Lake Albert
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: African Geography
| Lake Albert | |
|---|---|
|
|
|
| Coordinates | |
| Primary sources | Victoria Nile |
| Primary outflows | Albert Nile |
| Catchment area | |
| Basin countries | Democratic Republic of Congo Uganda |
| Max-length | 160 km |
| Max-width | 30 km |
| Surface area | 5,300 km² |
| Average depth | 25m |
| Max-depth | 58m |
| Water volume | 280 km³ |
| Shore length1 | |
| Surface elevation | 615 m |
| Islands | |
| Settlements | Butiaba Pakwach |
| 1 Shore length is an imprecise measure which may not be standardized for this article. | |
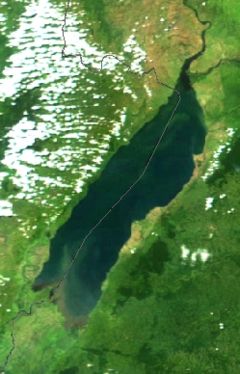
Lake Albert – also Albert Nyanza and formerly Lake Mobutu Sese Seko – is one of the Great Lakes of Africa. It is Africa's seventh largest lake.
Lake Albert is located in the centre of the continent, on the border between Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire). Lake Albert is the northernmost of the chain of lakes in the Great Rift Valley; it is about 160 km (100 mi) long and 30 km (19 mi) wide, with a maximum depth of 51 m (168 ft), and a surface elevation of 619 m (2,030 ft) above sea level.
Lake Albert is part of the complicated system of the upper Nile. Its main sources are the Victoria Nile, ultimately coming from Lake Victoria to the southeast, and the Semliki River, which issues from Lake Edward to the southwest. Its outlet, at the northernmost tip of the lake, is the Albert Nile (which becomes known as the Mountain Nile when it enters Sudan).
At the southern end of the lake, where the Semliki comes in, there are swamps. Farther south loom the mighty Ruwenzori Range, while a range of hills called the Blue Mountains tower over the northwestern shore. The few settlements along the shore include Butiaba and Pakwach.
In 1864, the explorer Samuel Baker became the first European to discover the lake; he named it after the recently deceased Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria.