Stockholm
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: European Geography
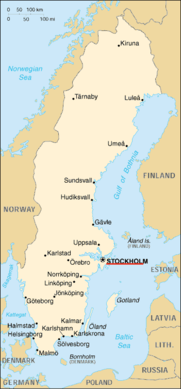
Stockholm ( IPA: ['stɔkhɔlm]; UN/LOCODE: SE STO) is the capital of Sweden, and consequently the site of its Government and Parliament as well as the residence of the Swedish head of state, King Carl XVI Gustaf.
Stockholm has been Sweden's political and economic centre since the 13th century. Today it is the largest municipality of Sweden, with a population of 776,000, while the populations of the Stockholm urban area and Metropolitan Stockholm are roughly 1.2 and 1.7 million, respectively. This makes Stockholm the largest city in the Nordic countries.
With its location on the east coast of Sweden at the mouth of Lake Mälaren, by the Stockholm archipelago, it is widely renowned for its beauty.
History
The earliest mention of Stockholm in writing dates from 1252, when the mines in Bergslagen made it an important site in the iron trade. The first part of the name (stock) means log, while the second (holm) means islet, and refers to the islet Stadsholmen in central Stockholm which for centuries constituted the main part of Stockholm.
The city is said to have been founded by Birger Jarl in order to protect Sweden from a sea invasion by foreign navies, and to stop the pillage of towns such as Sigtuna on Lake Mälaren. It is also said that the name derives from the spot where a log (stock) pushed into the waters, and following its currents, drifted upon an islet (holm). This location would thus constitute the best location for a harbour for returning ships.
The strategic and economic importance of the city made Stockholm an important factor in relations between the Danish Kings of the Kalmar Union and the national independence movement in the 15th century. The Danish King Christian II was able to enter the city in 1520. On November 8, 1520, massive executions of opposition figures, called the Stockholm Bloodbath, took place. This massacre set off further uprisings, which eventually led to the break-up of the Kalmar Union.
With the accession of Gustav Vasa in 1523 and the establishment of a royal power, the population of Stockholm began to grow, reaching ten thousand by 1600.
The 17th century saw Sweden rise into a major European power, reflected in the development of the city of Stockholm. From 1610 to 1680, the population multiplied sixfold. In 1634, Stockholm became the official capital of the Swedish empire. Trading rules were also created that gave Stockholm an essential monopoly over trade between foreign merchants and other Swedish and Scandinavian territories.
Between 1713–1714, Stockholm suffered from the Black Death. After the end of the Great Northern War and the destruction of several areas of the city in 1721, the city stagnated. Population growth halted and economic growth slowed. However, Stockholm maintained its role as the political centre of Sweden and continued to develop culturally under Gustav III. The royal opera is a good architectural example of this era.
By the second half of the 19th century, Stockholm had regained its leading economic role. New industries emerged, and Stockholm transformed into an important trade and service centre, as well as a key gateway point within Sweden. The population also grew radically during this time, mainly through immigration. At the end of the century, less than 40% of the residents were Stockholm-born. Settlement began to expand outside of the city limits. In the 19th century, a number of scientific institutes opened in Stockholm, including the Karolinska Institute.
In the late 20th century, Stockholm became a modern, technologically-advanced, and ethnically diverse city. Many historical buildings were torn down, including the entire historical district of Klara , and replaced with modern architecture. Throughout the century, many industries shifted away from work-intensive activities into more high-technology and service-industry areas.
The city continued to expand and new districts were created, such as Rinkeby, Tensta, and Sollentuna, some with high proportions of immigrants.
- Reference: German Wikipedia, de:Stockholm, in German.
Geography
Location
Stockholm is located on Sweden's east coast, where Lake Mälaren meets the Baltic Sea. The central parts of the city consists of fourteen islands, all part of the archipelago. The geographical city centre is virtually situated on the water, in the bay Riddarfjärden. (Coordinates: .)
