Union Flag
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: General Geography
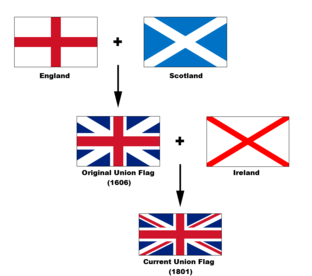
The Union Flag (commonly, the Union Jack) is the national flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. Historically, the flag has been used throughout the former British Empire. It still retains an official or semi- official status in many Commonwealth Realms. The current design (which is used as the national Flag of the United Kingdom) dates from the Union of Ireland and Great Britain in 1801.
Terminology: "Union Flag" or "Union Jack"?
The issue of whether it is acceptable to use the term "Union Jack" is one that causes considerable controversy. Although it is often asserted that "Union Jack" should only be used for the flag when it is flown as a jack (a small flag flown at the bow of a ship), it is not universally accepted that the "Jack" of "Union Jack" is a reference to such a jack flag; other explanations have been put forward . The term possibly dates from the early 1700s, but its origin is uncertain. The word Jack may have come from the name of James VI, King of Scots who inherited the English crown, causing the flag to be designed, that is Jac from Jacobus, Latin for James. The size and power of the Royal Navy internationally at the time could also explain why the flag was nicknamed the "Union Jack"; considering the navy was so widely utilised and renowned by the United Kingdom and Commonwealth countries, it is possible that the term "Jack" did occur due to its regular usage on all British ships using the "Jack Staff" (a flag pole attached to a ship on the bow). Even if the term "Union Jack" does derive from the jack flag (as perhaps seems most likely), after three centuries, it is now sanctioned by usage, has appeared in official usage, and remains the popular term. The BBC website disregards the term "union flag" because of its "great potential for confusion", preferring union jack (in lower case) The term "Union Flag", on the other hand, is the term preferred in official documents by vexillologists. The Merchant Shipping Act 1995 refers to the national colours of the United Kingdom as "the Union flag (commonly known as the Union Jack)".
History
The Union Flag before 1801
When James VI of Scotland inherited as James I of England in 1603, the crowns of the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland were united in him, although each remained independent states.
On 12 April 1606, a new flag to represent this personal union between England and Scotland was specified in a royal decree, according to which the flag of England (a red cross with a white background, known as St George's Cross) and the flag of Scotland (a white saltire with a blue background, known as the Saltire or Saint Andrew's Cross) would be "joyned together according to the forme made by our heralds, and sent by Us to our Admerall to be published to our Subjects." The original sketches which accompanied this specification are lost. Until the Acts of Union 1707 it was practice for the flag in Scotland to have the Saltire over the St George's Cross and vice versa when flown in England . This royal flag was at first only for use at sea on civil and military ships of both Scotland and England. In 1634, its use was restricted to the monarch's ships. Land forces continued to use their respective national banners.
After the Acts of Union 1707, the flag gained a regularised status, as "the ensign armorial of the Kingdom of Great Britain", the newly created state. It was then adopted by land forces as well. Various shades of blue have been used in the Saltire over the years. The ground of the current Union Flag is a deep "navy" blue ( Pantone 280), while the currently accepted Saltire uses a lighter "royal" blue (Pantone 300), following the Scottish Parliament's recommendation of 2003.
Wales had no explicit recognition in the flag because Wales had been annexed by Edward I of England in 1282, and since the Laws in Wales Acts 1535-1542 was legally part of the Kingdom of England. (The present-day Flag of Wales and St David's Cross emerged, or re-emerged, in the 20th century: the former based on a Royal badge and the latter on the arms of the Diocese of Saint David's.) The Kingdom of Ireland, which had existed as a personal union with England since 1541, was likewise unrepresented in the original Union Flag.
The pre-1801 Union Flag is also shown in the canton of the Grand Union Flag (also known as the Congress flag, The First Navy Ensign, The Cambridge Flag, and The Continental Colors), the first widely used Flag of the United States. It is also shown in the canton of the Commissioners' flag of the Northern Lighthouse Board, which is the only contemporary official representation of this flag.
The blazon for the old flag, to be compared with the current flag, is Azure, the Cross Saltire of St Andrew Argent surmounted by the Cross of St George Gules, fimbriated of the second.
Other proposed versions
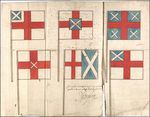
Various other designs for a common flag were drawn up following the union of the two Crowns in 1603, but were rarely, if ever, used . The two shown here include St George's cross with St Andrew's cross in the canton, and another version where the two crosses are side-by-side. Also, some Scots were upset that the Scottish flag was underneath the English flag in the version finally adopted, and preferred a version where the Scottish cross was on top (the English flag was placed between the cross of St Andrew and its background).
Many Welsh people have proposed modifying the Union Flag to include either the Red Dragon or the black and gold colours of the flag of Saint David, arguing that the current design fails to represent their country.
In June 2003, Nigel Turner proposed adding black stripes to the Union Jack in order to better reflect Britain's multiracial society ; this is also a response to the racist chant there ain't no black in the Union Jack.
Since 1801
The current Union Flag dates from 1 January 1801 with the Act of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Ireland and the Kingdom of Great Britain to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The new design added the red saltire cross of Saint Patrick's Flag for Ireland. This saltire is overlaid on the saltire of St Andrew, but still beneath the cross of St George. To make it clear Ireland was not superior to Scotland, the Irish cross was made thinner and half covered by the saltire of St Andrew. The arrangement has introduced a requirement to display the flag "the right way up"; see specifications for flag use, below. The red cross is thought to have come from the heraldic device of the Fitzgerald family who were sent by Henry II of England to aid Anglo-Norman rule in Ireland and has rarely been used as an emblem of Ireland by the Irish: a harp, a Celtic cross, a shamrock, or (since 1922) an Irish tricolour have been more common. However, the exact origin of the flag is unknown, with evidence of saltires being present on ancient Irish coins and maps. The St Patrick's saltire flag has been used in more recent times for St Patrick's Day in Northern Ireland, by various organisations wishing to avoid the sectarianism that may be implied by the use of either the tricolour or symbols of Unionism.
The current flag is blazoned Azure, the Crosses Saltire of St Andrew and St Patrick, quarterly per saltire, counterchanged Argent and Gules, the latter fimbriated of the second, surmounted by the Cross of St George of the third, fimbriated as the saltire.
Status
The Union Jack is used as a jack by commissioned Royal Navy warships. When at anchor or alongside, it is flown from the jackstaff at the prow of the ship. It can only be flown when underway to indicate that either a court-martial is in progress or to indicate the presence of an Admiral of the Fleet onboard; including the Lord High Admiral, the British Monarch.
No law has ever been passed making the Union Flag the national flag of the United Kingdom; rather it has become one through usage. Its first recorded recognition as a national flag came in 1908, when it was stated in Parliament that "the Union Jack should be regarded as the National flag". A more categorical statement was made by the Home Secretary in 1933, when he stated that "the Union Jack is the National Flag".
Civilian use is permitted, but stricter guidelines apply for use on naval vessels where the flag may not be used as a jack by merchant ships (see below). Interestingly, unauthorised use of the flag in the 17th Century to avoid paying harbour duties - a privilege restricted to naval ships - caused James' successor, Charles I, to order that use of the flag on naval vessels be restricted to His Majesty's ships "upon pain of Our high displeasure". Those restrictions remain, and still today it is a criminal offence to fly the Union Flag from a boat.
The Court of the Lord Lyon, which has criminal jurisdiction in heraldic matters in Scotland, confirms that the Union Flag "is the correct flag for all citizens and corporate bodies of the United Kingdom to fly to demonstrate their loyalty and their nationality."
The Union Flag has been in usage in Canada dating back to the British settlement in Nova Scotia in 1621. At the close of the Great Flag Debate of 1964, which resulted in the adoption of the Maple Leaf Flag as the Canadian national flag, the Parliament of Canada voted to keep the Royal Union Flag as an official flag of Canada and as the symbol of Canada's membership of the Commonwealth and her allegiance to the Crown. It is commonly flown alongside the Maple-Leaf Flag on Commonwealth Day and other royal occasions and anniversaries.
Use in other flags
Other nations and regions

The Union Flag was found in the canton (top left-hand corner) of the flags of many colonies of the UK, while the field (background) of their flags was the colour of the naval ensign flown by the particular Royal Navy squadron that patrolled that region of the World.
All administrative regions and territories of the United Kingdom fly the Union Flag in some form, with the exception of Gibraltar (other than the government ensign) and the Crown Dependencies. Outside the UK itself, it is usually part of a special ensign in which the Union Flag is placed in the upper left hand corner of a blue field, with a signifying crest in the bottom right.
Four countries currently incorporate the Union Flag as part of their own national flags: Australia, New Zealand, Tuvalu, and Fiji (although Fiji is a republic, unlike Australia and New Zealand).
In former British colonies, the Union Flag was used semi-interchangeably with territorial flags for significant parts of their early history. This was also the case in Canada until the introduction of the Maple Leaf Flag in 1965, but it is still used in the flags of a number of Canadian provinces like British Columbia, Manitoba and Ontario. Newfoundland and Labrador uses a modified version of the Union Jack, once the flag of province. Canadian law still allows the Union Flag, known in Canada as the Royal Union Flag, to be flown by private individuals and government agencies to show support for the Monarch and the Commonwealth.
In addition to Australia's National Flag many other Australian flags retain the use of the Union Flag, including: the Royal Australian Navy Ensign (also known as the Australian White Ensign), the Royal Australian Air Force Ensign, the Australian Red Ensign (for use by merchant and private vessels) and the Australian Civil Aviation Ensign. In addition, the flags of the six Australian States all retain the use of Union Flag in the canton. Finally, the Vice-Regal flags of the State Governors also retain the use of the Union Flag. See List of Australian flags for more information.
The Basque Country's flag, the Ikurriña is also loosely based on the Union Flag, reflecting the significant commercial ties between Bilbao and England at the time the Ikurriña was designed (1894). The Miskito people sometimes use a similar flag that also incorporates the Union Flag in its canton, due to long periods of contact in the Mosquito Coast.
The jack of the Russian Navy is a common equivalent to the British one with the St. George and St. Andrew crosses reversed in order and colours but unmistakable based on the same design.
The Union Flag was also used by the United States in their first flag, the Grand Union Flag. This flag was the same design as the one used by the British East India Company.
One state of the United States, Hawaii, incorporates the Union Flag in its state flag. The canton of the Flag of Hawaii reveals the British influence over those islands in the late 19th century.
| National and regional flags incorporating the Union Flag |
| Anguilla | Australia | Bermuda | British Antarctic Territory | British Columbia | British Indian Ocean Territory | British Virgin Islands | Canadian Red Ensign | Cayman Islands | Cook Islands | Falkland Islands | Fiji | Hawaii | Manitoba | Montserrat | New South Wales | New Zealand | Niue | Ontario | Pitcairn Islands | Queensland | Saint Helena | South Australia | South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands | Tasmania | Tristan da Cunha | Turks and Caicos Islands | Tuvalu | Victoria | Western Australia |
Ensigns

The Union Flag can be found in the canton of several of the ensigns flown by vessels and aircraft of the United Kingdom and its overseas territories.
Pilot Jack
The flag in a white border occasionally seen on merchant ships was sometimes referred to as the Pilot Jack. It can be traced back to 1823 when it was created as a signal flag, never intended as a civil jack. A book issued to British consuls in 1855 states that the white bordered Union Flag is to be hoisted for a pilot. Although there was some ambiguity regarding the legality of it being flown for any other purpose on civilian vessels, its use as an ensign or jack was established well in advance of the 1864 Act that designated the Red Ensign for merchant shipping. In 1970 the white-bordered Union Flag ceased to be the signal for a pilot, but references to it as national colours were not removed from the current Merchant Shipping Act and it was legally interpreted as a flag that could be flown on a merchant ship, as a jack if desired. This status was confirmed by the Merchant Shipping (Registration, etc.) Act 1993 and the consolidating Merchant Shipping Act 1995 which prohibits the use of any distinctive national colours or those used or resembling flags or pendants on Her Majesty's Ships, except the Red Ensign, the Union Flag with a white border, and some other exceptions permitted elsewhere in the Acts.
Flag days
Canada
In Canada, the Royal Union Flag is flown on specified days from federal buildings, airports, military bases and other government buildings on the following days:
- Second Sunday in March ( Commonwealth Day)
- Victoria Day- the official birthday of the monarch (the Monday preceding May 24)
- December 11- the anniversary of the proclamation of the Statute of Westminster 1931
The flag is only flown where physical arrangements allow (e.g., when there is more than one flag pole). The flag of Canada is never moved to make room for the Royal Union Flag.
United Kingdom
In the UK, the Union Flag is only flown on public buildings as decided by Department for Culture, Media and Sport or on the command of the British monarch. Currently the flag is flown on days marking the birthdays of members of the Royal family, the Wedding anniversary of the monarch, Commonwealth Day, Accession Day, Coronation Day, The Queen's official birthday, Remembrance Sunday and on the days of the State Opening and prorogation of Parliament. The Union Flag is flown at half mast from the announcement of the death of the Sovereign (save for Proclamation Day), or upon command of the Sovereign. Contrarily, the Royal Standard is never flown at half mast.
