasionally seen.
UNIX is also a trademarked name for a brand of carpet. However, US Trademark laws allow duplicate names if the products, as in this case, are easily distinguishable.
Common Unix commands
Widely used Unix commands include:
- Directory and file creation and navigation:
ls cd pwd mkdir rm rmdir cp find touch - File viewing and editing:
more less ed vi emacs head tail - Text processing:
echo cat grep sort uniq sed awk cut tr split printf - File comparison:
comm cmp diff patch - Miscellaneous shell tools:
yes test xargs - System administration:
chmod chown ps su w who - Communication:
mail telnet ftp finger ssh