Long pepper
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Food and agriculture; Plants
| iLong pepper | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
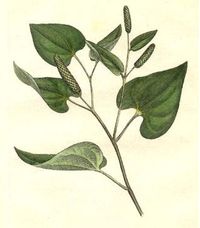 Long pepper's leaves and fruit
|
||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Piper longum L. |
Long pepper (Piper longum) is a flowering vine in the family Piperaceae, cultivated for its fruit, which is usually dried and used as a spice and seasoning. Long pepper is a close relative of the black pepper plant, and has a similar, though generally hotter, taste. The word pepper itself is derived from the Sanskrit word for long pepper, pippali. The fruit of the pepper consists of many minuscule fruits — each about the size of a poppy seed — embedded in the surface of a flower spike; it closely resembles a hazel tree catkin. Another species of long pepper, Piper retrofractum, is native to Java.
Prior to the European discovery of the New World, long pepper was an important and well-known spice. The ancient history of black pepper is often interlinked with (and confused with) that of long pepper. The Romans knew of both and often referred to either as just piper; many ancient botanists erroneously believed dried black pepper and long pepper came from the same plant. Only after the discovery of the New World and of chile peppers did the popularity of long pepper decline. Chile peppers, some of which, when dried, are similar in shape and taste to long pepper, were easier to grow in a variety of locations more convenient to Europe. Today, long pepper is an extremely rare ingredient in European cuisines, but it can still be found in Indian vegetable pickles, some North African spice mixtures, and in Indonesian and Malaysian cooking.