The current flag days where the Union Flag should be flown all over the UK are:
- January 20 (Birthday of The Countess of Wessex)
- February 6 (Anniversary of the accession of Queen Elizabeth II)
- February 19 (Birthday of The Duke of York)
- Second Sunday in March ( Commonwealth Day)
- March 10 (Birthday of Prince Edward, Earl of Wessex)
- April 21 (Birthday of Queen Elizabeth II)
- May 9 ( Europe Day)
- June 2 (Anniversary of the coronation of Queen Elizabeth II)
- June 10 (Birthday of Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
- June (no fixed date)- Official Birthday of Queen Elizabeth II
- July 17 (Birthday of the The Duchess of Cornwall)
- August 15 (Birthday of the Princess Royal)
- Second Sunday in November ( Remembrance Sunday)
- November 14 (Birthday of The Prince of Wales)
- November 20 (Anniversary of the wedding of Queen Elizabeth II and Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh)
In addition, the Union Flag should be flown in the following areas on specified days:
- March 1 (Wales only for Saint David's Day)
- April 23 (England only for Saint George's Day)
- November 30 (Scotland only for Saint Andrew's Day)
- The Day of the Opening of a Session of the Houses of Parliament ( Greater London area only)
- The day of the prorogation of a Session of the Houses of Parliament ( Greater London area only)
There is no specified day for March 17 ( Saint Patrick's Day) in Northern Ireland.
Non government organisations may fly the flag whenever they choose.
Specifications for flag use
A careful examination of the flag shows that it does not have reflectional symmetry, due to the slight pinwheeling of St. Patrick's cross, which is technically called the counterchange of saltires. Thus, it has a right side and a wrong side up. To fly the flag the correct way up, the broad portion of the white cross of St Andrew should be above the red band of St Patrick (and the thin white portion below) in the upper hoist canton (the corner at the top nearest to the flag-pole), giving the Scottish symbol precedence over the Irish symbol. This is expressed by the phrases wide white top and broad side up. Traditionally, flying a flag upside down is understood as a distress signal. In the case of the Union Jack, the difference is so subtle as to be easily missed by many. In the past this has been taken advantage of by the British Army. On one occasion, a British stronghold had been captured. The captured Britons were ordered to keep flying the flag so that it was not obvious that the stronghold had fallen. However, they flew it upside-down, thus alerting some sharp-eyed British reinforcements. It is, however, practicable with the various ensigns that are actually flown by British naval, commercial, and pleasure craft.
The normal dimensions of the flag are 1:2, except in the British Army where a 3:5 version is used. The British Army's flag is the Union Flag, but in 1938 a "British Army Non-Ceremonial Flag" was devised, featuring a Lion on crossed blades with the St Edward's Crown on a red background. This is not the equivalent of the ensigns of the other armed services, but is used at recruiting and military or sporting events, when the Army needs to be identified but the reverence and ceremony due to the regimental flags and the Union Flag would be inappropriate.
The colour specifications for the colours Union Jack (Royal) Blue, Union Jack Red and White are :
| Scheme | Blue | Red | White | Note: The colour schemes are not congruent. This is due to different specifications for different types of media (for example: screen, print, and so forth) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantone | 280 | 186 | Safe | |
| sRGB Hex* | #00247D | #CF142B | #FFFFFF | |
| Web-Safe Hex | #003399 | #CC0000 | #FFFFFF | |
| RGB | 0-33-115 | 198-16-24 | 255-255-255 | |
| CMYK | 100.72.0.18.5 | 0.91.76.6 | 0.0.0.0 | |
| MoD | 8711D | 8711H | 8711J | |
| NATO | 8305.99.130.4580 | 8305.99.130.4584 | 8305.99.130.4585 |
* Not official; these are Wikimedia Commons' own conversions of the Pantone.
Other names
- In Canada the flag is officially called the Royal Union Flag.
- In China the flag has the nickname Rice Flag (米字旗) since the pattern looks like the Chinese character "rice" (米).
- In Ireland the flag is sometimes called the Butcher's Apron among nationalists.. This reference was also used in the 2006 film The Wind That Shakes the Barley, implying that it was used in nineteenth- and early twentieth-century Ireland.
Trivia
- It is a criminal offence to fly the Union Flag from a civilian boat, unless it has a white border. .
- As it is a royal flag, it was abolished by Oliver Cromwell in 1649, before being restored, along with the monarchy, in 1660 .