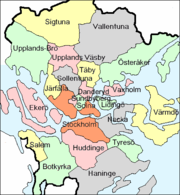
For details about the other municipalities usually considered part of Stockholm, see respective municipality. North of Stockholm Municipality: Järfälla, Solna, Täby, Sollentuna, Lidingö, Upplands Väsby, Österåker, Sigtuna, Sundbyberg, Danderyd, Vallentuna, Ekerö, Upplands-Bro and Vaxholm. South of Stockholm: Huddinge, Nacka, Botkyrka, Haninge, Tyresö, Värmdö and Salem.
Stockholm Municipality
Stockholm Municipality is an administrative unit defined by geographical borders. The officially adapted name for the municipality is City of Stockholm (Stockholms Stad in Swedish). As a municipality, the City of Stockholm is subdivided into district councils, or boroughs, which carry responsibility for primary school, social, leisure and cultural services within their respective areas. The City of Stockholm is usually described in term of its three main parts: Stockholm City Centre (Innerstaden), South Stockholm (Söderort) and West Stockholm (Västerort). The districts of respective parts are:
| Stockholm City Centre | South Stockholm | West Stockholm |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Climate
Due to the city's high northern latitude, the climate of Stockholm is extremely varied with distinct seasons. At the Winter Solstice in late December, the day lasts about six hours, whereas at the Summer solstice in late June, Stockholm's daylight period extends beyond eighteen hours. As a result, Stockholm is exposed to cold winters and mild summers. The highest temperature ever recorded in Stockholm was +38°C; the lowest was −32°C. While unevenly distributed during the year, the number of annual sun hours usually amounts to over 1800.
Typical temperatures for each season:
Winter: from +2 to −7°C (36 to 19°F)
Spring: between +5 and 15°C (41 to 59°F)
Summer: 20–25°C (68 to 77°F) or warmer
Autumn: between +5 and 18°C (41 to 64°F)
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg high °F (°C) | 30 (−1) | 30 (−1) | 37 (3) | 48 (9) | 61 (16) | 70 (21) | 72 (22) | 68 (20) | 59 (15) | 50 (10) | 41 (5) | 34 (1) | 50 (10) | |
| Avg low temperature °F (°C) | 23 (−5) | 23 (−5) | 27 (−3) | 34 (1) | 43 (6) | 52 (11) | 55 (13) | 55 (13) | 48 (9) | 41 (5) | 34 (1) | 27 (−3) | 36 (2.5) | |
| Rainfall millimeters | 39 | 27 | 26 | 30 | 30 | 45 | 72 | 66 | 55 | 50 | 53 | 46 | 539 | |
| Mean number of rain days | 18 | 15 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 15 | 14 | 15 | 14 | 17 | 18 | 173 | |
| Source: World Weather Information Service | ||||||||||||||
Politics and government
Municipalities are responsible for government-mandated duties, and elections for the City Council are held every four years, parallel to the general elections.
Following the 2006 municipal elections, the seats are divided in the following way:
| The governing parties | Parties in opposition |
|---|---|
|
|
The current Mayor of Stockholm is Kristina Axén Olin.
Economy
The vast majority of Stockholmians work in the service industry, which accounts for roughly 85% of jobs in Stockholm. The almost total absence of heavy industry makes Stockholm one of the world's cleanest metropols.
The last decade has seen a significant number of jobs created in high technology companies. Large employers include IBM, Ericsson, and Electrolux. Arguably one of the world's leading IT centres is located in Kista, in northern Stockholm.
Stockholm is Sweden's financial centre. Major Swedish banks, such as Swedbank, Handelsbanken, and Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken, are headquartered in Stockholm, as are the major insurance companies Skandia and TryggHansa. Stockholm is also home to Sweden's foremost stock exchange, the Stockholm Stock Exchange (Stockholmsbörsen). Finally, about 45% of Swedish companies with more than 200 employees are headquartered in Stockholm.
In the last years, tourism has played an important part in the city's economy. Between 1991–2004, annual overnight stays increased from 4 to 7.7 million.
Largest companies by number of employees:
- Ericsson -- 8,430
- Posten -- 4,710
- Skandinaviska Enskilda Banken (SEB) -- 4,240
- Swedbank -- 3,610
- Södersjukhuset (Southern Hospital) -- 3,610
- Nordea -- 2,820
- Handelsbanken -- 2,800
- IBM Svenska -- 2,640
- Securitas -- 2,360
- Connex -- 2,300
- ISS Facility Services -- 2,000
- Sveriges Television (public television) -- 1,880
- Sodexho -- 1,580
Education
Research and higher education in the sciences started in Stockholm in the 18th century, with an education in medicine and various research institutions, such as the Stockholm Observatory. The medical education was eventually formalized in 1811 as the Karolinska Institutet. The Royal Institute of Technology (Kungliga Tekniska Högskolan, or KTH) was founded in 1827 and is currently Scandinavia's largest higher education institute of technology with 13,000 students. Stockholm University, founded in 1878 with university status granted in 1960, has 35,000 students as of 2004. It also incorporates many historical institutions, such as the Observatory, the Swedish Museum of Natural History, and the botanical garden Bergianska trädgården. The Stockholm School of Economics, founded in 1909, is one of few private institutions of higher education in Sweden.
In the fine arts, educational institutions include the Royal College of Music, which has a history going back to the conservatory founded as part of the Royal Swedish Academy of Music in 1771, the Royal University College of Fine Arts, which has a similar historical association with the Royal Swedish Academy of Arts and a foundation date of 1735, and the Swedish National Academy of Mime and Acting, which is the continuation of the school of the Royal Dramatic Theatre, once attended by Greta Garbo. Other schools include the design school Konstfack, founded in 1844, the University College of Opera (founded in 1968, but with older roots), the University College of Dance, and the Stockholms Musikpedagogiska Institut (the University College of Music Education).
The Södertörn University College was founded in 1995 as a multidisciplinary institution for southern Metropolitan Stockholm, to balance the many institutions located in the northern part of the region.
Other institutes of higher education are:
- Ersta Sköndal University College
- The Stockholm School of Theology (Teologiska Högskolan, Stockholm)
- The Swedish School of Sport and Health Sciences ( Gymnastik- och idrottshögskolan, or GIK)
- The Stockholm Institute of Education (Lärarhögskolan i Stockholm)
Demographics
The Stockholm region is home to around 20% of Sweden's total population, and accounts for about 25% of the gross domestic product.
The geographical notion of "Stockholm" has changed throughout the times. By the turn of the 19th century, Stockholm basically consisted of the area today known as City Centre, roughly 35 km² or 1/5 of the current municipal area. In the ensuing decades several other areas were incorporated (such as Brännkyrka Municipality in 1913, at which time it had 25,000 inhabitants, and Spånga in 1949). The municipal border was established in 1971 – with the exception of Hansta, in 1982 purchased by Stockholm Municipality from Sollentuna Municipality and today a nature reserve.
Of the population of 765,044 (2004), 370,482 were men and 394,562 women. The average age is 39.8 years; 40,5% of the population is between 20-44 years.
309,480 persons, or 40.4% of the population, over the age 15 were unmarried. 211,115 persons, or 27.5% of the population, were married. 85,373, or 11.1% of the population, had been married but divorced.
Historical population
Population in the City of Stockholm from 1750 to present:
| Year | Stockholm | Nationwide | Stockholm % of nation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1750 | 60,018 | 1,780,678 | 3,4 |
| 1800 | 75,517 | 2,347,303 | 3,2 |
| 1850 | 93,070 | 3,482,541 | 2,7 |
| 1900 | 300,624 | 5,136,441 | 5,9 |
| 1910 | 342,323 | 5,522 403 | 6,2 |
| 1920 | 419,440 | 5,904,489 | 7,1 |
| 1930 | 502,213 | 6,142,191 | 8,2 |
| 1940 | 590,503 | 6,371,432 | 9,3 |
| 1950 | 744,143 | 7,041,829 | 10,6 |
| 1960 | 808,294 | 7,500,161 | 10,8 |
| 1970 | 740,486 | 8,091,782 | 9,2 |
| 1980 | 647,214 | 8,317,937 | 7,8 |
| 1985 | 659,030 | 8,358,139 | 7,9 |
| 1990 | 674,452 | 8,590,630 | 7,9 |
| 1995 | 711,119 | 8,837,496 | 8,0 |
| 2000 | 750,348 | 8,882,792 | 8,4 |
| 2005 | 771,038 | 9,047,752 | 8,5 |
In the latest century, the population of nearby municipalities of Stockholm County has become important to mention next to the population of Stockholm Municipality, as many municipalities are constituting parts of Stockholm urban area and as such often considered part of the general term "Stockholm".
As of 2000, Stockholm urban area extended into 11 municipalities ( Stockholm 750,000 inh.; Huddinge 82,891; Järfälla 60,254; Solna 56,605; Sollentuna 53,715; Botkyrka 48,268; Haninge 40,151; Tyresö 36,483; Sundbyberg 33,868; Nacka 25,170; Danderyd 24,600) and a total population of 1,200,000 inhabitants. If counting the entire Stockholm County, with its 26 municipalities, the population reaches 1,800,000 inhabitants.
Culture
Apart from being a large city with an active cultural life, Stockholm, as Sweden's capital, houses many national cultural institutions. Most notably, there are two UNESCO World Heritage sites in the Stockholm area: the Royal Palace Drottningholm (within Ekerö Municipality) and the Forest Cemetery Skogskyrkogården.
The oldest part of Stockholm is the Stockholm Old Town, Gamla stan, with its main part on the islet Stadsholmen. It features the medieval street system, where two main streets (Österlånggatan and Västerlånggatan) cross it, and several small alleys diverging towards the water. Some notable buildings of the Gamla Stan are the large German Church (Tyska kyrkan), several mansions and palaces: the Riddarhuset (the House of Nobles), the Bonde Palace, the Tessin Palace and the Oxenstierna Palace.
During 1998 Stockholm was selected as the European City of Culture.
Literature
Authors connected to Stockholm include the poet and songwriter Carl Bellman (1740–1795), novelist and dramatist August Strindberg (1849 - 1912), and novelist Hjalmar Söderberg (1869-1941), all of whom made Stockholm part of their works. Other authors with notable heritage in Stockholm were the Nobel Prize laureate Eyvind Johnson (1900–1976) and the popular poet and composer Evert Taube (1890–1976). The novelist Per Anders Fogelström (1917-1998) wrote a popular series of historical novels depicting life in Stockholm from the 19th to the mid-20th century.
General architecture
The city's oldest part is “Gamla Stan” (Old Town), on the small islands of the city's early development. It still mainly featuring its original medieval street net. The oldest building in Stockholm is the Riddarholmskyrkan from the late 13th century. After the castle fire in 1697 when the medieval castle was destroyed, today's Stockholm Palace was erected in baroque style. Storkyrkan Cathedral, the episcopal seat of the Bishop of Stockholm stands next to the castle. It was founded in the 13th century but is featuring baroque exteriors from the 18th century.
Already in the 15th century, the city expanded outside of its original borders. Some pre-industrial, small-scale buildings from this era can still be found in Södermalm. During the 19th century and the industrialization, the city rapidly grew with planning and architecture inspired by the large cities of the continent such as Berlin and Vienna. Notable works of this includes public buildings as the Royal Swedish Opera and private developments such as the luxury housing developments on Strandvägen.
