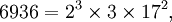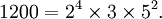Fundamental theorem of arithmetic
2007 Schools Wikipedia Selection. Related subjects: Mathematics
In number theory, the fundamental theorem of arithmetic (or unique factorization theorem) states that every natural number greater than 1 can be written as a unique product of prime numbers. For instance,
There are no other possible factorizations of 6936 or 1200 into prime numbers. The above representation collapses repeated prime factors into powers for easier identification. Because multiplication is commutative, the order of factors is irrelevant and usually written from smallest to largest.
Many authors take the natural numbers to begin with 0, which has no prime factorization. Thus Theorem 1 of Hardy & Wright (1979) takes the form, “Every positive integer, except 1, is a product of primes”, and Theorem 2 (their "Fundamental") asserts uniqueness. The number 1 is not itself prime, but since it is the product of no numbers, it is often convenient to include it in the theorem by the empty product rule. (See, for example, Calculating the GCD.)
Applications
The fundamental theorem of arithmetic establishes the importance of prime numbers. Prime numbers are the basic building blocks of any positive integer, in the sense that each positive integer can be constructed from the product of primes with one unique construction. Finding the prime factorization of an integer allows derivation of all its divisors, both prime and non-prime.
For example, the above factorization of 6936 shows that any positive divisor of 6936 must have the form 2a × 3b × 17c, where a takes one of the 4 values in {0, 1, 2, 3}, where b takes one of the 2 values in {0, 1}, and where c takes one of the 3 values in {0, 1, 2}. Multiplying the numbers of independent options together produces a total of 4 × 2 × 3 = 24 positive divisors.
Once the prime factorizations of two numbers are known, their greatest common divisor and least common multiple can be found quickly. For instance, from the above it is shown that the greatest common divisor of 6936 and 1200 is 23 × 3 = 24. However if the prime factorizations are not known, the use of the Euclidean algorithm generally requires much less calculation than factoring the two numbers.
The fundamental theorem ensures that additive and multiplicative arithmetic functions are completely determined by their values on the powers of prime numbers.
Proof
The theorem was essentially first proved by Euclid, but the first full and correct proof is found in the Disquisitiones Arithmeticae by Carl Friedrich Gauss.
Although at first sight the theorem seems 'obvious', it does not hold in more general number systems, including many rings of algebraic integers. This was first pointed out by Ernst Kummer in 1843, in his work on Fermat's last theorem. The recognition of this failure is one of the earliest developments in algebraic number theory.
Euclid's proof
The proof consists of two steps. In the first step every number is shown to be a product of zero or more primes. In the second, the proof shows that any two representations may be unified into a single representation.
Non-prime composite numbers
Suppose there were a positive integer which cannot be written as a product of primes. Then there must be a smallest such number: let it be n. This number n cannot be 1, because of the convention above. It cannot be a prime number either, since any prime number is a product of a single prime, itself. So it must be a composite number. Thus
- n = ab
where both a and b are positive integers smaller than n. Since n is the smallest number which cannot be written as a product of primes, both a and b can be written as products of primes. But then
- n = ab
can be written as a product of primes as well, a contradiction. This is a minimal counterexample argument.
Proof by infinite descent
A proof of the uniqueness of the prime factorization of a given integer uses infinite descent: Assume that a certain integer can be written as (at least) two different products of prime numbers, then there must exist a smallest integer s with such a property. Denote these two factorizations of s as p1 ... pm and q1 ... qn, such that
s = p1p2 ... pm = q1q2 ... qn.
No pi (with 1 ≤ i ≤ m) can be equal to any qj (with 1 ≤ j ≤ n), as there would otherwise be a smaller integer factorizable in two ways (by removing prime factors common in both products) violating the above assumption. Now it can be assumed without loss of generality that p1 is a prime factor smaller than any qj (with 1 ≤ j ≤ n). Take q1. Then there exist integers d and r such that
- q1/p1 = d + r/p1
and 0 < r < p1 < q1 (r can't be 0, as that would make q1 a multiple of p1 and not prime). Multiplying both sides by s / q1, the result is
- p2 ... pm = (d + r/p1) q2 ... qn = dq2 ... qn + rq2 ... qn/p1.
The second term in the last expression must be equal to an integer, which can be called k, i.e.
- k = rq2 ... qn/p1.
This gives
- p1k = rq2 ... qn.
The value of both sides of this equation is obviously smaller than s, but is still large enough to be factorizable. Since r is smaller than p1, the two prime factorizations we get on each side after both k and r are written out as their product of primes must be different. This is in contradiction with s being the smallest integer factorizable in more than one way. Thus the original assumption must be false.
Proof using abstract algebra
Let n be an integer. Zn is a finite group and therefore has a composition series. By definition, the factors in a composition series are simple. Hence the factors in a composition series of Zn are of the form Zp for some prime number p. Since the order of Zn is the product of the orders of the factors of the composition series, this gives a factorization of n into prime numbers. But the Jordan-Hölder theorem says that our composition series is unique, and hence the prime factorization of n must be unique.