In the 20th century, the nationalistic thrives spurred a new architectural style, inspired by medieval as well as renaissance ancestry and current influences of Jugend / Art Nouveau style. The maybe most well-known landmark of Stockholm, the Stockholm City Hall, was erected 1911-1923 by architect Ragnar Östberg. Other notable architectural works of those times are the Stockholm Public Library and the Forest Cemetery, Skogskyrkogården
In the 1930s modernism characterized the development of the city as it grew with new residential areas such as the development on Gärdet and industrial development such as the KF manufacturing industries on Kvarnholmen in the Nacka Municipality. In the 1950s, suburban development entered a new phase with the introduction of the Stockholm metro. The modernist developments of Vällingby and Farsta was internationally praised. In the 1960s the suburban development continued, but the industrialised and mass-produced blocks of flats did not prove to create attractive housing.
Along with the suburban development, the most central areas of the inner city was redesigned. Sergels Torg, with its five high-rise office towers was created in the 1960s, followed by total clearance of large areas for new developments. The most notable buildings from this period is the ensemble of the House of Culture, City Theatre and National Bank at Sergels Torg, designed by architect Peter Celsing.
Museums
Stockholm is one of the most crowded museum-towns in the world with some 70 museums, visited by over 9 million people per year.
The most renowned national museum is the Swedish National Museum of Fine Arts, with Sweden's largest collection of art: 16,000 paintings and 30,000 objects of art handicraft. The collection stems back to the days of Gustav Vasa in the 16th century, and has since been expanded with works by artists such as Rembrandt, and Antoine Watteau, as well as constituting a main part of Sweden's art heritage, manifested in the works of Alexander Roslin, Anders Zorn, Johan Tobias Sergel, Carl Larsson, Carl Fredrik Hill and Ernst Josephson. Most of Stockholm's state-operated museums have free entrance.
The Museum of Modern Art, or Moderna Museet, is Sweden's national museum of modern art. It has works by foremost modern artists such as Picasso and Salvador Dalí.
Other notable museums:
- Stockholm City Museum
- Skansen, the archetype of open air museums, inaugurated 1891.
- The Vasa museum, now with the reconstruction of the missing parts of the Vasa Ship.
Outer suburbs
The outer Stockholm suburbs (Förort in Swedish) are places with diverse cultural background. Some areas in the (somewhat) outer suburbs, including those of Tensta, Jordbro, Fittja, Husby, Rinkeby, Kista, Hagsätra, Rågsved, Södertälje, Huddinge, have high percentages of immigrants or second generation immigrants of Middle Eastern, former Yugoslavian, African nationality or of other immigrant descent (Such as South Asian & Hispanic). Other parts of the outer suburbs, such as Hässelby, Vällingby & Hökarängen, as well as some of the suburbs mentioned above, have a majority of ethnic Swedes (Rinkeby is the Stockholm suburb with least Swedes, but still as many as 10%). Through high influx of immigration a new language has formed from speech in Arabian, Serbo-Croat etc " Rinkeby Swedish" named after the suburb Rinkeby.
Some areas in the outer suburbs of Stockholm also have a low average income and high unemployment rates, as well as medium to high crime-rates. Other areas in the outer suburbs (Such as Bromma & Danderyd, both dominated by ethnic Swedes living in detached single-family homes, just like in the American suburbs) have a high average income and low unemployment rates, as well as low crime-rates.
Theatres
Among Stockholm's many theatres distinguish the Royal Dramatic Theatre (Dramaten), as one of Europes most renowned theatres, and the Royal Swedish Opera, inaugurated back in 1773. Other notable theatres are the Stockholm City Theatre, the Peoples Opera (Folkoperan), the Modern Theatre of Dance (Moderna dansteatern), the China Theatre, the Göta Lejon Theatre, the Mosebacke Theatre, and the Oscar Theatre.
Sports
The most popular spectator sports are football and ice hockey. The three most popular football teams in the Stockholm region are AIK, Hammarby IF and Djurgårdens IF. In ice hockey, Stockholm's highest rated team is Djurgårdens IF.
Historically, the city was the host of the 1912 Summer Olympics. From those days stem the Stockholms Olympiastadion which has since hosted numerous sports events, notably football and athletics, and is the current home arena of Djurgårdens IF. For the ice hockey team, the home arena is Stockholm Globe Arena, one of the largest spherical building in the world, but it is also hosting concerts and other events.
Stockholm also hosted all but one of the Nordic Games, a winter multi-sport event that predated the Winter Olympics.
In addition, there have been a number of "Getaway in Stockholm" Videos where multiple high-power vehicles evade police. One of the numerous filmed escapes involved a Porsche 911, where another had a Toyota Supra and a Ford Cosworth evading police.
Gallery of notable buildings
Transport
Public transport
Stockholm has an extensive public transport system. It consists of the Stockholm Metro (Tunnelbanan); three regional/suburban rail systems: commuter rail (pendeltåg), Roslagsbanan, and Saltsjöbanan; three light rail systems: Nockebybanan, Lidingöbanan, and Tvärbanan; and a large amount of bus lines.
All the land-based public transport in Stockholm County, except the airport buses/trains, is organised by Storstockholms Lokaltrafik (SL), with the operation and maintenance of the public transport services delegated to several contractors, such as Connex who operate the metro and regional/suburban railways except for the commuter rail. The archipelago boat traffic is handled by Waxholmsbolaget.
The SL has a common ticket system in the entire Stockholm County, which allows for easy travel between different modes of transport. The tickets are of two main types, single ticket and travel cards, both allowing for unlimited travel with SL in the entire Stockholm County for the duration of the ticket validity. A single ticket costs 20 SEK (2.17 EUR; 2.75 USD) and is valid for one hour. The duration of the travel card validity depends on the exact type, they are available from 24 hours up to a year. A 30-day card costs 600 SEK (65 EUR; 82 USD). Tickets of both types are available with reduced price for persons under 20 and over 65 years old.
Roads
Stockholm is at the junction of the European routes E4, E18 and E20.
Stockholm city has had a trial period with electronic toll collection. This trial was between January 3rd 2006 and July 31st 2006
Remaining toll and penalty fees due to overdue payments can be paid at "Pressbyrån" and 7-Eleven in the whole country until December 31st 2006. It is also possible to pay at a bank, internet bank or with card on the net.
During the trial period the following was valid: The City Centre is within the Stockholm congestion tax zone. All the entrances and exists of this area have unmanned electronic toll collection stations operating with cameras reading the registration plates, alternatively a transponder. All vehicles entering or exiting the congestion tax affected area, with a few exceptions, are to pay up to 20 SEK (2.17 EUR; 2.80 USD) per passage, depending on the time of the day. The maximum tax amount per vehicle per day is 60 SEK (6.50 EUR; 8.40 USD).
A general election was held September 17th 2006, however, a decision of whether or not to permanently implement the tax has not yet been reached.
Ferries
Stockholm has regular ferry lines to Helsinki in Finland (commonly called " Finlandsfärjan"); Saint Petersburg, Russia; Tallinn, Estonia; Riga, Latvia; and to the Åland islands.
The large Stockholm archipelago is served by the Waxholmsbolaget archipelago boats.
Airports
- International and Domestic:
- Stockholm-Arlanda Airport
- Stockholm-Bromma Airport
- Only international
- Stockholm-Skavsta Airport
- Stockholm- Västerås Airport
Flygbussarna bus lines run to and from central Stockholm from all the airports, and the Arlanda Express airport rail link runs between Arlanda Airport and Stockholm.
Twin towns
The policy of Stockholm is to have informal town twinning with all capitals of the world, with its main focus being those in northern Europe. Stockholm does not sign any formal town twinning treaties, although the city claims to have established such treaties in the past which are still valid.